Author: Brodsky Sergey Evgenievich Deputy Chief Physician, Candidate of Medical Sciences in the specialties: dentistry and medical microbiology A broken tooth is the cause of discomfort during eating, which can lead to the development of inflammatory processes in the hard and soft tissues of the tooth, root and gum . Therefore, if a defect is detected, you should immediately consult a dentist, who will select the correct method for restoring the tooth.
Causes of tooth fracture
Part of a tooth can chip or break as a result of exposure to internal and external factors. The first group of reasons include:
- pathologies associated with disruption of intrauterine development of surface and hard tissues of the tooth;
- metabolic disorders associated with impaired absorption of calcium, magnesium and phosphorus, provoked by rickets suffered in childhood, the use of diuretics, and poor nutrition;
- diseases of the digestive tract, accompanied by changes in the acidity of saliva, which has a destructive effect on tooth tissue.
A tooth in the gum can break under the influence of a number of external factors, including:
- injuries to the skull and jaw during a fight, road accident;
- tooth injury during dental procedures;
- eating solid foods;
- thermal injury due to the simultaneous consumption of cold and hot food and drinks;
- advanced carious processes;
- incorrect structure of the dentition.
Hidden caries (both under a filling and on a “healthy” tooth)
As a rule, such caries develops asymptomatically, for more than one month or even a year, it does not manifest itself in any way, but destroys the tooth tissue from the inside. And at some inopportune moment, a part of the tooth, thinned by caries, breaks off.
What to do?
Treat the tooth at the dentist: remove all tissues affected by caries and restore the tooth (with a filling, ceramic inlay or crown, depending on the degree of its destruction). And be sure to check all other teeth for hidden caries!
How to avoid?
See your dentist for preventive examinations more often in order to promptly detect hidden caries at an early stage, when treatment is easier, faster and cheaper.
Possible complications
A fracture of a baby tooth in a child usually does not lead to complications, as it is accompanied by the removal of a temporary tooth and subsequent observation.
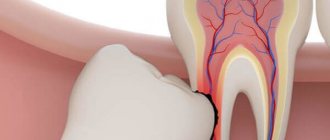
In adults, trauma to a permanent tooth can lead to its loss and a long recovery process. Delayed contact with the dentist leads to:
- To an abscess of the maxillofacial area.
- The formation of phlegmon is a purulent-necrotic inflammation that can lead to sepsis or meningitis.
- Tooth loosening and loss.
- Acute pulpitis.
- Pulp atrophy, that is, its replacement with connective tissue.
- Inflammation of the periosteum (periostitis).
Long-term consequences of injury include root resorption, that is, resorption of the bone tissue surrounding the tooth. This phenomenon is normally observed in children when changing baby teeth.
If, after a minor injury, a person does not go to the dentist, then it should be taken into account that the integrity of the tooth may be compromised. A crack or break is not always noticeable outwardly, and the painful syndrome is mild. In this case, the tooth may not withstand normal chewing load. This can lead to a complete fracture.
Incorrectly restored tooth
- Poor performance of the filling , violation of technology and methodology during restoration (we will not dwell on this).
- The type of restoration is inadequately selected, in a word, “too big a filling” (i.e. they put a filling in cases where it can no longer be placed, but there are all the indications for “more serious” ceramic restorations (inlays, crowns).
I would like to dwell on the second reason in more detail.
Competent dentists know that there is an index of tooth surface destruction (DSI), which must be taken into account before restoring teeth in order to do it correctly. For you, dear patient, I will describe it in a simplified way. If the tooth is not severely damaged (conditionally up to 40% of the surface), a filling is an excellent way to restore it. Destruction of 40 to 70% of the surface requires the manufacture of a ceramic inlay or strengthening of the tooth with various pin structures.
If there is a significant degree of destruction of the tooth surface (more than 70%), the tooth should be correctly restored with a crown. In a word, the type of tooth restoration depends on the degree of destruction.
What's wrong with a filling?
Each recovery method has its own indications. So, a filling is necessary and can be placed in cases of small and medium degrees of tooth decay. If the decay is significant, a large filling can split the tooth in half.
Let's find out why!
Any material (even metal) expands when heated (remember the temperature of the tea you drink!). Temperature changes are a fairly common occurrence that our teeth encounter (from hot tea to ice cream). The coefficient of thermal expansion of filling materials is still higher than that of tooth tissue. That is, when hot food is consumed, the filling expands more than the tooth tissue that surrounds it. The larger the volume of the filling, the greater the expansion (this is why a large volume of the filling is so undesirable).
Of course, this expansion is minimal, not noticeable to any eye and not perceptible. However, add to it a chewing load (which far exceeds temperature deformations), a large filling, thinned tooth tissue, and the likelihood of chipping increases many times over.
Unlike filling materials, ceramics (from which crowns and inlays are made) have a closer coefficient of thermal expansion to the tooth tissues, and therefore do not contribute to its chipping. In addition, it is stronger. That is why it is correct to restore severely damaged teeth not with fillings, but with ceramic restorations. There are other physical phenomena that affect the change in the size of the filling and, as a result, the splitting of the tooth.
All of the above, of course, is true only with an adequately completed restoration (even fillings, even crowns). An inaccurate hand of a master can lead to chipping even with ceramic restorations, and on the contrary, a skillful hand can place a large filling so that it will last a long time. However, there is a limit to everything and it is better not to go beyond the indications for restorations if you want to get guaranteed and reliable work.
