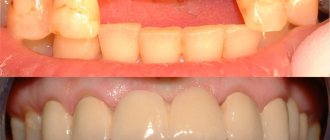
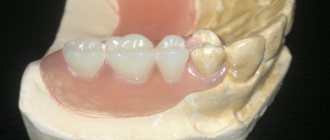
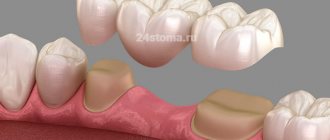
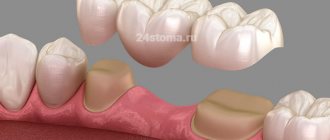
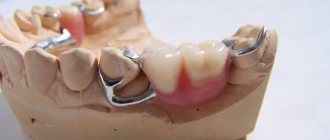
Prosthetics with solid-cast bridges are now being used more and more often due to the possibility of eliminating a large number of defects using this method. To understand what this restoration option is, let’s consider how the structure is manufactured in a clinical laboratory setting, and what advantages and disadvantages it has.
What are solid bridges?
Manufacturing of a combined solid-cast bridge prosthesis
A bridge is a structure with supporting elements and several artificial crowns that replace missing teeth. The concept of “solid cast” implies that the structure is cast simultaneously.
The manufacture of a one-piece bridge prosthesis eliminates the adhesion of various elements to each other. The structure is made from casting various alloys, and most often it is gold, silver, palladium, chromium, cobalt.
Simultaneous casting of the prosthesis makes it possible to improve its quality in terms of strength and performance of basic functions. They are now valued in dentistry due to their improved manufacturing techniques and relatively low cost, which allows this restoration option to be considered by a large number of patients.
What they look like
A solid cast bridge resembles a bridge. The design consists of several connected crowns, which allows you to replace a defect on one side of the jaw. Two crowns from the prosthesis are supporting; they are fixed to healthy teeth. Externally, the metal frame has a specific color, which affects aesthetics, which is why this restoration option is being considered for replacing the chewing group of teeth.
Important! The main difference between a solid-cast bridge structure is that it is a single whole without joints or soldered elements.
Such products can be improved by combining different manufacturing options, spraying, and coating with a polymer overlay. This method of restoration is considered for the loss of chewing teeth.
This is what a solid-cast bridge prosthesis of chewing teeth looks like.
Bridges can be placed on the front teeth, but their appearance does not even closely match the natural tissues of the tooth, so more aesthetic options are selected to restore the “smile zone.” If the choice was made on a solid-cast bridge structure, then it is possible to cover it with a composite, which will make the appearance more natural.
Zirconium dioxide dental bridges –
Zirconium dioxide ceramic bridges are manufactured using CAD/CAM technology, which involves milling bridges from pressed zirconium dioxide blocks on a computer-controlled machine. Sintered zirconium dioxide has a strength comparable to metal (more than 900 MPa). Thanks to this, zirconium dental bridges can be made of any length - even horseshoe-shaped bridges with a length of 12-14 teeth (which cannot be made from any other types of metal-free ceramics).
We have already said above that a zirconium bridge is the gold standard for prosthetics of the chewing group of teeth. But there are questions about the aesthetics of zirconium dioxide bridges, and when prosthetizing the front teeth, you may encounter a big problem (the bridge will stand out against the background of the patient’s own teeth). The fact is that there are 2 types of bridges and crowns made of zirconium dioxide, and they differ from each other not only in aesthetics, but also in the risk of ceramic chips.
1) “Traditional” zirconia bridges –
For such bridges, only the internal frame will be made of zirconium dioxide, which is lined with ceramic mass, or rather porcelain, on the outside (Fig. 14). And this is due to the fact that most dental laboratories use cheap versions of zirconium dioxide blocks. This zirconium dioxide has a bright white color, plus it is completely opaque, and as a result, such a material does not allow achieving a certain degree of translucency, which is characteristic of natural tooth enamel.
Crowns and bridges made from such material will have an unnatural milky white color, plus there will be no translucency characteristic of natural teeth. Therefore, in order to improve aesthetics, only the internal frame is milled from such zirconium dioxide, which gives strength to the structure, and then the dental technician, by applying layers of porcelain, gives the crowns of the bridge the final shape and color. But even despite this, the aesthetics of such crowns and bridges will be far from perfect.
