Price
- Primary appointment (examination, consultation) with a dentist (special offer) 100001
For free
Promotion
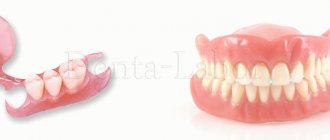
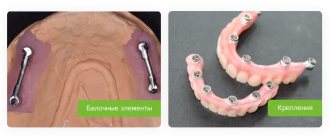
- Dental prosthetics Complete removable plate dentures 153003
35 000 ₽
- Manufacturing of removable dentures from Thermoplastic material 153005
49 000 ₽
- Dental prosthetics using implants Acrylic covering prosthesis with a cast frame made of CoCr alloy (excluding the cost of fixing elements: locators, spherical abutments) 154001
60 000 ₽
- Prosthetics of all jaw teeth on 4 implants
149 900 ₽
Promotion
A complete removable denture is an orthopedic design that simulates the upper or lower dentition in the absence of all teeth. Its base imitates gums and ensures fixation of the device. Artificial crowns are soldered into the base. There are removable complete dentures and conditionally removable ones. The patient can independently remove the first ones at any time. Conditionally removable structures are fixed on implants and can only be removed by a doctor. The method of prosthetics is selected taking into account the nuances of the clinical case and the patient’s preferences.
Purpose, operating principle
The chin sling is used to solve the following problems:
- immobilization of the jaw position for a limited time, indicated for fixation when transporting the patient;
- for constant wear during the period of complete recovery, that is, bone fusion;
- to correct certain pathologies caused by trauma.
The duration of wearing a bandage or mouthguard depends on the condition of the jaw apparatus. Usually this is a temporary fixation for up to two to three days. Sometimes the device is used to correct malocclusions. It is worn outside, the tension is adjusted using special elastic ties.
Installation of an orthodontic product is prescribed in the following cases:
- facial height is insufficient;
- the lower jaw protrudes strongly, excessive growth is diagnosed;
- the profile is concave, there is facial asymmetry;
- aesthetics are impaired due to the mesial position;
- the lower third of the face is reduced;
- the chin protrudes strongly;
- there is retrusion of the teeth of the upper row;
- reverse overlap of the frontal section;
- negative pathologies during the development of rows.
Types of removable dentures in complete absence of teeth
Plate acrylic
Classic acrylic insert jaws are made of hard plastic. Fixation is ensured by a wide lamellar base. When biting, air comes out from under the base and a suction effect occurs. Pros: affordable price, maintainability, aesthetics. The disadvantages include deterioration of fixation as the contours of the prosthetic bed change with the need for relining, large sizes, and the need to adapt to the device. Plastic contains monomers that can cause allergies. Artificial teeth absorb dyes and odors, and after 2-3 years they lose their aesthetic properties.
Acry-Free
Monomer-free plastic Acri Free, produced in Israel, is more elastic than acrylic and does not cause allergies. Products from it are made using the injection molding method, which ensures precise fit of the base to soft tissues, as well as tight fixation. The compactness and translucency of the artificial gum make the false jaw convenient, comfortable, and aesthetically pleasing. The resistance of the structure to chewing loads prevents damage to soft tissues and also somewhat slows down atrophy. Orthopedic devices from Akri-Free are recognized as the best alternative to plastic false jaws, but they cost more.
Nylon
The main characteristic of the material of nylon prostheses is elasticity. The base is thinner, softer, and more compact than plastic, which makes false teeth comfortable for the patient. The translucency of the base ensures aesthetics. However, softness is also a disadvantage of nylon. The base quickly loses its shape, which negatively affects fixation. The device cannot be repositioned. During chewing of food, the load is not distributed, but is locally transferred to soft tissues, which causes pain in patients. The porous material absorbs dyes and changes the smell.
Types of construction
To treat injuries or eliminate orthodontic pathologies, different types of devices can be used:
- A simple type is used to fix bone fragments after a fracture.
- Parietomental. Used for fractures of the lower or upper jaw, it is a bandage that does not change for several days. The bandage is rigid, it is applied immediately after the injury, further wearing and timing depend on the course of the disease, the results achieved and other factors.
