What is periodontology and periodontology?
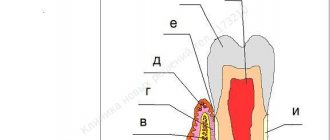
The tissues that are located around the subgingival part of the teeth are called periodontium. It has a multilayer structure: gums (mucous membrane covering the teeth in the cervical area); dental root cement; periodontium (tissue between the cementum and the socket); periosteum (tissue covering the bone) and alveolar process (part of the jaw tissue on which the dental units are located). These tissues securely hold the tooth in the socket (alveolus). The branch of dentistry that studies the periodontium, its functions and diseases is called periodontology.
Causes and symptoms of periodontal problems
How do you know if your periodontist needs help?
Even a non-specialist can easily notice symptoms indicating the onset and progression of a pathological process. First of all, this is redness of the gum tissue around one, several or all teeth. There may be bleeding and/or itching of the gums, increased sensitivity when eating or brushing, and varying degrees of swelling. Often inflammation is accompanied by the appearance of bad breath. When the pathological process is far advanced, pus forms and the gum line drops significantly, exposing the necks of the teeth. Symptoms depend on how deeply the tissue is affected. Diseases to which periodontal tissues are susceptible:
- gingivitis - the name of the disease itself is translated as “inflammation of the gums.” The most common form is catarrhal form, manifested by bleeding and excessive sensitivity of the gum tissue. There is also a hypertrophic variant of the disease, characterized by an increase in the density of the gums and their growth. The ulcerative form is manifested by ulcerations of the gingival surface, turning it gray and even the death of some areas.
- Periodontitis is most often a consequence of untreated gingivitis. It is expressed by the formation of purulent contents, atrophy of the alveolar process, and exposure of the neck of the teeth. As a result, teeth become loose, periodontal pockets increase (up to 5 mm), and pain appears. The most serious complications are tooth loss, bone tissue destruction;
- periodontal disease. Dentists have different views regarding the classification of this disease. Some believe that this is an aggressive form of periodontitis, while others classify it as a separate category. But, nevertheless, the protocol for its treatment does not change depending on the type of classification. With this disease there is no purulent discharge or formation of periodontal pockets.
Causes of periodontal inflammation:
- poor oral hygiene;
- mechanical, chemical, thermal injuries of the gums;
- pathology of occlusion (bite);
- improper dental prosthetics, resulting in injury to the gum tissue;
- excessive smoking;
- weakening of the immune system due to various diseases, stress, hormonal changes in the body;
- diabetes mellitus, HIV, oncology;
- hereditary factor.
Relevance. Immunomodulation is becoming increasingly relevant in gerontodental practice, the purpose of which cannot be empirical and requires the study of relevant laboratory parameters. Studying the composition of gingival fluid allows us to evaluate not only the aging processes of the immune system and their impact on the clinical course of periodontitis, but also the effectiveness of the therapy. To evaluate the effectiveness of transcranial electrical stimulation (TES) in the treatment of periodontitis in elderly people, to substantiate the clinical and diagnostic value of laboratory parameters of gingival fluid during immunomodulatory therapy. Materials and methods. A clinical, prospective, controlled, randomized, unblinded, comparative study was conducted. Two clinical groups (68 people) of people aged 60-74 years suffering from periodontitis were examined. All patients received the same basic therapy. In group 2, TES was prescribed. An assessment was made of the dynamics of the level of IL-1β, TNF-α, IL-10, sIgA and LDH in the gingival fluid, as well as the reduction of periodontal indices: bleeding and PMA (in%) in the following periods: before treatment, on the 7th, 14th th, 21st and 30th days after the start of observations. Results. It was found that the complex treatment regimen for periodontitis, including TES (immunomodulation), has greater clinical effectiveness in comparison with traditional therapy (starting from the 14th day, there were statistically significant differences in clinical and laboratory parameters between groups 1 and 2 (p <0.05)). On the 30th day of observation, the described trends continued: gingival fluid levels in both groups continued to decline. Moreover, their values in group 2 were statistically significantly lower than in group 1 (IL-1β level (pg/ml) was: 16.90 ± 0.33 and 18.80 ± 0.38; TNF-α (pg/ml): 11.90 ± 0.37 and 14.4 ± 0.4; IL-10 (pg/ml): 11.00 ± 0.35 and 12.90 ± 0.36, respectively) ( p < 0.05). Conclusion. TES (as a component of complex treatment) has greater clinical effectiveness in comparison with the traditional treatment regimen for periodontitis in elderly patients. Of great importance in gerontodental practice is the laboratory analysis of the composition and properties of gingival fluid, as well as the selection of its most indicative immunological and biochemical components: IL-1β, TNF-α, IL-10, sIgA, LDH. This enables the periodontist not only to confirm the observed dynamics of clinical manifestations of periodontitis in the elderly, but also to verify the consistency of immunomodulation.