Plus, this manufacturing method has another disadvantage. We have already said above that zirconium dioxide has the strength of a metal (from 900 MPa), however, the layer of porcelain mass on the surface of the zirconium frame has a strength of only 80-120 MPa. This leads to chips of the ceramic mass (according to statistics, within 6 years they occur in approximately 10% of patients). The chips are repairable, but the reliability of such repairs leaves much to be desired.
Conclusions : we do not recommend using zirconium dioxide bridges (made with a surface layer of porcelain) for prosthetics of chewing teeth, because in this case there will be a high risk of chipping. When replacing front teeth with prosthetics, this option is not very successful, because the crowns of the bridge will still have an unnatural milky tint, standing out against the background of your own teeth (Fig. 15-16). Plus, there is still a risk of chipping the porcelain lining.
The aesthetics of such structures are
Such milky-white crowns and bridges made of zirconium dioxide will look acceptable only in one case - if you are going to simultaneously prosthetize all the teeth that fall into the smile line on both the upper and lower jaws (i.e. at least the fifth teeth inclusive ). Otherwise, such a bridge will be very noticeable against the background of your own teeth.
2) Zirconium bridges using “Multi-layer” technology –
But the problem of poor aesthetics and chipping was solved by the advent of the next generation of zirconium dioxide blocks/discs. Currently, a number of manufacturers produce zirconium dioxide with “Multi-layer” technology. Discs made from such zirconium dioxide are “pre-colored”, i.e. they have a color gradient that is characteristic of the enamel of real teeth. The second difference: due to the stabilization of zirconium dioxide by yttrium, such blocks will have varying degrees of “transparency”, i.e. translucency.
As a result, crowns and bridges made from such material will have a gradient of color and transparency, which will vary from the neck of the tooth to the incisal edge (the cusps of the chewing teeth). Those. The closer to the incisal edge, the lighter and more transparent the zirconium dioxide becomes. But multi-layer technology can provide more than just good aesthetics! In this case, there is no need to use surface layers of porcelain, and therefore crowns and bridges will be made of monolithic zirconia.
Clinical case No. 1 – below you can see the aesthetics of newly made single crowns and bridges made of zirconium dioxide, made using the “Multi-layer” technology (they are not yet fixed in the oral cavity, but are on a plaster model of the patient’s teeth). The bridge prosthesis in the projection of 14-15-16 teeth is made with artificial pink gum, and the remaining units are made in the form of single zirconium crowns. With these photos we want to show a smooth transition of color and transparency.
Therefore, if you want to get decent aesthetics, then when you go to a dental clinic, you need to find out whether they use “Multi-layer” zirconium dioxide. High-quality discs using this technology: these are 2 variants of Katana® discs - UTML or STML (Japan), as well as Prettau® Anterior (Germany). The cost of one such disk starts from 16,500 rubles. For example, a disc made of ordinary white opaque zirconium dioxide costs only 4,500 rubles, and therefore many clinics, in an attempt to save on costs, work with cheap, outdated materials.
Conclusions: if you need a bridge prosthesis on implants, or a bridge prosthesis in the area of chewing teeth, then a bridge made of monolithic zirconium dioxide using the Multi-layer technology is not the cheapest, but the best option. When it comes to front teeth prosthetics, if you want to get the best aesthetics possible, there are limitations. For example, if you are planning to make a bridge or crowns on all front teeth (falling into the smile line), then Multi-layer zirconium dioxide will allow you to get the ideal aesthetic result.
However, if you need a bridge for only 3-4 teeth, then even with the help of the Multi-Layer technology, a dental technician is unlikely to be able to make such a structure absolutely indistinguishable from neighboring natural teeth. In this case, to achieve ideal aesthetics, it is worth choosing a bridge not from zirconium dioxide, but from pressed Emax ceramics. This is due to the fact that when working with Emax, the dental technician will have significantly more color options in his arsenal (than when working with any option of zirconium dioxide), which will make the bridge as similar as possible to the neighboring teeth.
Cost – for zirconium bridges, the price for 2022 in Moscow will be on average from 30,000 to 40,000 rubles (for 1 Unit/crown). Thus, the cost of a 3-unit bridge will be at least 90,000 rubles. However, in a number of clinics you may well be offered a price of less than 30,000 per unit, but in this case the bridge will clearly not be “multi-layer” or monolithic.
Materials used
For the manufacture of solid-cast prostheses, gold (both in pure form and sputtering) and stainless metals, or rather their alloys, are used.
The materials used can be combined, and such a prosthesis will be classified as combined or with veneer. The following materials are used as the base material for the manufacture of a solid-cast bridge:
- gold;
- silver and palladium;
- cobalt and chromium.
