Causes of jaw clenching during trismus
- inflammation of the masticatory muscles;
- inflammation of the gums;
- caries;
- abscess;
- inflammation of the periosteum of the lower jaw;
- jaw injuries (cracks, fractures, dislocations);
- dousing with cold water;
- animal or insect bites.
Trismus can also be a consequence of the following diseases:
- osteomyelitis of the jaw;
- periostitis;
- neurosis;
- epilepsy;
- meningitis;
- hysteria;
- arthrosis of the jaw joint;
- cancerous tumors;
- convulsions;
- rabies;
- tetany;
- paralysis;
- tetanus;
- pulpitis in the acute stage, etc.
Causes of neuralgia of the submandibular and sublingual nodes
The following factors can provoke the development of neuralgia of the submandibular and sublingual nodes:
- physical impact - prolonged or regular hypothermia of the ganglia;
- chronic inflammatory processes in the oral cavity - stomatitis, multiple caries, gingivitis, periodontitis;
- infectious pathologies - viral diseases, sepsis, syphilis, tuberculosis;
- chronic diseases of the digestive system and pelvic organs;
- negative consequences of surgical interventions - removal or prosthetics of teeth;
- foci of infection in nearby organs - sore throat, otitis media, sinusitis.
Often neuralgia can appear due to intoxication of the body with poisons, salts of heavy metals, and low-quality alcohol. It can also develop against the background of allergic and endocrine diseases, and be one of the manifestations of hypovitaminosis.
The main stages of trismus
- third - a person can open his mouth 10 mm, the most difficult stage;
- second - the patient can open his mouth 10-20 mm;
- first - the patient opens his mouth 30-40 mm, respectively.
In all cases, a person should immediately consult a doctor. You may need treatment in a hospital setting. In the process of clenching the jaw, there is a high probability of damage to the gums and chipped teeth. If help is not provided in time, oxygen starvation may occur.
Dental diagnosis of trismus involves:
- visual examination of the patient;
- to unclench the jaw, the dentist injects a drug that relaxes the muscles;
- To make the diagnosis more comfortable for the doctor and patient, an anesthetic drug is also administered;
- In addition to the dentist, you may need to consult a neurologist, surgeon, or traumatologist.
Loaf, loaf
Quite often, cheekbones cramp when yawning if you “overdid it” and opened your mouth too wide. Sometimes the jaw cramps in sleep when the muscles involuntarily contract. There are times when the jaw muscles cramp in completely unexpected situations.
Imagine a magnificent wedding in Slavic traditions. There are hundreds of guests, the tables are laden with dishes, the bride is dressed in a snow-white dress with a flowing veil. Everyone prepared for the event for a long time, thought through all the stages of the celebration, and the toastmaster is actively holding competitions. And one of the main characters - the loaf - is brought out for everyone to see.
According to an ancient custom, the bride and groom each take a bite from the loaf, and the one who grabs the largest piece becomes the head of the family. In our age of emancipation, a woman does not want to yield to a man in anything. The newly-made wife opens her mouth wide to defeat her husband, and suddenly realizes with horror that her jaw is cramped... The action quickly moves to the nearest emergency room. There the bride is given a relaxing massage, and the pain goes away. At this time, the toastmaster masterfully entertains the guests, acting out a scenario for stealing the bride. The story has a happy ending, but friends and relatives will never let the couple forget this story.
How to properly treat trismus of the masticatory muscle?
Treatment of the problem involves:
- immobilization of the jaw by applying a bandage or splint;
- eliminating the underlying cause of trismus (disease or specific condition);
- taking neuropsychic stimulants and sedatives;
- a course of taking muscle relaxants;
- a course of antibiotics (for inflammatory processes);
- physiotherapy;
- peace and release from physical work.
If the patient’s condition is severe, observation in a hospital is necessary under the supervision of a maxillofacial surgeon, neurologist, traumatologist, etc.
After eliminating acute symptoms, a person is recommended a special diet:
- plenty of fluid;
- chopped food;
- vegetables and fruits;
- natural juices.
If it is impossible to eat normally, food is supplied through a tube, and liquid is supplied through the skin.
To restore the functions of the masticatory muscle, the patient is recommended to perform special therapeutic and preventive exercises.
It is important to completely cure trismus, and not just suppress its symptoms. If the cause is not removed, the problem will reoccur. Spasms put a powerful strain on the teeth, gums, and nervous system. It is very important to contact an experienced dentist with a surgical profile, who will help cure the disease and tell you what to do in emergency situations. The 32 Dent network of clinics in Moscow employs specialists who will provide such comprehensive assistance for trismus of the masticatory muscle and other serious problems.
If you have a problem similar to that described in this article, be sure to contact our specialists. Don't diagnose yourself!
Why you should call us now:
- We will answer all your questions in 3 minutes
- Free consultation
- The average work experience of doctors is 12 years
- Convenient location of clinics
Single contact phone number: +7
Make an appointment
Why does pain occur in the upper jaw?
Injuries
Damage occurs as a result of household, street, sports, automobile, and industrial injuries.