Methods for treating gum inflammation
Treatment of gum inflammation is a complex of therapeutic and (or) surgical measures aimed at eliminating the causes of inflammation and restoring periodontal functions.
Treatment is prescribed by a periodontist after a visual and hardware (if necessary) examination. The list of therapeutic measures depends on the factors that initiated the onset of the disease and the severity of the pathological process. Treatment methods for periodontal diseases:
- elimination of the causes that caused the pathology (for example, bite correction, replacement of dentures, stabilization of blood glucose levels, etc.);
- professional cleaning with an ultrasonic scaler and AirFlow device;
- applications and rinsing with antiseptic and medicinal preparations;
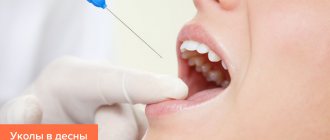
- administration of drugs by injection into the gingival surface;
- massage to strengthen gums;
- electrophoresis and other physiotherapy procedures;
- excision of gingival margins (for hypertrophied gingivitis);
- course of antibiotics and vitamins;
- treatment with the “Vector” device;
- laser treatment of periodontal pockets, in severe cases – curettage (surgical cleansing);
- splinting loose teeth;
- plastic surgery of gum recession;
- bone grafting.
Important: periodontists of the “Smile” network of clinics are proficient in modern methods of treating periodontal tissues; our centers are equipped with the latest equipment for diagnosing and treating gum inflammation. You can make an appointment for a consultation by phone or by using the “Book online” or “Request a call” options on our website.
When is it time to contact a periodontist?
The most common periodontal diseases are gingivitis and periodontitis.
Periodontal disease is much less common. The treatment of these diseases is carried out by a periodontist. But most often an integrated approach is required. If necessary, in our clinic you can visit a dentist, surgeon, orthopedist and orthodontist. This will not only relieve the unpleasant symptoms of gingivitis or periodontitis, but also eliminate the cause of their development. Many patients ignore the first symptoms of this pathology, considering them to be of little significance. Meanwhile, an inflammatory process that has just begun is much easier to stop than an advanced one. Treatment in this case will not require surgery and will be much cheaper. It is necessary to contact a periodontist if you have the following symptom complex:
- Bad breath;
- Bleeding, swelling, sore gums;
- Food getting stuck between teeth;
- Accumulation of plaque and tartar.
At the stage when the patient is concerned about such problems, they can be eliminated in literally 1-2 visits. That is why the doctors of the Dental Studio
It is not recommended to delay a visit to a specialist.
Delayed treatment can lead to the following negative consequences:
- Formation of deep periodontal pockets;
- Tooth mobility;
- Recession (lowering) of gum tissue;
- Premature tooth loss;
- Pain when eating.
Conservative periodontology
is a branch of dentistry that uses non-surgical methods for diagnosing and treating periodontal diseases. They are preferred for the vast majority of patients, as they are non-invasive. Conservative, that is, non-surgical methods are used whenever surgery can still be avoided. Only when they are ineffective do they move on to more radical measures.
Treatment of gums in periodontology begins with a consultation with a specialized specialist. Appointment at the Dental Studio
led by doctors with many years of experience. The doctor will conduct an examination and, if necessary, send the patient for an x-ray to assess the condition of the bone tissue. As part of the treatment and prevention of periodontal diseases, Vector therapy is carried out. Using the Vector device, supragingival and subgingival deposits, which are the cause of microbial inflammation, are removed.
In modern periodontics, laser gum treatment is becoming increasingly popular. This technique is in great demand and enjoys well-deserved trust. In our clinic, the doctor uses the Optodan laser device. Low-impulse laser light of the infrared spectrum promotes the regeneration of affected tissues, restores normal microcirculation, and suppresses the activity of pathogenic microflora. The procedure is considered physiotherapeutic, is well tolerated by patients, is painless, and shows good results during a course of treatment. The duration of the course and the intervals between procedures are determined individually, taking into account the degree of development of the pathological process and the characteristics of its course in a particular patient.
Prices for gum treatment in periodontics are available to a wide range of patients. It is important to correctly assess the significance of treatment: an advanced process inevitably leads to loosening and loss of teeth. Prosthetics and implantation will cost much more.
