Chief editor of the site:
Snitkovsky Arkady Alexandrovich
Chief physician of the professorial dentistry “22 Century”, dentist, orthopedic dentist
Author of the article:
Scientific team of dentistry “22 Century”
Dentists, candidates and doctors of medical sciences, professors
Types of Dental Implants
Today, every modern dental clinic offers such a service as dental implantation. Let's look at the basic terms and concepts, as well as types of dental implants.
Basic terms
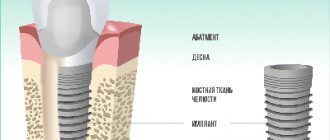
- A dental implant is a structure that is installed into the jaw bone during surgery and replaces the roots of the teeth, and also serves as a support for prosthetics;
- An abutment is a supragingival structure that imitates a tooth stump. It can be integral with the implant (non-separable design) or as a separate structure (demountable design);
- The healing abutment is a supragingival intermediate structure. Essential for creating a beautiful natural gum margin. (in the case where the abutment and implant are a single whole, not used);
- Osseointegration is a direct structural and functional connection between living bone tissue and the surface of the implant implanted into it.
What is transocclusal (screw) fixation?
When attaching a crown to an implant, two types of fixation of a dental crown to an implant are used: screw and cement.
Screw fixation can be implemented in two ways. The first is that the abutment is permanently connected to the crown, the structure is inserted into the implant and fastened to it with a screw (a through hole for the screw is first made in the crown). The second is that the abutment is installed on the implant, the crown is installed on the abutment and attached to it with a screw. The hole in the crown is called a tunnel; it is closed with a tooth-colored filling.
When using screw fixation, the technician will require higher qualifications, because... even small deviations from the size will not allow you to install a crown in your bite
Cement fixation . First, the abutment is screwed to the implant, and then the crown is fixed with cement mortar (composite adhesive) with shock-absorbing properties - just like a regular crown on the tooth stump.
The screw type of fixation is more reliable, convenient and safe. If you need to fix something, you can drill out a filling on the tooth, unscrew the screw and remove the crown. This allows you to save the rest of the structure, correct the mistake and place the crown again.
Cement fixation is used when installing bridges on two or more implants. In this case, high precision must be observed (in order to attach the bridge to the required number of implants). This method of fixation “forgives” the errors of the dentist and technician, but it will be difficult to remove the prosthesis later. Recently, advanced technologies have been used in dentistry, and installation errors occur only due to the low qualifications of the doctor or violation of established standards. Therefore, cement fixation of prostheses is used less and less.
Implantation can be:
- Direct (performed immediately after tooth extraction);
- Delayed (3 months or more pass after tooth extraction).
Prosthetics can be performed simultaneously with the installation of an implant or also after a certain time (two-stage technique).
The choice of one or another implant or method of operation depends on the patient’s general condition , oral hygiene, the volume and quality of the jaw bone tissue, and the patient’s financial capabilities.
Prosthetics prospects
Completion of osseointegration is not the end of the process. Now you need to put the prosthesis on the artificial root. It can be single (crown), bridge or full jaw. Comfort when chewing, diction, and aesthetics depend on the capabilities of prosthetics. The wider they are, the better for the patient, especially in complex clinical cases. Therefore, dentists say that when choosing an implant, you need to focus not only on the manufacturer, but also on the condition of the patient’s jaw. The question is not whether Korean or German, Swiss or Israeli implants are, but which of them are better suited for a particular case.
Dental implant materials
Dental implants
Depending on what material the implant is made of, there are:
Metal
Most dental implants are made of titanium and its alloys. The peculiarity of this material is such that the body does not recognize it as something foreign. In this regard, excellent biocompatibility is noted. It is also characterized by high strength and lack of toxic effects.
Ceramic
Ceramics occupies a special place in dentistry in terms of aesthetics. Its color and light transmission allow it to imitate natural teeth as closely as possible. But when it comes to implantation, aesthetics are not so important. Biocompatibility comes first. The interaction between ceramics and bone tissue has not been fully studied. Thus, we cannot say affirmatively and positively about osseointegration. Therefore, the choice of this type of material remains a big question .
Crowns based on zirconium dioxide
A dental crown on a ceramic implant on a zirconium dioxide frame is also practically no different from a standard crown. The difference from metal-ceramics for an implant is that the abutment for metal-free crowns must be ceramic.
If a ceramic crown is installed on a metal abutment, then firstly, the ceramic, with constant contact with the metal abutment, will quickly crack and become unusable, and secondly, the metal will shine through the translucent ceramic layer, giving the tooth a dark bluish color. In the photo you can see the appearance of crowns made of metal-free ceramics installed on implants and fixed to ceramic abutments.
The cost of a prosthesis will be higher than a metal-ceramic one both due to the crown itself and the abutment.
Advantages of crowns made of metal-free ceramics:
- High aesthetic properties. Products made from metal-free ceramics are indispensable for prosthetics of front teeth, which are visible when talking and smiling. Zirconium dioxide refracts light in the same way as natural tooth enamel, so even an experienced dentist will not always be able to distinguish such crowns from natural hard tooth tissues.