The bruise is characterized by moderate pain that goes away after a few days. Fractures of the upper jaw are accompanied by extremely intense acute pain, rapidly increasing swelling, facial asymmetry, and stepped dentition. In case of fractures of the alveolar process, lacerations are visible on the mucosa, and sometimes the end of the displaced bone fragment is determined. The occlusal contact is sharply impaired, the teeth are mobile. With an isolated fracture of the walls of the maxillary sinus, severe aching pain in the upper jaw, infraorbital area, significant swelling, and hemorrhages is observed. Nasal breathing is difficult. With combined damage to the bone walls of the sinuses, a clinical picture of a concussion and profuse nosebleeds are revealed. Perforation of the maxillary sinus occurs during dental procedures. If the damage was not detected, swelling of the cheeks, a nasal tone of speech, pressing or bursting pain in the jaw, and projections of the sinuses subsequently appear.
In some cases, radiating pain in the jaws is detected in victims with subluxation of the cervical vertebra. Irradiation to the back and shoulders is also possible. The clinical picture includes a forced position of the head, neck pain, muscle tension, and sometimes dizziness, weakness, convulsions, and paresthesia in the arms.
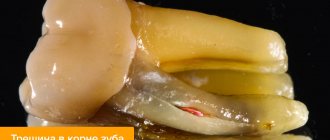
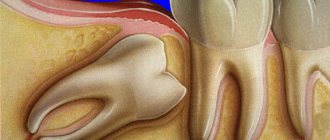
Dental reasons
Discomfort and mild pain may be associated with the use of removable dentures and orthodontic structures. Pulling, pressing, aching pains occur in children due to malocclusion, including those caused by deformation of the upper jaw with a cleft lip and cleft palate. Some soreness is normal after tooth extraction, especially molars and wisdom teeth.
With the development of alveolitis, the pain disappears, and then reappears 3-5 days after tooth extraction. Intense pulsating sensations are noted in the projection of the socket, intensify as inflammation progresses, and sometimes cover the upper jaw and half of the face. Attacks of severe pain spreading along the trigeminal nerve are characteristic of acute diffuse pulpitis. More local pain is observed in acute periodontitis.
Upper jaw pain
Purulent processes
Intense tugging, tearing, bursting pain occurs with purulent inflammation of the upper jaw and nearby soft tissues. Combined with hyperthermia, deterioration of general condition, intoxication syndrome. The most striking clinical picture occurs in acute osteomyelitis. The disease begins suddenly, the symptom progresses quickly, and the temperature rises to high levels. A foul odor emanates from the mouth, and pus accumulates in the gum pockets.
Periostitis has less severe symptoms. With a high intensity of pain, the general condition is slightly disturbed, the temperature is subfebrile. In patients with a perimandibular abscess, the abscess is limited, located in the soft tissues, the condition is moderate or closer to satisfactory. With perimaxillary phlegmon, the infection spreads quickly, twitching, shooting pains intensify with the slightest movements of the jaw, the condition is serious.
With abscesses of the salivary glands, the first symptoms are dry mucous membranes and an unpleasant taste in the mouth. Hyperthermia up to 40°C is noted. Maximum pain is determined in the projection of the affected salivary gland, complemented by pronounced swelling. Irradiation is noted in the upper jaw, neck, and ear.
Neuralgia
With ganglionitis of the pterygopalatine ganglion, a clinical picture of neuralgia of the trigeminal nerve is observed in the zone of innervation of its 2nd branch – n.maxillaris. An attack of intense shooting pain develops spontaneously, often occurring at night. Pain sensations predominate in the upper jaw, eye, hard palate, and at the base of the nose, spreading to nearby anatomical zones. The episode lasts from several minutes to several hours, complemented by autonomic disorders: lacrimation, profuse salivation, hyperemia of half the face.
Atypical facial neuralgia, which is more often detected in middle-aged women, is considered as another possible cause of the symptom. Pathology is provoked by dental procedures. The pain is dull, sometimes burning. They do not reach the intensity typical of other neuralgia. They quickly transform from paroxysmal to permanent.
Diseases of the ENT organs
In otolaryngology, the manifestation is more often provoked by odontogenic sinusitis against the background of injuries, dental diseases, and endodontic treatment. The acute form is characterized by heaviness, bursting unilateral pain in the upper jaw, intensifying when lowering the head, and throbbing headache. There is a sharp pain when chewing food, a subjective feeling of lengthening of the teeth. For chronic sinusitis, the clinic unfolds gradually. The symptom is also combined with a headache, radiating to the forehead, temple, and orbit.
Radiating pain in the upper jaw, orbit, and temporal region can be observed in acute purulent otitis and is caused by irritation of the trigeminal nerve during infiltration of the mucous membrane of the tympanic cavity. Supplemented by severe pain in the ear, intoxication syndrome. A similar irradiation is found in mastoiditis, which develops simultaneously with otitis media or a few days later, manifested by profuse suppuration from the ear, throbbing pain behind the ear.