Structures made of chromium and cobalt can be improved by manufacturing in their natural form, gold plating, or ceramic coating to resemble natural hard tissues of teeth.
How much does a dental bridge cost?
Moscow prices for bridges consist of the cost of the casts required for the manufacture of the structure, the prosthesis itself, its fitting and installation. The cost of the dental bridge itself depends, first of all, on the material used. Thus, the most budget option is plastic, but plastic structures are used only as temporary prostheses, the most expensive are all-ceramic bridges with a zirconium dioxide frame, metal-ceramics are inferior to them in cost, but practically not inferior in quality. Also, how much a dental bridge costs is influenced by the price category of the dental clinic where a dental bridge can be made in Moscow. Thus, installing the most budget bridge in economy class dentistry will cost an average of 3,000 rubles, and in a VIP clinic prices will start from 20,000 rubles for a structure consisting of two supporting crowns and one artificial tooth between them. You can find out how much it costs to install a dental bridge by reading the price list on or by calling our clinic directly. The administrator will also tell you what is included in the price and which procedures are paid separately.
Types
The following types of structures are distinguished:
- Coated with gold prostheses.
Sprayed bridge
- Without spraying - they look like polished metal.
Solid cast bridge without spraying
- With lining - has a composite or plastic lining on the front surface. There is a drawback - the risk of cracks and chips.
Solid cast bridge with veneer
- Combined - the design can be solid in the area of the chewing crowns and ceramic in the smile area to improve aesthetics.
Combined dentures
Preparation for prosthetics
Preparation for the installation of an orthopedic structure can be therapeutic, surgical, orthopedic and orthodontic. Types of preliminary sanitation can be combined, depending on the condition of the oral cavity and the type of defect.
How do you prepare for prosthetics at the dentist:
- Assessment of oral health.
- Carrying out professional cleaning to remove hard dental deposits.
- Carrying out anti-inflammatory therapy if necessary.
- Removal of carious cavities, treatment of pulpitis, periodontitis and other existing pathologies of teeth and mucous membranes.
- Depulpation of teeth (according to indications).
The surgical type of preparation includes the following activities:
- Removal of teeth that cannot be treated. Indications include chronic periodontitis, cysts, and pathological mobility of crowns.
- Removal of soft tissues due to their hypertrophy (hypertrophic gingivitis).
- Complex treatment of dentofacial pathologies.
Orthodontic preparation includes returning the normal bite of healthy teeth through the use of braces, aligners, and plates. Treatment is necessary to correct the position of individual abutment crowns and to create space in the oral cavity for fixation of the bridge structure.
The orthopedic preparation stage includes procedures such as:
- Making corrective aligners to move the advanced crown to the opposite side where the tooth is missing. In this way, the orthopedist creates a place to install the structure.
- Making functional mouthguards to relax the masticatory muscles. Such an event is indicated for hypertonicity in order to prevent breakage of the bridge after installation.
When can you build a bridge?
It is important to correctly draw up a prosthetic plan and ensure the stability of the supporting teeth.
Movable units or those affected by caries cannot serve as the basis for the structure. An upper or lower bridge is installed on natural teeth. When asked by patients: “Is it possible to install a bridge structure on an implant on one side and a tooth on the other?” there can only be a negative answer. A real, living dental unit has some mobility, and the implant is fixed rigidly, motionless, as in the following photo:
The bridge will loosen the implanted artificial root and place an inadequate load on the natural tooth. Plus, the service life of the implant is long, often lifelong. Real units are more vulnerable. The supports can be either two real teeth or a pair of implants.
If a tooth has been removed, but the crowns and roots of the units located next to the gap are strong enough, then a bridge is one of the rational and inexpensive methods of prosthetics.
Clinical and laboratory stages of manufacturing a bridge prosthesis
Stages and their features (K - clinical, L - laboratory):
- K - the dentist makes a diagnosis, selects the type of construction together with the patient, prepares the abutment crowns, after which impressions are taken.
- L - creation of a plaster model, selection of the color of the prosthesis, creation of a temporary structure.
- K - fitting the temporary product, checking occlusion.
- L - casting of a permanent bridge structure.
- K - fitting of the prosthesis.
- L - cladding or spraying.
- K - installation of the structure in the oral cavity, assessing the quality of its fit, fixation with special cement.