- Metal-free ceramics do not cause irritation to the oral mucosa and, in principle, do not provoke the development of allergic reactions.
- The frame material is selected to match the natural shade of the tooth enamel of neighboring teeth, so artificial teeth will not stand out against the background of natural teeth in any lighting.
According to the form they are distinguished:
Cylindrical
Thanks to the porous structure, a strong connection with the surrounding bone tissue is ensured. Currently, cylindrical implants are produced dismountable, designed for a two-stage application method.
Screw
In order to have an idea about these implants, let's look at the structure of the jaw bone.
The cortical plate is a kind of shell, the strongest, consisting of 95% mineral salts.
Spongy bone is the main layer of bone tissue, represented by crossbars and septa with many small vessels (capillaries). It is in this section that the roots of the teeth are located.
The basal layer is a continuation of the spongy layer, but the septa are located closer with a small number of vessels. Maximum strength and thickness .
Screw implants have a number of advantages:
- Cone shape;
- They are installed in place of the roots of natural teeth, that is, in the spongy layer. When chewing, they also transfer the load to the surrounding bone tissue, thereby maintaining metabolic processes in it at the proper level. It turns out that this type of implant is the most physiological;
- The presence of threads, which increases the area of contact with bone tissue, and, consequently, faster osseointegration is noted;
- They can be collapsible or non-removable, one- and two-stage, have a smooth, rough surface or a coating of bioactive materials;
- They come in different diameters and lengths, which expands the indications for their use.
One of the main conditions for the use of screw implants is the presence of a sufficient volume of high-quality bone. But even if there is a lack of it, it is possible to establish them with the help of additional operations (sinus lifting, bone grafting, etc.). Only the duration of treatment and recovery will change.
In today's market you can see many implant manufacturers. Let's take a look at the leading representatives.
Implant selection criteria
Material characteristics are a very important component of the implantation system. But dental implants made from the same material, manufactured by different companies, or even by the same company - but in different “lines”, can be very different. The success of restoration also depends on the following aspects:
- the implant must be standard, manufactured at a factory: production is carried out using milling, intense plastic deformation (a rarer type). Individual structures made in a regular dental laboratory are not recommended for installation, because their service life is short (about 7 years),
- shape of the structure: now the best are considered to be root-shaped and cylindrical,
- type of thread: it can be sharp with the ability to self-cut, it can be compression - compact the bone tissue around itself,
- surface: it can be smooth and polished by a laser, or rough - processed in an electrolyte solution or using sandblasting. Active substances that stimulate the growth and restoration of bone tissue cells - fluorine, calcium, phosphorus and others - are also applied to the surface.
- sterilization: modern technologies at the production stage allow for 5-stage treatment to remove impurities,
- a correctly selected model for a specific clinical case: therefore, before implantation, patients undergo tests and undergo a computed tomography scan of the jaw. This way, the doctor can identify important features (for example, changes in hormone levels, the presence of inflammation, atrophy of the jaw bone) and choose an implant based on the indications. And in his choice he is helped by 3D planning in a computer program, for example, Simplant, NobelClinician,
- a good implantologist: this item can be put at the top of the list, because the success of implantation depends on the professionalism of the doctor and his responsible approach to the matter.
Advantages and features:
- Each implant is covered with a unique TiUnit material, thanks to which the process of osseointegration occurs much faster (in its structure and composition it is very close to bone tissue);
- 3D planning of the operation, which is the key to the accuracy and high aesthetics of the finished structure;
- Due to the design features of the thread and the body of the implants themselves, tissue trauma is minimal;
- A wide range of implants in diameter and length makes it possible to install them even in the most seemingly difficult clinical situations;
- Simplicity, logic and accuracy in the surgical protocol (operation);
- All Nobel implants have identification numbers. Fake is impossible.
The only downside worth noting is the high cost.
ASTRA TECH implants
ASTRA TECH implants
The system was developed by Swedish scientists and is popular in many countries.
Advantages and features:
- Made of the highest class titanium, which has excellent biochemical qualities;
- Modified OsseoSpeed surface, which accelerates the process of osseointegration;
- The connection of the implant to the Conical Seal Design abutment is located below the gum level, which allows for a more even distribution of the chewing load;
- Patented microthread in the upper part of the implant (in the neck area), which also improves the distribution of chewing pressure;
- The company provides a lifetime guarantee.
Among the disadvantages, high cost can be noted.
Hi-Tec implants
Hi Tec Implants is one of the leading Israeli companies that has been producing a wide range of implants for over 20 years. During this period, the company has established itself as a representative of quality materials at an affordable price .
Advantages and features:
- A wide selection of types of structures, which allows you to choose the optimal one for each specific clinical situation;
- The implants are made of the highest quality titanium;
- Simple surgical protocol (operation progress);
- Having our own full-cycle production allows us to ensure a high level of quality control of dental implants (implants) and a reasonable cost.
Thus, this implantation system combines high quality and reasonable cost. Among mid-level implants, Hi-Tec takes first place.
