A tooth injury is a bruise, dislocation or fracture as a result of a blow, fall or other mechanical impact. Most typical:
- Injury to the front milk teeth in children aged 1-2 years, when children are just starting to walk, but still have poor coordination of movements, often fall and hurt themselves, and run into hard objects.
- Dental trauma at the age of 7-10 years, when children learn to rollerblade and skateboard, play ball, climb, and sometimes fight.
Chronic injury is also possible when a child constantly chews hard objects, and chips of enamel and microcracks appear on the teeth.
IMPORTANT! Information from the article cannot be used for self-diagnosis and self-medication! Only a doctor can prescribe the necessary examinations, establish a diagnosis and draw up a treatment plan during a consultation!
Bruised baby tooth in a child
Most often, bruises occur in preschool children with baby teeth. In appearance, the bruised tooth may not be in an arch with the rest of the teeth, it may look slightly raised above the other teeth due to swelling of the gums. The tooth hurts when chewing and pressing. If a child’s tooth is bruised, what should parents do? The best thing to do in this case is to apply cold to the area of swelling on the face and take the child to the dentist, and if he has determined for sure that this is indeed a bruise, treatment will most likely not be required. It is enough to avoid hard foods for a month to give the tooth the opportunity to “grow” back. In some cases, an incomplete dislocation of the tooth is added to the bruise, and the dentist, under local anesthesia, will set the tooth in place and fix it with a splint.
Symptoms
External signs will also differ depending on the strength of the impact. Externally, a bruise manifests itself with the following symptoms:
- The tooth hurts after a blow. Any mechanical injury leads to pain, but if it is intense and does not go away for a long time, severe injury can be suspected.
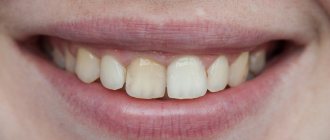
- The crown has darkened. This indicates that the blood vessels are damaged and hemorrhage has occurred in the soft tissue.
- Numbness of the face, swelling. These signs indicate severe damage to the nerve endings.
- Mobility of teeth after bruise. They begin to wobble, the gums swell.
Even if your teeth don’t hurt much after the blow, the pain goes away quickly and there are no other external manifestations, you should consult a dentist. It is possible to speak accurately about possible complications only after examination and x-rays.
Tooth dislocation in a child
A tooth is said to be dislocated if the tooth falls out completely as a result of an impact or is turned out of its socket and is supported only by soft tissues. A dislocated baby tooth in a child is usually not treated; the dentist simply removes it permanently. A permanent tooth can be saved if it is dislocated, but only if the roots of the tooth are not broken, and if it is possible to deliver the tooth to a dental clinic within two hours after the injury, and until that moment keep it in water (it is best in mineral water or in milk) so that the pulp does not have time to die. The dentist carefully sets the tooth into place and applies a splint.
Impacted dislocation of a baby tooth also occurs in children. With this injury, the tooth seems to go inside the gum. In this case, the dentist may recommend not to intervene and simply wait until the injured tooth begins to “erupt” again. Do not try to remove it from the socket yourself; this may damage the buds of the permanent tooth under the injured milk tooth.
Reasons for the development of gingivitis in children
The abundance of causes of the disease can be divided into two large groups.
Common reasons include:
- colds, especially if they occur frequently;
- sore throat and chronic sinusitis;
- hormonal disorders;
- gastrointestinal diseases.
Among the local reasons it is worth highlighting:
- poor-quality fillings, which, when destroyed, injure soft tissues;
- caries (infection from the cavity quickly enters the gums);
- crowded teeth;
- violations during the installation of braces;
- Tight lips that interfere with quality teeth cleaning.
Separately, it is worth noting the most important reason, since all of the above are only a catalyst for the development of the disease. So, the main reason why gingivitis begins to develop is poor oral hygiene, which can manifest itself both in improper brushing of teeth and in incorrectly selected toothpaste and brush.
Symptoms of the disease
Gingivitis has quite a few characteristic signs by which one can guess the onset of the disease:
- bleeding gums;
- pain during cleaning;
- swelling of the gums;
- severe redness of the gums in the case of an acute phase of inflammation;
- when the disease becomes chronic, the gums may acquire a bluish tint.