The prosthetic procedure will require 2 visits to the dentist’s office:
- First. The defect is assessed, the doctor considers the optimal restoration options, and clarifies with the patient which restoration method is preferable. On the first visit, the oral cavity is sanitized and the supporting elements are ground. The dentist takes impressions, sends them to the laboratory and places temporary aligners.
- Second. The dentist places a ready-made solid bridge, finds out how well it fits the patient, and whether there are any defects. When everything is in order, the structure is fixed with composite cement.
Important! When there are inflammatory pathologies of the mucous membrane or other relative contraindications, several visits to a specialist will be required until the problem is eliminated.
If the quality of the finished product does not match, it will require correction. In this case, prosthetics will also be extended over more than two visits.
Advantages of cast dentures
Cast dentures can be single or bridge-like, covering several teeth. Depending on which part of the dentition needs to be replaced, there are crowns used to completely replace a tooth, structures that restore a damaged tooth in the presence of a stump, crowns that restore the height of a tooth, and half-crowns necessary to support dentures in the mouth. In order to determine what type of prosthetic dental structure is needed in a particular case, a detailed consultation with a dentist is required.
Metal cast dentures have been used in dentistry for many decades; over the years they have been repeatedly improved, maintaining and increasing their positive qualities. Using this technique, permanent prosthetic structures for teeth are made.
Among the main advantages of dentures made by casting are the following:
- The method of manufacturing such dental prostheses ensures their tight fit without damaging the oral mucosa. This not only increases the aesthetics and comfort when using dentures, but also reduces the likelihood of oral diseases.
- Thanks to the materials and manufacturing methods used, prosthetic structures made by casting are characterized by a long service life. Dentures require replacement or adjustment no more than once every 10 years.
- The materials from which such dentures are made prevent the accumulation of pathogenic microbes in the mouth.
- Safety for teeth is ensured by the strength of the materials from which such dentures are made. They allow you to avoid grinding and deformation of teeth, which is important when installing cast bridges, which cover healthy teeth on both sides of the missing teeth to be replaced.
- The affordable cost of such dental prostheses is an important factor for many clients of dental clinics, since among them there are often pensioners and other socially vulnerable segments of the population.
- Precision in the manufacture of dentures is ensured by casting technology. Due to the fact that the cast dental prosthesis is made in one piece and does not require soldering of small parts, it fits tightly in the mouth and occupies the space in the mouth that was intended for natural teeth.
- Comfort when wearing and the patient’s quick adaptation to a new denture is one of the main advantages from the point of view of those who will wear it.
These distinctive features of cast oral dentures make them popular and widely used in prosthetic dentistry.
Installation process
The entire installation process of a solid cast structure includes the following activities:
- Sanitation of the oral cavity.
- Turning of abutment crowns using anesthesia. About 1.5 mm of tissue is removed. The crown is given a special shape for a secure fit of the prosthesis.
- Taking an impression.
- Trying on a temporary prosthesis with its subsequent fixation.
- Trying on a permanent structure and checking the quality of fit.
- Fixation of the permanent structure with cement.
Advantages and disadvantages
| pros | Minuses |
| Homogeneous design, lack of solder, which increases the strength of the product. Unlike other prostheses, solid ones almost never break, because there are no weak joints | Low aesthetics |
| High strength and durability | The cost is higher than a cast prosthesis |
| Tight fit to the tooth, which prevents food particles from getting under the crown, and this prevents secondary caries and destruction of enamel under the prosthesis, and also reduces the likelihood of damage to the structure | Great thermal conductivity |
| High functional efficiency due to precise modeling of support elements and intermediate parts | Risk of discomfort when eating hot food |
| No darkening factor in the structure in the soldering area | Cannot be determined in case of metal allergy |
| Wax can be used to thicken the walls of an orthopedic product. | The need to grind healthy crowns, which over time leads to their destruction due to malnutrition |
| The one-piece design is better tolerated by patients, the risk of prosthetic stomatitis is reduced | High load on abutment teeth can cause them to become loose |
How to put a bridge on teeth -
Installing a bridge on teeth is carried out as follows... The teeth located on the sides of the missing one will act as support for the bridge. If only 1 tooth is missing, crowns are usually taken on one tooth on each side of the missing one. If 2 teeth are missing in a row, then a total of at least 3 teeth are taken under the bridge supports (one on one side of the dentition defect, and two on the other).