Lamellar
Plate implants
The intraosseous part is a wide thin plate with a textured surface (macrorelief in the form of a snake or corrugated structure) and holes. Such implants are practically not used, as they have more disadvantages than advantages.
Firstly, they differ in shape from the roots of natural teeth, thus they are not able to withstand and distribute the chewing load in the proper volume. Therefore, the service life is not long.
The only positive thing that can be noted is the low cost.
Structure of a dental implant
A root-shaped implant, as mentioned above, is the most common and sought-after type of dental implant. What does a dental implant consist of? Root-shaped structures have three parts: root, abutment and crown. A titanium rod replaces the root of a lost tooth. The abutment externally is an artificial tooth ground for a crown. It serves as a link between the components of the implant - the rod and the prosthesis, and is also the basis for the latter. Root-like artificial roots are divided into cylindrical and helical. The latter are more in demand in implantology, as they have a thread applied to their surface, which contributes to a more durable fusion of the titanium rod with the jaw bone. Dental implants come in different sizes – they can be short or long, thick or thin. See the photo below for what a dental implant looks like.
Photo of a dental implant
Combined
The shape and size of such implants are determined strictly individually, depending on the number of lost teeth, the thickness of the jaw bone and other factors.
Highlight:
- Lamellar-root-shaped;
- Disc: for weak, atrophied bone in cases where bone grafting is impossible;
- Transosseous: used for severe atrophy of the jaw bone, installed through an incision in the chin area;
- Ramus-frame dental implants: a fairly extensive design that covers almost the entire jaw. It is used for severe bone atrophy and serves as a support for both removable and fixed prostheses.
Such implants are used only in cases where screw installation is not possible. The operation requires more time, the process is complex and traumatic . The recovery period is much longer, and the service life is short.
General and specific contraindications
Who is contraindicated for dental implants? Implantation is a surgical operation and, like any other operation, it has contraindications. They are divided into two types: general for any type of implantation and specific dental ones.
The following concomitant diseases are common to all types of implantation (and to surgical interventions in general):
- violation of coagulation (blood clotting), diabetes mellitus, tuberculosis, chronic rheumatism - these diseases complicate wound healing and implant placement;
- pregnancy and lactation;
- childhood and adolescence – children and adolescents continue to grow, and this is fraught with displacement of implants or their rejection, or slowdown in the growth of individual organs as a result of the installation of dental implants in them;
- diseases of bone tissue that reduce its regenerative abilities;
- diseases of the nervous system;
- cancer during exacerbation, HIV and AIDS, specific diseases of the immune system that weaken the body as a whole and do not allow it to recover after operations.
The following can be considered specific contraindications to dental implantation:
- when installing implants in the upper jaw, it is necessary to take into account such factors as the proximity of the sinuses (aka the maxillary sinuses), as well as the width and density of the bone at the point of contact of the jaw with the sinuses; in some cases, the implantation procedure may be preceded by a sinus lift;
- chronic, including inflammatory diseases of the oral mucosa;
- patient's failure to comply with oral hygiene;
- insufficient height and density of bone tissue at the site of proposed implantation (this applies to both the upper and lower jaws) - in such a case, bone grafting can correct the situation.
It is worth noting that diabetes and advanced age are not currently included in the list of contraindications for dental implantation.
Dental implants in the upper jaw
Basal
Such implants are installed in the basal layer of the jaw bone tissue. It is denser than the spongy layer. This ensures good primary stabilization. Prosthetics can be performed 3-5 days after the operation.
The intraosseous part and the abutment are a single unit. Therefore, it is impossible to correct the supragingival part after installing the implant. There are many cases of loss of aesthetics - dentures look unnatural and do not adhere well to the periodontal tissues.
The process of installing basal implants is not very complicated and traumatic, but basal implants have more “cons” than advantages.
Firstly, this is not titanium (after installing this type of implant, the orthopedic doctor simply bends them with forceps, creating parallelism), but it is titanium that has the property of “fusing” with the bone.
Secondly, with Basal implantation, osseointegration does not occur and it is rather the denture that holds the implants in the bone, and not vice versa.
Thus, at first glance, there are more advantages of basal implants, but the disadvantages are so significant that their use is questionable.
Lifespan of dental implants
Although implantation is significantly more expensive than traditional prosthetics, with a long-term calculation the costs are equalized. This is due to the fact that traditional bridges, crowns, clasp or nylon dentures need to be replaced on average every 5 to 7 years, and the supporting teeth will have to be ground down again each time. How long does a dental implant last? The minimum service life of a dental implant is about 30 years, and if all the doctor’s instructions are followed, the implant will last you a lifetime. Most manufacturing companies, including world industry leaders, who invest considerable funds in the latest developments, provide a multi-year or even lifetime warranty on their products. This applies to the part of the structure that is located inside - that is, the root (base plate, etc.) and the abutment. A crown installed on an abutment has a more limited service life, but it is also significantly longer than that of a traditional prosthesis installed on ground natural teeth. This is on average 10 – 15, sometimes 20 years. If we are talking about implantation for a young person, then, of course, he will be interested in what happens to implants in old age. With proper care and preventive examinations, nothing should happen to the artificial root.