Conclusion : you should not expand the indications for conventional fillings too much; they are not capable of qualitatively restoring a badly damaged tooth. But in case of minor tooth decay, fillings have proven themselves to be excellent!
Let me give you a photographic example.
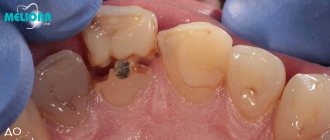
The patient complained that it was painful for her to bite on one of her teeth, that something “crunched” in it.
Upon examination, we determined: tooth 4 on the upper jaw: it has a medium-sized filling (at first glance). And a movable, broken tooth wall, which is held together only by the gums. This wall is no longer attached to the tooth.
The broken fragment of the tooth is mobile, easily moved to the side, but has not yet been removed.
View of the tooth after removing the broken wall: the cheek wall was chipped under the gum. A large filling and a thin remaining tooth wall on the palatal side are visible. Some doctors may try to restore such a tooth using a crown (with preliminary extension); some doctors will offer a perhaps more predictable option: removal and subsequent implantation.
Why are teeth restored incorrectly?
It’s absurd, but often the dentist follows the patient’s lead. The patient, not fully understanding all the subtleties and features of the distribution of the load when chewing, refuses the inlay or crown and asks the doctor to “put a filling”, they say, I’ll work with it a little more, and only then the crown! As a result, at the most inopportune moment, a “piece” of the tooth breaks off. As a result, such “pity” of the doctor for the patient turns out to be a bigger problem for the patient than timely adequate tooth restoration.
By clicking on the “Make an appointment” button, I consent to the processing of my personal data.
I have read and agree with the conditions for processing personal data set out on the website ds-chocolate.ru.
Consent to the processing of personal data
How to properly restore teeth?
When treating a tooth, the doctor must remove all carious tissues, old fillings, movable walls, if any, completely clean the tooth and only then assess the degree of destruction (which walls and cusps have survived, whether they are able to bear the load, how the load on this tooth will be distributed during different methods of restoration, whether chips of any wall are possible, whether its restoration will lead to a split of the root, etc.). After such an assessment, it is determined how to properly restore the tooth: is it possible to put a filling, or does it need to be “strengthened with a pin,” or would it be more correct to use a ceramic inlay or a crown.
Conclusion: a properly selected restoration will preserve the tooth for many years, protect it from further destruction, and the patient from having to redo the work in a few years.
How exactly is treatment carried out?
The actual treatment process depends on the condition of the tooth. In particular:
- If the patient has a small chip as a result of a fracture, then restoration of the crown is possible with composite materials. It is necessary for aesthetic purposes, as well as to prevent the spread of caries.
- In case of a vertical (longitudinal) fracture, the remainder of the tooth is removed. The patient is usually offered prosthetics, and if everything is in order with the oral cavity, there are no contraindications, then they can begin on the same day. That is, an implant can be implanted in place of the tooth root. The minimum time between tooth extraction and implantation eliminates the issue of the need to increase bone volume.
- If the crown is broken at the root, an artificial crown is installed that will completely repeat the shape of the “native” tooth. As a rule, metal-ceramics are used as the main material for prosthetics, but other options are possible.
- If a fracture occurs in a chewing tooth, then in this case the level of load must be taken into account. That is, the pin must be made of titanium. Also, subsequently, a crown that can withstand such a load is carefully selected.
- If a pulpless tooth is fractured, a crown or implant must be installed.
Also, modern technologies make it possible to carry out prosthetics using micro-locks. It implies rapid healing and less trauma to the mucous membrane. Plus, the spread of this technology has made it more popular.
Injury
Single or chronic - the third reason for possible tooth chips
A single injury occurs when there is a blow, an accident, or accidentally biting on a hard object while chewing.
There are three types of chronic injury
- Due to malocclusion (when the teeth do not close correctly, some teeth may receive excessive load, close in the wrong areas, at the wrong angle, or with an opponent that is not their power). For example, a powerful fang of the lower jaw can be positioned in such a way that when closed, it will severely injure the incisor on the upper jaw, which is much inferior to it in size and power. As a result of such long-term closure, the incisor can get into big problems, and the patient will face the need for treatment or removal.
- Due to the absence of other teeth (when a number of teeth are missing, their work is performed by the remaining ones; excessive load may one day result in a fracture of the tooth, a break in its wall, or a split in the root).
- Due to bruxism (“idle” teeth grinding) or other parafunctional manifestations.
How to avoid?
- Be sure to restore missing teeth (there are a lot of ways today, there are even temporary prosthetics if for some reason you need to postpone dental treatment).
- Consult an orthodontist, orthopedist or periodontist about bite problems and undergo orthodontic treatment if indicated.
- Get advice from an orthopedist/gnathologist and psychotherapist about the possible causes of bruxism and take possible measures that the doctor recommends.
What to do if your tooth chipped?
See a dentist.
The doctor will remove the broken wall, take x-rays of the tooth, and evaluate its safety. If the tooth is not broken much, the root is not damaged or almost not damaged, then it can be restored. Then the tooth is prepared (if necessary, dental canals are treated, caries and old filling materials are cleaned), how badly it is damaged is assessed and the best way to restore it is selected (filling, inlay or crown). If the tooth cannot be saved, it is removed and replaced with an implant or other available method.