- Standard. This is a rigid type of bandage, made in accordance with the basic requirements for such devices. The sling is used for immobilization during injuries, when transporting a patient, to avoid complications after fractures.
- Soft type of construction by Pomarantseva-Urbanskaya. The base is a fabric chin pad with elastic bands and tapes for fixation.
- With head element. This type of design consists of a plastic mouth guard and a cap. The individual elements are fastened using rubber bands that allow you to regulate the pressure and impact.
Which is better
The main characteristics of acrylic, nylon and Akri-Free prostheses are presented in the table below.
| Property/material | Plastic | Akri-Free | Nylon |
| Life time | 2.5-5 years | 5-7 years | 1-5 years |
| Aesthetics | average | high | high |
| Fixation | satisfactory | good | unsatisfactory |
| Dimensions | large | compact | compact |
| Repair | available | available | not possible |
| Flexibility | low | optimal | high |
| Strength | satisfactory | high | satisfactory |
| Allergy | possible | No | possible |
Among modern removable covering structures, products made from Acri-Free are considered optimal. Compared to them, plate apparatuses are very large, heavy, change taste perception, and require adaptation over the course of 2 weeks. Nylon quickly loses its shape, aesthetics, and quality of fixation. They will soon have to be changed, while devices from Acre-Free can simply be adjusted.
Fracture of the lower jaw
Differential diagnosis
If a fracture of the lower jaw is suspected, a differential diagnosis is made with a dislocation of the temporomandibular joint, as well as between a fracture and a bone bruise [8,10].
Fracture and bruise of the bone lead to swelling of the soft tissues of the face and bruising [7]. However, with a bruise of the jaw, there is no violation of the closure of the jaws and no crepitus (crunching). A fracture of the lower jaw, on the contrary, is accompanied by a change in the bite, jaw joint line and the appearance of a crunch, which is caused by the displacement of bone fragments [11,20]. With a bruise, there is no sign of a “bone step”, which is present with a fracture and is determined by palpation. To confirm the diagnosis, additional examination is carried out using X-ray diagnostics, CT and MRI[9,20].
Dislocation of the temporomandibular joint and fracture of the lower jaw are accompanied by the inability to move the chin forward. A distinctive feature is the position of the dentition and chin - with a dislocation they move forward, and with a fracture - posteriorly. The diagnosis can be made after the results of an x-ray; with a dislocation, the head of the temporomandibular joint is not in its “usual” place [1,8].
Clinical examination
Clinical examination of a patient with a mandibular fracture includes the following methods.
- External (physical) examination.
It is carried out to determine the integrity and swelling of soft tissues, identify hematomas, and facial asymmetry [2].
- Palpation (palpation).
Allows you to establish the configuration of the lower jaw, identify the gradation of the bone (recessions, irregularities), the density of edema, exclude subcutaneous formations (emphysema, infiltration, hematoma), determine the degree of mobility of jaw fragments at the fracture site [11,18].
- Instrumental examination of the oral cavity.
Makes it possible to identify damage to the mucous membrane and bone of the alveolar process of the lower jaw, dislocation of the temporomandibular joint, relationship and fractures of the teeth of the upper and lower jaws[15].
Plain radiography
Used to visualize the bones of the skull and face in frontal and lateral projections. An image in a direct projection allows us to identify combined jaw fractures with damage to the skull. Based on the results of lateral images, the following is determined:
- number of fractures, type and location;
- the size of the gap between the jaw fragments and the presence of displacements between them;
- presence/absence of teeth in the fracture line.
If a mental (along the central line of the jaw) or fracture of the condylar process of the mandibular branch is suspected, a targeted X-ray is taken[3].
Orthopantomography
Orthopantomography is a type of X-ray diagnostics and makes it possible to obtain a high-resolution, all-round (panoramic) image of the jaws. The method allows a detailed assessment of the condition of the jaws and teeth, maxillary sinuses, and sinuses [19].