What happens if periodontal inflammation is not treated?
Often patients, if gum inflammation is not accompanied by pain, treat it rather frivolously, letting the situation take its course. This is a fundamentally wrong and even dangerous position. Periodontal diseases can be successfully treated in the initial stages. In advanced cases, enormous efforts by doctors will be required to save the patient’s teeth from falling out. And the patient’s quality of life will deteriorate significantly. He will be haunted by constant pain and bad breath. He will not be able to eat normally, and problems with the gastrointestinal tract will appear or worsen. The infection can penetrate through the bloodstream into any of the organs and cause complex diseases, including the development of sepsis.
Remember: the lack of treatment for periodontal inflammatory processes can result in tooth loss and death caused by sepsis. Do not delay visiting a doctor when the first symptoms of gum inflammation appear. Take care of your health!
Danilevsky (Periodontology)
PERIODONTAL DEVELOPMENT
Ectodermal epithelium is involved in the formation of the tooth and periodontium.
imesenchyme of the primary oral cavity, into which the epithelium sinks, forming the labial and dental plates (Fig. 1, A). On the buccal-labial surface of the dental plate, due to the uneven growth of the epithelium, flask-shaped outgrowths are formed in accordance with the number and location of teeth, which later turn into enamel organs. The mesenchyme, located at the base of the epithelial outgrowth, forms the dental papilla, which gives rise to the pulp, and subsequently dentin.
Connective tissue formations surrounding the epithelial primordium
dental papilla, form the so-called tooth sac. From the elements of the latter, root cement, ligamentous apparatus, and the bone base of the alveolar process are formed. This completes the first stage of tooth development—the formation of tooth germs.
During the period of differentiation of dental tissues, the formation of histological structures of the tooth and periodontium occurs. The cells of the outer epithelium of the enamel organ make up the outer layer of enamel, which later grows together
gum, forms the so-called primary epithelial attachment. During the eruption of the tooth crown, epithelial cells significantly increase
change further, lose their nuclei, flatten, turning into connective epithelium (Fig. 1, B, C).
The tooth root is formed due to the so-called peri-radicular epithelial sheath - a section of the enamel organ in which the transition of epithelial cells of the inner layer to the outer layer occurs. This vagina gradually descends in the form of an elongating skirt from the enamel organ to the base of the dental papilla. At this time, its internal cells induce differentiation of the peripheral cells of the papilla into odontoblasts of the tooth root, which form root dentin. Connective tissue fibers grow into the epithelial vagina, and it gradually disintegrates; remnants of epithelial cells in the form of Malasse islands can be found in the periodontium. Poorly differentiated connective tissue cells of the dental sac come into contact with newly formed dentin and differentiate into cementoblasts, which form root cement.
By the time the tooth erupts, only 1/3 of the root has been formed.
After tooth eruption, complete root formation in baby teeth lasts 2.5 years, in permanent teeth - for 3 years. During this time, the epithelial sheath forms the contours of the root apex and apical foramen with the further formation of dentin and cement (Fig. 2).
Recommendations from prevention experts
- Regular and thorough oral hygiene twice a day
- Cleaning teeth after every meal (rinsing, flossing)
- Course use of special preventive toothpastes
- Complete balanced nutrition
- Compliance with all medical prescriptions for the treatment of diabetes and other serious diseases
- Maintaining immune status at the proper level
- Quitting smoking (reducing the number of cigarettes you smoke)
The network of dental clinics “Smile” offers periodontology services: treatment of gum inflammation. Contacting our centers has several significant advantages:
- We employ highly qualified specialists;
- we follow diagnostic and treatment protocols that meet international standards;
- We use a system of family and cumulative discounts;
- we guarantee a stable cost of treatment according to the approved price list.
You can contact any of the branches of our clinic in Moscow, located within walking distance from metro stations:
- Alekseevskaya (VDNKh district, etc. Mira), address: st. 3rd Mytishchiskaya house 3, building 2;
- Shelepikha, address: Shelepikhinskaya embankment, address: building 34, building 1.
Do not delay your visit to the periodontist; make an appointment as soon as the first symptoms appear. This will significantly shorten the duration of therapy and reduce costs. Our doctors will provide effective dental care regardless of the severity of the disease. We will take care of your health!