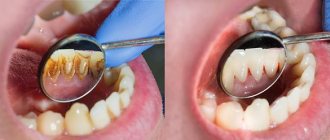
Often with the naked eye you can notice a large amount of accumulated plaque and tartar, and there may also be many teeth affected by caries.
In addition, gingivitis can be caused by diseases that have nothing to do with the oral cavity:
- heart and vascular diseases;
- disorders affecting the gastrointestinal tract;
- respiratory diseases.
The above factors reduce immunity, as a result of which the gums lose their ability to resist toxins formed in plaque.
What is the best way to treat?
As was said a little above, gingivitis occurs due to accumulated soft plaque, so the first thing you need to do is get rid of it. Plaque can be removed using ultrasound - this is a simple and absolutely painless procedure. Using a special attachment, the dentist touches dental plaque, which is destroyed by ultrasound. By the way, ultrasound allows you to get rid of not only soft plaque, but also hardened formations on the teeth.
It is necessary to understand that plaque can be effectively removed, especially if inflammation has begun, only with ultrasound: rinsing with various means, using special toothpastes and gels with the addition of antibiotics can temporarily remove the symptoms of gingivitis, but these methods are not able to eliminate its cause. As soon as you stop using these medications, bleeding will return and the disease will continue to progress. Therapy aimed at reducing the inflammatory process is justified only after the deposits have been removed.
Anti-inflammatory therapy is usually prescribed as follows:
- Rinse with Chlorhexidine solution. The maximum duration of use of the drug is 10 days. Rinsing should be done twice a day for at least 30-40 seconds per procedure. The solution, which has a bitter taste, which not all children will like, has no contraindications based on the child’s age.
- Rinse with Miramistin (prescribed after the child reaches the age of 3 years). You need to rinse three times a day. The drug is inferior in its effectiveness to Chlorhexidine and is significantly higher in price.
- Rinse with infusions of chamomile or sage (it is not recommended to use oak bark).
In addition to rinses, many doctors prescribe ointments and gels. It is believed that the gel is more effective than ointment because, due to its consistency, it has the ability to remain on the gums for a long time, which promotes better absorption. In addition, the medicinal substances contained in the product penetrate much better into the tissues from the gel than from the ointment.
The most effective and proven gels on the positive side are the following:
- Cholisal is a drug that simultaneously has two effects: analgesic and anti-inflammatory. It is used for gingivitis and the beginning of teething (the drug is rubbed directly into the place where the tooth is emerging). There are no age restrictions. The gel can be used for a maximum of one and a half weeks, twice a day. After applying the product, it is recommended to eat within two, or preferably three, hours.
- Metrogil Denta. Used after 6 years. Apply directly with your finger or a cotton swab to the gums near all teeth; there is no need to rinse off the gel.
Many parents often decide to treat their child on their own, not wanting to see a dentist. But you need to understand that the use of anti-inflammatory drugs will have no effect if you do not get rid of the deposits, so you will still have to set aside time to visit the dentist. If you ignore the advice, then:
- symptoms of bleeding will disappear, but will reappear after completion of the course of therapy;
- gingivitis can become chronic, causing periodontitis.
In addition to anti-inflammatory therapy, oral cavity sanitation and silvering are carried out - a method that does not require drilling, but has a lot of disadvantages.
How to avoid the occurrence of gingivitis?
The following remedies will help prevent gum bleeding:
- High-quality oral hygiene. Parents should instill in their children oral care skills from an early age. Not all adults know that hygiene measures must begin before the first tooth begins to erupt.
- Using the right paste. If the child does not have gingivitis, then you can use any paste designed for children. If your child does not brush their teeth well enough, you can purchase a paste with amino fluoride.
- Stick to your diet - avoid snacking, limit the consumption of fast carbohydrates (carbonated drinks, sweets). Of course, you don’t need to completely deprive your child of sweets, but you can give them only immediately after the main meal, after which you should brush your teeth.