Computed tomography (CT)
The method is used to identify bruises, pathologies of joints, ligaments, sinuses and bones, and damage to the neurovascular bundle. During computed tomography, at least 16 sections of the area under study are performed, which allows for a detailed examination of any changes and deviations from the norm [1,18].
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI)
The most informative and modern research method for diagnosing jaw fractures is magnetic resonance imaging [17]. Makes it possible to assess fracture-related damage to soft tissues, ligaments, cartilage and capsules of the temporomandibular joints (TMJ). MRI can determine the presence of TMJ effusion and inflammation [5,20].
Features of fixation on the upper and lower jaw
On the upper jaw
Fixation of the false upper dentition occurs due to the alveolar ridge, as well as the hard palate. Increasing the contact area of the structure ensures tight attachment. The main condition for reliable fixation is the exact coincidence of the contours of the plate base with the prosthetic bed. The elasticity of the Acri-Free material makes it possible to create a palatal bridge of minimal size without compromising the strength of the structure’s attachment.
On the lower jaw
The inserted bottom row is attached to soft tissue only. The anatomical features of the jaw do not allow the introduction of additional elements to increase the contact surface in order to improve the quality of fixation. The orthopedic device is attached only by the base, which must be precisely adjusted in shape to the prosthetic bed.
Application of sling dressings
A sling-shaped bandage is very convenient when it is necessary to apply it to protruding parts of the body:
- outer area of the nose;
- chin and jaw area;
- back of the head;
- forehead area;
- eyes, while the bandage can be applied to one or both eyes;
- crown area.
A sling bandage on the lower jaw can be installed in cases of dislocation or fracture of the jaw, as well as in situations where it is necessary to fix the position of the jaw.
Sequence of production and use
The fabric will be needed based on the specific location of the bandage:
- If the bandage is intended to be placed on the chin or nose, the width of the bandage should be 6-8 cm, length – 60-70 cm.
- For a bandage on the back of the head and forehead, the width of the fabric should be 15-25 cm, length - 1 meter.
Important: the person applying the bandage must wear sterile gloves or thoroughly clean their hands before manipulation.
Instructions for applying a sling bandage:
- the strip of fabric must be cut at both ends, approximately 20 cm of uncut material should remain in the middle, this is how a sling is made;
- the one who applies the bandage must face the patient;
- the patient should be warned that a bandage will be applied, sit straight and calm, the head should be directed straight without bending;
- Use sterile tweezers to hold the sterile bandage and place it on the open wound, if any;
- the uncut part of the sling material is placed on a napkin, the ends of the bandage are fixed on the opposite side of the head;
- The lower sling straps are fixed on the upper part of the head, the upper ones - on the lower part, closer to the cervical region.
A variety of ways to apply a sling bandage
Differences in the position of the bandage depending on the location of the injury:
| Localization of injuries | Installation of the bandage | Special attention |
| Nose injury | The bandage is crossed and stretches from the affected area through the ears. The ends of the bandage are secured in the back of the head and neck. | The material should not injure the auricle or obscure it, making it difficult for the patient to hear. |
| Damage to the frontal area | The bandage is placed on the forehead, its ends cross and go to the occipital and lower occipital zone. | |
| Chin and jaw injury | The fabric of the bandage completely fixes the lower jaw. The lower end after the cross is attached in the crown area. The upper one is directed to the back of the head, where another cross is made and finally secured on the patient’s forehead. | The material should not be tightened too tightly so as not to interfere with the patient’s free breathing. |
| Wound to the back of the head | From the back of the head, the ends, after crossing, are directed to the forehead and chin area and are attached there. | |
| Trauma to the parietal area | After installing the middle of the bandage, the ends are crossed and secured in the occipital and submandibular area. | |
| Eye damage | For this wound, crossing the ends of the bandage is not required. They are fixed on the parietal and occipital zones. | As they move, they should surround, but not touch, the ears. |
Important: this type of bandage can be applied to the victim by anyone for a short period of time, before seeking medical help; for long-term wearing, a sling-shaped bandage must be applied by a doctor or any other physician.
The photos and videos in this article will tell you how to properly apply this type of bandage to your jaw and chin.