In most cases, the term “neurosis” is associated with emotional lability, irritability, and a general deterioration in well-being. But sometimes neurotic disorders manifest themselves with completely unexpected symptoms, which causes an incorrect diagnosis and, accordingly, ineffective treatment. In some cases, the tongue may react to stressful situations and anxiety during neuroses. There is a distinct discomfort that is not associated with organic pathologies of the oral cavity. This condition is called glossalgia or language neurosis. Medicines prescribed by general practitioners either do not work or have only a short-term effect, but doctors at the Leto mental health center, if the psychogenic nature of the disease is suspected, offer a comprehensive examination to exclude somatic diseases. After confirming the diagnosis, we select psychotherapy tactics and, if necessary, add medications.
Causes of glossalgia
As with other somatoform neurotic disorders, the etiology of language neurosis is closely related to the influence of stress factors. This is any situation that is psychologically traumatic for a person, for example:
- conflicts in the family, serious quarrel with relatives, betrayal of a spouse, divorce;
- demotion (or lack of long-awaited career advancement), job loss;
- personal or global financial crisis, especially against the backdrop of the need to make regular loan payments;
- suffered a serious illness and fear of re-illness (relapse);
- any disaster (experienced earthquake, flood, fire, transport accident, etc.).
Persons who tend to repeatedly exaggerate the scale of existing problems are predisposed to language neurosis. Usually they lack optimism, do not like fun, do not like to joke themselves, and avoid noisy companies for fear of appearing funny. They are very demanding of others and are afraid of losing control of the situation. Therefore, in families where one or both parents have signs of a neurotic syndrome, the unquestioning authority of the father or mother usually “reigns”, children suffer from overprotection.
How to help a child?
It is worth understanding that these habits do not arise on their own and not because of bad behavior. Comments and reminders that you should not stick your tongue out will not work - you need to work with the root cause of the disorder.
- Restore nasal breathing.
Orthodontists often prescribe consultations with an otolaryngologist, since the dental system and respiratory organs are closely connected. Removal of adenoids, treatment of chronic diseases, normalization of the microclimate at home to reduce the frequency of acute respiratory viral infections, hardening and other restorative procedures - all this can be prescribed by a doctor to achieve remission.
ENT can help restore health for proper tongue function
- Contact an orthodontist.
Only in this order, otherwise the treatment will not be effective. As soon as the child is able to breathe with his mouth closed, you can move on to correcting the position of the teeth and tongue.
For this purpose, children's orthodontic devices have been created:
- Plates.
- Trainers.
- Twin Block device.
- Children's aligners Kinder Smile.
All these devices are removable and act quite gently, guiding teeth during the period of their active growth. Wearing requires parental supervision, but with proper use, problems are solved quite quickly - within a few months.
Only after this can you begin classes with a speech therapist - when the malocclusion and the main manifestations of tongue dysfunction are eliminated, the correction of sound pronunciation will be much more successful.
Symptoms of tongue neurosis
The syndrome has a very variable clinical picture; often the patient himself cannot find the appropriate words to describe his feelings. But the most common complaints are:
- tingling, numbness, itching, burning of the tongue, lips and oral mucosa;
- sensations of puffiness, swelling and heaviness of the tongue, as if it had been “sprinkled with pepper” or “scalded with boiling water”, dry mouth;
- impaired taste sensitivity, decreased salivation, often against this background appetite worsens and weight decreases;
- raw pain in the palate, tonsils, back of the throat;
- partial numbness of the mucous membrane;
- sensation of a foreign body in the mouth.
Discomfort occurs periodically; at the initial stage of the disorder, the duration of this kind of “attack” is 2–5 minutes, gradually unpleasant sensations appear more and more often and become permanent over time. Numbness of the tongue during neurosis, like other symptoms of the disorder, increases with the consumption of alcohol, peppery foods, pickles, too cold or vice versa, hot food and drinks.
The patient is convinced that because his tongue is swollen, he cannot speak clearly. A person reduces communication to a minimum, prefers correspondence to conversation and personal meetings, which does not have the best effect on speech functions and socialization skills in general.
A coated tongue during neurosis is uncharacteristic; the presence of plaque indicates the presence of a bacterial or viral process, but it is possible that it is of a secondary nature. For example, due to severe discomfort, a person constantly touches his face and lips with his hands, which provokes the development of an infectious process.
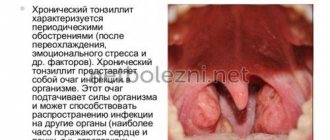
In addition, glossalgia often leads to a decrease in local immune defense. That is why tongue neurosis is often accompanied by stomatitis, laryngitis, chronic tonsillitis and/or pharyngitis.
Symptoms from the psycho-emotional sphere are also characteristic. A person experiences constant anxiety and internal tension. Characterized by insomnia with nightmares and restless dreams, irritability and intolerance, gloominess.
Diagnosis of tongue neurosis
The fact is that the etiology of numbness, coating on the tongue and other manifestations of oral discomfort is sometimes not associated with stress. The reasons for such unpleasant sensations may be:
- Diseases of the digestive tract. In particular, the backflow (reflux) of intestinal contents into the trachea causes pain and a burning sensation in the throat and tongue.
- Circulatory disorders due to cardiac disorders.
- Neurological and endocrine pathologies.
- Allergic reaction to topical medications (rinses, lozenges, etc.).
- Infection of the oral cavity (usually stomatitis, fungal diseases).