How to put a bridge on teeth: diagram and photo
Installing a bridge requires grinding down the supporting teeth for crowns, and here it must be taken into account that for different types of artificial crowns the thickness of the preparation will differ. For metal-ceramics, teeth are ground from the chewing surface by 2.0-2.5 mm, from the lateral surfaces by 1.5 mm (Fig. 4). For crowns made of metal-free ceramics - only 1.5 and 1.0 mm, respectively (Fig. 5). Moreover, the more tooth tissue is preserved under the artificial crown, the longer its service life will be.
Schemes for preparing teeth for crowns –
Moreover, please note that in the gingival zone, the tooth crown is ground in such a way that a so-called “ledge” (i.e., a step, Fig. 6) is formed along the entire perimeter of the tooth stump. The service life of the crown will largely depend on the quality of the ledge formation, because poor/inaccurate fit of the crown to the neck of the tooth in the area of the ledge - leads to the gradual entry of bacteria under the crown and the beginning of decay of the tooth tissue. And this happens very often.
Preparation of supporting teeth for prosthetics –
In many cases, teeth under artificial crowns are subject to depulpation, i.e. the nerve will need to be removed. This is due to the fact that deep in the tooth there is a neurovascular bundle (pulp), and the more tissue is ground off when preparing a tooth for a crown, the higher the risk of nerve injury. Accordingly, because Under metal-ceramics, more tooth tissue is ground off - here it is possible to leave mainly only large molars alive (they have a greater thickness of hard tissue around the nerve).
But for ceramic crowns, almost 2 times less tooth tissue is ground off, and in this case, almost all the teeth can be left alive. Keeping your teeth alive is very important because... after removal of the neurovascular bundle, the tooth stops receiving moisture and nutrition from the inside, which leads to an increase in the fragility of the hard tissues of the tooth and reduces its service life. The cost of removing nerves and filling root canals will depend on the number of root canals in the supporting teeth, and on average will be (for 1 tooth) –
- tooth with 1 root canal – from 2500 rubles,
- tooth with 2 channels – from 3800 rubles,
- tooth with 3 channels – from 5,000 rubles.
Dental bridge: before and after photos
Important: if the adjacent teeth from the missing one do not have fillings and are alive, then prosthetics with a bridge and grinding down the adjacent teeth for crowns is actually a very bad idea. The price of a dental bridge of 3 units made of ceramics or good metal-ceramics (taking into account the cost of preparing teeth for prosthetics) is almost always higher - when compared with the cost of installing 1 economy-class implant.
A dental bridge should be done only if the adjacent teeth from the missing one have large fillings (taking up more than 1/2 of the tooth crown in volume), and also if the nerves have been removed from them. Remember that the service life of the best crowns will be, at best, no more than 10-15 years, and what will happen to the supporting teeth after this time, and whether they can be re-used with prosthetics is still a big question. Your own living teeth (as opposed to artificial crowns) can last you much longer.
Contraindications
One-piece denture in the mouth
There are relative and absolute restrictions that do not allow the installation of a solid-cast bridge. The first include conditions that this method of recovery completely excludes. Relative contraindications are considered individually.
A solid-cast bridge is not used in the following conditions:
- defects when more than 1 molar, 2 premolars and 4 incisors are missing;
- infectious and inflammatory pathologies of the jaw bones, including osteomyelitis and osteoporosis;
- psychological illnesses that do not allow the patient to take care of himself, as well as epilepsy;
- oncological diseases;
- pathologies accompanied by blood clotting disorders;
- allergy to the materials used or anesthetic substance.
Relative restrictions to this recovery option will be:
- teeth grinding at night or bruxism;
- acute period of inflammatory pathologies of the oral mucosa;
- poor oral hygiene;
- pathological abrasion of enamel;
- severe pathologies of periodontal tissues with frequent relapses;
- abnormal dental bite that cannot be corrected.
Solid bridge
The product is made using special casting. The advantage is that the crown itself fits firmly to the ground tooth, so the places in contact with the gum and possible gaps are not clogged with food debris.
This type completely eliminates destruction. There are also disadvantages to this design. This is primarily a great sensitivity to hot. A person experiences discomfort when eating hot food.
Service life and care
With proper care, a solid-cast bridge can last for 15 years without breaking. The service life of such a product is practically unlimited, but it is important to visit a doctor regularly in order to identify problems in time and solve them at the initial stage.
What you need to do to properly care for a solid bridge:
- regularly clean your mouth in compliance with standard hygiene rules;
- use a toothbrush, dental floss and a special brush daily to clean the spaces between the gum and the structure;
- use an oral irrigator several times a week;
- visit the dentist every few months for professional oral hygiene and assessment of the condition of the orthopedic structure;
- rinse and clean the mouth after each meal, for which it is enough to use a deodorizing mouthwash or a solution prepared at home from herbs, which will prevent inflammatory diseases.