How Vector works
It is the use of the Vector device that is the gold standard of modern periodontology. It generates ultrasonic vibrations of a strictly defined frequency, under the influence of which tartar is separated from the surface of the enamel. The doctor runs a thin tip over the surface of the teeth, paying special attention to the cervical area. A water jet irrigating the tip of the device washes away deposits from under the gums. The procedure has a polishing effect. The surface of the teeth becomes smoother, which means plaque formation slows down. Treatment of gums in periodontology in Moscow today is impossible to imagine without Vector-therapy. Its effectiveness and safety are time-tested. Patients note positive dynamics after the first procedure: swelling, pain, and itching decrease. The gum tissue becomes evenly colored and denser. If you have any questions regarding treatment with the Vector device, you can contact our doctor during your initial consultation.
Advantages of Vector therapy
- The procedure does not harm tooth enamel;
- Allows you to completely remove microbial film from the tooth surface;
- Positive effect already 2-3 days after the procedure;
- Periodontal pockets are cleaned without curettage, without surgical intervention;
- No anesthesia is required and the procedure is well tolerated.
The procedure has a powerful healing effect. It has proven itself well and is used all over the world. The peculiarity of conservative periodontology is the repeated nature of the impact. If surgical intervention is performed once, then conservative methods usually require a course of use. Cleaning with the Vector device is usually carried out twice with an interval of 1 month.
Conservative treatment of periodontitis
Periodontitis today, along with caries, is one of the most common diseases of the oral cavity. It is an inflammatory process localized in the area of one or more teeth. The course of periodontitis is accompanied by the formation of periodontal pockets. Bacteria and food particles accumulate in them, which leads to swelling, soreness, suppuration and bad breath. Treatment tactics are selected individually, taking into account the root cause of the disease.
General treatment regimen
As a rule, conservative therapy includes the following steps:
Stage 1
– elimination of common factors that provoke gum disease:
- Training in oral hygiene rules. Maintaining hygiene during treatment and subsequent remission is of paramount importance.
- Professional oral hygiene. Cleaning helps remove plaque and hard deposits. This contributes to the creation of an apathogenic environment in the oral cavity.
- Treatment of caries. It must be carried out without fail to eliminate foci of proliferation of pathogenic bacteria.
During the examination, the doctor can identify what was the root cause of the development of periodontal disease. In some cases, this may be an incorrect bite or poorly selected orthopedic structures. In this regard, the patient is referred for consultation to a specialized specialist: an orthodontist or an orthopedist. Elimination of the factor that became the trigger leads to a significant improvement in the condition of the oral cavity.
Stage 2 – elimination of the inflammatory process in the gum tissue
After professional oral hygiene or Vector therapy, the gums are treated with antiseptic agents. The doctor also prescribes ointments, elixirs, oral baths, mouth rinses, antiseptics, etc. for home use. The choice of medications is carried out according to indications on an individual basis.
Stage 3 – elimination of periodontal pockets
If conservative methods fail to stop the inflammatory process, curettage of periodontal pockets is performed. The procedure can be performed open or closed. The doctor completely cleans the pocket of pathogenic microorganisms, dead epithelial cells, food particles, and deposits. The surface of the root is polished, the pocket is washed with antiseptic compounds. Don't be afraid of curettage. The intervention is performed locally using anesthesia. The tissues of the gums and oral mucosa regenerate very quickly, so the healing process does not take much time. The doctor will set a date for a follow-up examination to evaluate the results of the curettage and decide on a further plan of action.
Stage 4 – recovery period
During the recovery period, it is very important to follow the recommendations of your doctor. First of all, this concerns the rules of oral hygiene. Also, you should avoid injuring the problem area. Do not eat too hot, spicy, or hard foods until the gum tissue has completely healed.
Stage 5 - clinical monitoring of the patient’s condition
Each patient who has been diagnosed with periodontitis must visit a doctor 2 times a year for monitoring and routine professional oral hygiene. Other problems that arise should be resolved in a timely manner: treat caries, carry out dental prosthetics if necessary. This set of measures will allow you to maintain the oral cavity in order and avoid relapse of the disease and associated inconveniences.
Splinting teeth
Another equally dangerous disease is periodontal disease. It is less common and is not inflammatory, but atrophic in nature. The bone tissue of the alveolar process of the jaw changes its structure, becomes looser, gradually collapses, and the height of the partitions between the teeth decreases. As a result, the teeth become mobile and fan out. To prevent their further loosening and create conditions for the restoration of the tissues surrounding the tooth, splinting is performed. To do this, use thin white fiberglass tape. On the unnoticeable surfaces of the teeth (lingual, chewing), a groove is formed into which the tape is placed. It allows you to reduce the range of tooth movements.