Often characteristic symptoms occur after visiting the dentist. Glossalgia often appears after prosthetics due to injuries during orthopedic manipulations, allergies to the material from which the prostheses are made. The syndrome can also be a consequence of malocclusion, constant injury to the oral mucosa by unsuccessfully placed fillings, or dental plaque.
Many experts forget about the rather rare, but noteworthy syndrome of “galvanism” - insignificant electrical discharges that appear in the mouth in the presence of fillings or prostheses made of metal alloys, due to which the tongue becomes numb and pain appears.
To exclude the somatic etiology of the disorder, consultation with a dentist, ENT specialist, neurologist, cardiologist and gastroenterologist is necessary. The patient is also asked to take a general and biochemical blood test and do an ECG. It is advised to undergo a study to determine the indicators of local immunity of the oral cavity, assess the enzymatic activity of the salivary fluid, the content of protein and other elements in it, and the pH level.
Tongue dysfunction: how it affects teeth
The habit of breathing through the mouth, including during sleep, leads to increased tongue dysfunction. The child begins to stick out his tongue more often (and the tongue is the strongest oral muscle), make additional efforts and press his tongue on the teeth.
What will happen to the teeth if such a habit develops?
- A diastema may form - a gap between the front teeth.
- The contacts of the teeth in the frontal region may be disrupted, then an open bite will appear - a pathology that is quite difficult to correct: it causes noticeable harm to the condition of the teeth, since the entire load falls on the chewing teeth in the lateral regions.
Open bite in a child
- The front teeth can rotate (turn around their axis) or form a protrusion - a forward tilt.
Children's teeth are quite pliable, as the child grows, the size of his jaws and the space in the row of teeth constantly increase. Therefore, the effort exerted by the tongue is quite enough to move the teeth, but they will no longer be able to return back to the correct position on their own.
One more problem
In addition to orthodontic disorders, difficulties with pronouncing sounds will increase. Speech therapy correction is designed for the correct structure of the teeth and the functioning of the tongue, so classes with a speech therapist will be very long and ineffective if the main cause of poor diction is not eliminated.
Cost of services
| CONSULTATIONS OF SPECIALISTS | |
| Initial consultation with a psychiatrist (60 min.) | 6,000 rub. |
| Repeated consultation | 5,000 rub. |
| Consultation with a psychiatrist-narcologist (60 min.) | 5,000 rub. |
| Consultation with a psychologist | 3,500 rub. |
| Consultation with Gromova E.V. (50 minutes) | 12,000 rub. |
| PSYCHOTHERAPY | |
| Psychotherapy (session) | 7,000 rub. |
| Psychotherapy (5 sessions) | 30,000 rub. |
| Psychotherapy (10 sessions) | 60,000 rub. |
| Group psychotherapy (3-7 people) | 3,500 rub. |
| Psychotherapy session with E.V. Gromova (50 minutes) | 12,000 rub. |
This list does not contain all prices for services provided by our clinic. The full price list can be found on the “Prices” , or by calling: 8(969)060-93-93. Initial consultation is FREE!
Principles of treatment
The treatment regimen proposed by the doctors of the Leto clinic is aimed at restoring normal psycho-emotional status, eliminating symptoms that bother the patient and preventing secondary complications. If the tongue twitches during neurosis or other symptoms of the syndrome are pronounced, drug treatment is indicated. It includes:
- sedatives;
- non-benzodiazepine anxiolytics;
- according to indications (for example, for severe insomnia) - antipsychotics;
- B vitamins, tocopherol, omega complex;
- nicotinic and ascorbic acid, drugs based on adenosine triphosphoric acid, glycine;
- iron supplements.
Various physiotherapeutic procedures that have a relaxing and calming effect have proven themselves well. We recommend:
- massage of the collar area;
- ozone and oxygen therapy;
- transcutaneous and transcranial electrical stimulation;
- hirudotherapy;
- laser therapy.
Regardless of clinical manifestations, neurotic disorders are an indication for consultation with a psychologist. The doctor will help the patient understand the cause of such unpleasant sensations, tell him how to properly respond to conflict and stressful situations, and help him find a solution to the problems that bother him.
Tongue neurosis is a rare disease, but quite amenable to outpatient treatment. You can get more detailed information from our consultants by calling 24/7 anonymous phone number 8(969)060-93-93 .
How to correct malocclusion and tongue position.
There must be an integrated approach. Modern orthodontics offers various ways to straighten teeth. But as we have already seen, straightening teeth is ineffective without eliminating the causes leading to these changes.
Therefore, the solution to the problem of malocclusion should be aimed at the entire complex of pathological changes: restoration of the anatomically correct position of the tongue, development of the correct stereotype of swallowing, chewing, head position, posture.
Osteopathic treatment offers exactly this approach: restoration or formation of the correct relationship of anatomical structures
- Correction of weakened or excessively tense muscles of the face, neck, floor of the mouth and the tongue itself, this will lead to the restoration of the correct position of the tongue in the oral cavity and uniform participation of the corresponding muscle chains in the processes of chewing and swallowing.
- The effect on the bone structures that form the cavities of the nose and mouth leads to the restoration of the physiological volumes of these cavities and helps improve nasal breathing, chewing, swallowing and speech.
- Motor innervation of the tongue, swallowing and chewing is provided by the hypoglossal nerve, which exits the cranial cavity through the canal of the hypoglossal nerve, where in some cases it may be compressed. Until a certain age, mobility is maintained in this zone and using osteopathic methods it is possible to restore the physiological correspondence of these anatomical structures.