Important! Installation of a one-piece denture makes it impossible to carry out standard professional oral hygiene. The dentist uses special cleaning products and brushes to clean your teeth. It is also unacceptable to use the irrigator in high pressure mode, directing the stream at the prosthesis.
A dental bridge fell out: what to do?
Dental bridges, as well as dental crowns, as well as other orthopedic structures, have a service life, after which they must be replaced. Modern materials and manufacturing and installation technologies make the shelf life of orthopedic structures quite long, but this does not negate the mandatory removal of a dental bridge whose shelf life has expired. Unfortunately, many patients, if not the majority, ignore the need to remove the bridge and replace it with a new one until the problem becomes a rib, that is, until the dental bridge falls off.
A timely, regular visit to the dentist will help to avoid such a problem, who will be able to detect that the dental bridge has become loose or has begun to collapse, before the patient feels it himself. The fact is that the shelf life of a bridge is limited not so much by the properties of the manufacturing material itself (with proper care it is practically not subject to erosion), but by the fragility of the composite materials with which the lateral crowns of the bridge are attached to the supporting teeth, as well as the danger of development under these crowns secondary caries, which is aggravated by the fact that the supporting teeth are most often “dead”, pulpless, which reduces their resistance to carious lesions. So how is a dental bridge removed? Considering that after removing the bridge, a new one needs to be installed in its place (in rare cases, it is possible to install the same structure if it is not damaged, but with fresh cement), it is very important not to damage the supporting teeth in order to avoid even further grinding of them. For this purpose, special ultrasonic devices are used, which cause the cement between the crown and the tooth to crumble, after which the bridge is removed.
If the dental bridge breaks and falls off, you must immediately consult a doctor, since the ground supporting teeth should not be open, this will lead to their damage, in addition, the bridge could become detached traumatically, and only a specialist can notice and correct this.
Very often on various forums you can come across the question: “What to do if the dental bridge is wobbly?” The answer is simple: consult a doctor immediately. Perhaps the installation technology was violated or the design was not accurately adjusted to the ground abutment teeth. If the dental bridge begins to sway several years after installation, this may indicate the presence of the above-mentioned secondary caries or partial destruction of the cement between the crown and the tooth tissues.
It is also necessary to consult a specialist if you experience toothache under the bridge. This is another sign of secondary caries. If the gums hurt at the point of contact with the central part of the bridge, perhaps the structure was set too deeply, which caused rubbing of the soft tissues by the edge of the bridge, and this in turn can lead to the formation of bruises and bedsores, and in advanced cases, to an inflammatory process.
If chips or microcracks have formed on the artificial enamel of a dental bridge (in the case of ceramic and metal-ceramic structures), it is most often possible to repair dental bridges with composite materials directly in the patient’s oral cavity. In some cases, it is also possible to repair structures made of plastic and metal-plastic. WARNING: If you swallow a dental bridge or a fragment of it, go to a clinic or emergency room. An ultrasound examination of the gastrointestinal tract may be required, since the sharp edges of the chips can damage the mucous membranes of the stomach, esophagus and intestines.
Price
The approximate cost of a solid-cast bridge varies from 7,000 rubles. The price differs depending on the length of the defect and the metal alloys used.
The cost will be higher if the structure is additionally coated with ceramics to improve the appearance. Also, the price differs for combined dentures and products with veneering.
To choose a prosthetic method, consult an orthopedic dentist. The doctor will conduct the necessary research, select which prosthesis is best suited in a particular situation, and tell you about all the intricacies of subsequent prosthetics.
How much do metal-ceramic crowns cost?
The cost of metal ceramics consists of:
- metal base (a gold frame, of course, costs more than a palladium alloy);
- ceramics (the price of ceramic mass depends on the manufacturer. For example, a jar of MC Emotions Opaque powder - 3200 rubles for 20 g);
- volume of work of a dental technician;
- electricity costs (firing);
- depreciation;
- additional expenses (taxes, rent, payment for third-party services).
As a result, the approximate cost of manufacturing a fixed metal-ceramic prosthesis is from 5,000 rubles. And then you need to add the price for diagnostics, preliminary treatment, preparation, installation. The total cost of visiting a dental clinic (1 crown) can reach 250 thousand rubles.
Prices on the website of any clinic are approximate. Each case is individual, so it is better to prepare in advance for an increase in costs by about a third.