What to do if a child has a dental injury
- If the injury is combined with a fall or a strong blow, you should immediately visit the emergency room and make sure that the child does not have a concussion or fractures, including facial bones - jaw, nose, etc.
- If other injuries are excluded or you are sure that it was the tooth that was damaged, you can immediately go to an urgent appointment with the dentist. If you have a tooth injury, we will see you immediately, since the speed of action often determines whether the tooth can be saved.
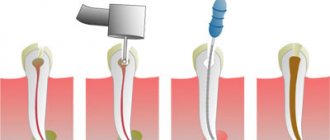
- The dentist numbs the area of the injury, determines the type of injury and prescribes treatment. In some cases it starts immediately, sometimes you need to wait a little. Treatment of a tooth injury can last up to a month.
It is important to correctly diagnose and treat an injured tooth to prevent complications. Meet our tooth fairies and check prices.
Complications
What to do after a tooth injury? The answer is clear - contact your dentist immediately. Even if it seems to you that the injury was not severe, you do not experience pain, there is no bleeding. Not a single blow passes without leaving a trace on the body, and its consequences will sooner or later make themselves felt. A bruise can lead to various complications:
- Dying of the pulp. During a bruise, nerve endings are damaged, neighboring tissues gradually die, an inflammatory process develops, purulent formations and cysts form.
- Darkening of the crown. Occurs due to rupture of blood vessels. At first the enamel takes on a pink tint and then darkens. The crown tissues do not receive the necessary nutrients. Even if it is possible to maintain the integrity of the tooth, it will stand out in the row due to the changed color. Regular bleaching cannot remove darkening.
- Periodontal damage. In this case, the bruise leads to the development of periodontitis.
Children's bruises do not go away without a trace, so if your baby falls and hits himself, he needs to be shown to the dentist. A long-term consequence of such injury is abnormal growth of permanent teeth.
Prevention of dental injuries
There are typical situations in which children injure their teeth. For example, a quarter of front tooth injuries between the ages of 1 and 3 years occur in the bathtub when a child slips and hits the edge of the bathtub, so try not to leave your baby unattended in the bathtub. Pay attention to protecting your teeth with a mouthguard when your child plays sports, especially hard and contact sports (hockey, various types of wrestling, basketball), rollerblading or skateboarding. Contact your orthodontist in a timely manner, because... a large percentage of injuries to permanent teeth are associated with their incorrect position, i.e. existing bite pathology, which means an additional risk.
At the same time, you should not blame yourself for not looking after your child and causing dental injury. Children are restless, they love to explore the world and take risks, and we cannot always protect them from such accidents.
make an appointment with a pediatric dentist online or by phone: +7(812)3310000
Causes of suppuration
If you have purulent discharge from your gums, there is a pimple in which pus accumulates, you feel pain, your teeth ache, then you should not hesitate, but immediately go to the doctor. If you start a purulent inflammation that has formed in the gum, serious consequences can occur. All this can even lead to blood poisoning.
As for a purulent pimple, it can be of any size. For some, it may resemble a pea in shape, and sometimes it can reach the size of half a walnut. But it is worth knowing that you cannot judge the severity of the problem by the size of this pimple. If there is a purulent pimple and it is small, then if left untreated, it can increase significantly within a day.
Suppuration can occur for the following reasons:
- The gum was injured by a fragment of a tooth that was broken. A poor quality crown that hangs over the edge of the gum can also scratch the gums;
- hygiene procedures were performed using a very hard toothbrush;
- a man carelessly picked his teeth with a toothpick.
You should know and understand that every manipulation that relates to teeth must be carried out carefully and carefully so as not to touch the gums. If pus appears, a person must realize that there is already an inflammatory process. And it needs to be treated without delay.
What to do?
The main thing is never to heat the place that hurts. Once upon a time, grandmothers said that you need to bandage your cheek with a warm scarf, but you shouldn’t do this. Inflammation cannot be heated. If the temperature rises, the process becomes even stronger. If there is pus, you should apply a piece of ice to the area that hurts.
If the pus comes out of the gums, you shouldn’t think that everything is gone. Drug treatment is necessary to stop the process. But antibiotics must be prescribed by a doctor.