Tumors of the upper jaw
Against the background of benign neoplasia of the upper jaw (fibromas, cementums, osteomas, osteoblastoclasts), the pain is usually mild, dull, and aching. They do not occur in all patients. They grow slowly over a long time in parallel with the growth of the tumor. Sometimes they are complemented by progressive facial asymmetry. An exception is osteoid osteoma, which is characterized by intense pain that worsens when eating and at night.
With malignant tumors of the upper jaw (cancer, sarcomas), pain appears in the early stages. At first periodic, dull, aching or pressing. They quickly intensify, become permanent, acute, painful, unbearable. They radiate to adjacent anatomical zones. They are supplemented by tooth loss, infiltration of nearby tissues, decay with the formation of ulcers, and enlargement of regional lymph nodes.
Other reasons
Aching, initially paroxysmal, then constant pain in the upper and lower jaw is observed with bruxism and myofascial syndrome. In both cases, the cause is constant excessive load on the masticatory muscles. In patients with Horton's disease, the symptom is caused by irradiation and is combined with a dull headache that gradually increases over several weeks, more pronounced in the temporal region.
How long does it take to cure trismus?
Typically, full muscle recovery can take one to three weeks, depending on the cause of the trismus. More time will be needed for fractures of the jaw, which must heal properly and subsequently develop.
To prevent trismus of the masticatory muscle, you must:
- do not cause diseases of teeth and gums;
- get vaccinated against rabies and tetanus (rabies and, as a result, lockjaw can be fatal);
- In case of blows or damage to the jaw, seek emergency help from dentistry;
- avoid stressful situations, nervous tension;
- when engaging in contact sports, wear special helmets and mouthguards for protection;
- undergo regular preventive examinations with a trusted dentist. These are the doctors who work in the 32 Dent network of clinics, where you will be happy to see you at any time. Contact us!
Prevention measures
If, due to genetics, you are not prone to problems with enamel, you can try to prevent other causes. Experts in this regard recommend maintaining hygiene, monitoring oral health, and regularly visiting the dentist for preventive care. It would also be a good idea to review your diet and diversify it with foods high in vitamin A: eggs, carrots, liver, dried fruits and fresh apricots.
Calcium and fluoride are important microelements for the health of hard tissues of the oral cavity. The first is found in high concentrations in hard cheeses, fish, dairy products, cabbage, and leafy greens. Fluoride is found in seafood, seaweed and nuts. But you will have to give up carbonated sweet drinks - they have an extremely negative effect on the condition and density of the enamel. It is also worth limiting the consumption of too acidic fruits and juices, sweets and simple carbohydrates.
To strengthen your teeth, you should eat foods rich in calcium and fluoride.
When teeth come together with a certain frequency, especially for no apparent reason, it is better not to ignore the symptom, but to immediately consult a dentist for advice. The phenomenon may be pathological in nature and indicate certain dental problems, diseases of the soft tissues of the oral cavity, or even disturbances in the functioning of internal organs and systems. The sooner you seek qualified help, the easier and faster it will be possible to stop the pathological process.
- Fadneva O.V. Clinical manifestations of increased sensitivity of hard dental tissues, 2001.
Types of seizures
If involuntary contraction of muscle fibers is caused by overexcitation of the cortical part of the brain, such convulsions are classified as epileptic. Non-epileptic ones are provoked by diseases of the central nervous system, imbalance of nutrients, and unfavorable external conditions.
Also, involuntary muscle contractions can be classified according to their nature:
- tonic – long-term, turning into a state of tension;
- myoclonic – short;
- clonic - jerky, cyclically repeating and alternating with relaxation.
Based on localization, these phenomena are divided into generalized and local. The former cover a significant part of the body (arms, legs, face, neck, side, torso, and sometimes extend to the respiratory tract). The latter occur in separate areas (for example, only in the back or only in the buttock).
Treatment
Conservative therapy
Treatment tactics depend on the causes of chin numbness. Patients with trigeminal neuralgia are prescribed anticonvulsants. The dosage is gradually increased until a therapeutic effect is achieved. Reception is continued for several months, and then the dose is gradually reduced. The regimen is supplemented with antihistamines, antispasmodics, and means to improve microcirculation. Blockades are performed according to indications. Among the effective physiotherapeutic techniques are diadynamic currents, galvanization, and ultraphonophoresis.
To relieve a migraine attack, NSAIDs are used; in severe cases, drugs from the triptan group are used. For repeated vomiting, antiemetics are used. To prevent paroxysms, long-term treatment with antidepressants and anticonvulsants is carried out. For herpes zoster, antiviral therapy is administered with acyclovir. Mental disorders are corrected with the help of psychotherapy, sometimes in combination with psychotropic drugs.
Antibiotics are indicated for wounds, open fractures, and osteomyelitis of the jaw. First, broad-spectrum antibacterial drugs are used, and later the medication is replaced taking into account the antibiotic sensitivity of the pathogen. Patients with pernicious anemia require lifelong treatment with B12 drugs, elimination of conditions that led to the development of vitamin deficiency.