Introduction
The information world is very huge. Each of us is haunted by a million points of view
for any problem in any field of knowledge, you just need to ask a search query. The same thing happens in medical circles on the Internet - discussions of health problems are widely represented by both patients and doctors and often reach the point of absurdity:
For example, in questions:
- loosening of the tooth,
- exposure of the neck of the tooth,
- why are my gums and teeth exposed?
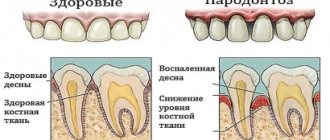
that is, in situations where the gums on a tooth have receded, patients are always confused: they have periodontal disease
, then suddenly it changed to
periodontitis
, then periodontal disease returned again. And the search for an answer to the question becomes endless.
The problem of “how to treat periodontal disease” is picked up by doctors who only add fuel to the fire by recommending medications and even folk remedies for periodontal disease, without having sufficient competence to do so.
Let's consider these points of view professionally, and try to convey one simple truth, which for the vast majority of patients (and even some doctors) will be a revelation: the diagnosis of periodontal disease of the gums
» —
does not exist
.
An expert point of view is expressed by the famous periodontist, Doctor of Medical Sciences Laura Mikhailovna Tebloeva:
As a rule, for patients who come to me and say: “I have periodontal disease,” I always clarify - did you make this diagnosis yourself or did you see a doctor? Often patients answer that they have this information from their doctor. It turns out that the patient did not read somewhere and determine the diagnosis of “periodontal disease” for himself, but, unfortunately, such a diagnosis was made by a doctor.
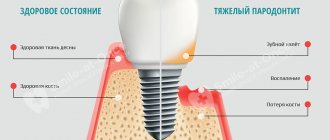
Stages of periodontal disease
Periodontal disease can be acute or chronic. Depending on the degree of spread of the pathology, there are the following types of disease:
- localized - the necks of the teeth are exposed in a separate area;
- generalized - pathological processes develop throughout the dentition.
Periodontal disease develops over several years; depending on the patient’s condition, the disease is divided into stages:
- Early - the presence of initial changes in tissues, which can be determined by the dentist during examination;
- The first is increased sensitivity of teeth to hot and cold foods, receding gums;
- The second is pronounced exposure of the dental necks, sensitivity, the formation of gaps between the teeth and the appearance of dental cement instead of enamel;
- The third is severe receding gums, gradual loosening of teeth;
- The fourth is the advanced stage: the teeth become very loose, making it difficult to eat. At this stage, tooth loss occurs.
Always treat gum problems
When a patient comes to the doctor, he complains about something. What symptoms does he see a doctor with before receiving a diagnosis of periodontal disease? What worries him?
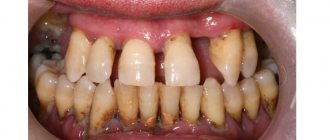
Literally, patients tell the doctor this: my gums have sagged, my gums have become exposed, my lower gums have receded. And for some reason the symptom of gum subsidence automatically means that the patient has the so-called. periodontal disease.
More experienced patients, who have already heard a lot of professional terms, who delve into the professional colloquial language of doctors, say this: “The necks of the teeth have become exposed a little, the teeth have become a little higher.” But, according to statistics, most patients complain about sagging gums.
And so, when patients come to the doctor with complaints about the problem of exposed tooth necks, the doctor diagnoses them with periodontal disease. Of course, he begins to treat them. And to treat it specifically for periodontal disease.
But time passes, money also goes away, and the question of why the gums recede and the necks of the teeth become exposed, why the gums recede, has not been resolved. And the patient still has periodontal disease.
Why does it appear
Periodontal disease is a chronic pathology that develops due to impaired blood supply to the gums. Most often, this disease occurs with age, the reason for this is a general deterioration in health, a slowdown in metabolic processes, and diseases of the cardiovascular system.
But periodontal disease can appear in young people, even children. This can happen due to poor oral hygiene, malocclusion or weak immunity. The cause is insufficient consumption of vegetables and fruits, large amounts of sweets and soft foods, smoking, hormonal imbalance, and long-term use of medications.
What tactics are used to treat periodontal disease?
I want to start with the fact that patients who come with a diagnosis of periodontal disease, they need, every single one, treatment... not from the periodontist to whom they initially turned.
If we talk about the tactics of managing patients with the so-called. periodontal disease, which then come to me again, it’s a shame to voice this, but the treatment of periodontal disease was carried out right up to injections of Lincomycin into the exposed gum.
According to statistics, almost always the treatment of periodontal disease in adults with medications is burdened with a course of some antibiotics and physical therapy.
And most importantly, the task of all these manipulations is completely unclear: what do doctors want to achieve in this way, to destroy some kind of flora or to stop some destructive processes in the gums? It is very difficult for me to say what happens to the competence of a doctor who injects antibiotics for the so-called. periodontal disease, but this is absolute blasphemy. Is it possible to cure periodontal disease by destroying the flora? As a result, the gums will never recover.
Treatment of gum periodontal disease reaches the point of absurdity
I would like to note the widest range of drugs and folk remedies that patients use to attempt self-treatment of periodontal disease at home. Among the folk remedies, one can note the treatment of periodontal disease with hydrogen peroxide, and even treatment with soda:
What about the use of various toothpastes for periodontal disease? What goals do patients have? The purpose of toothpaste is preventative, not curative. And no toothpaste will eliminate inflammation, because there is no such inflammation in periodontal disease.
It is not difficult to guess that in these combinations of procedures the question of how to cure periodontal disease remains open.
Antibiotics and antiseptics
Pathogenic microorganisms are not the main cause of periodontal disease, but their vital activity indirectly contributes to its development - it is no coincidence that a significant proportion of patients suffering from this disease exhibit one or another degree of decreased immunity. Accumulating in enlarged periodontal pockets and interdental spaces, the bacterial mass can cause inflammation, which in normal cases is not characteristic of this disease. That is why, in case of periodontal disease, it is often recommended to use various agents that can destroy pathogenic microflora and reduce the risk of secondary infection.
In the most severe cases, antibiotics in the form of capsules or tablets are used for this purpose, such as doxycycline and metronidazole, trichopolum, lincomycin. Broad-spectrum antibiotics effectively suppress the activity of microflora and contribute to the rapid elimination of inflammatory and infectious manifestations that complicate the course of the disease. However, long-term use of antibiotics is undesirable due to side effects and suppressive effects on the natural microflora of the body. They can only be used as prescribed by a doctor.
For a more gentle disinfecting effect, it is recommended to use rinses, gels, sprays and other external products containing antiseptics. In particular, the antibacterial rinse ASEPTA, which contains benzydamine and chlorhexidine. The adhesive balm ASEPTA, which contains metronidazole and chlorhexidine, thanks to its sticky base, is retained on the gums for a long time and has a long-term healing effect. Extracts of sage, witch hazel, chamomile, as well as xylitol, which are part of the ASEPTA Fresh mouthwash, also have a mild antiseptic and anti-inflammatory effect.
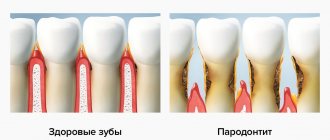
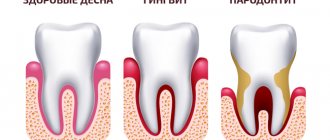
There is no inflammation with periodontal disease
When does the so-called periodontal disease, there is no inflammatory process in the gums. The clinical picture of “periodontal disease” differs sharply from periodontitis; it is with periodontitis of the tooth that inflammation occurs.
And injections into the gums, endless restorations of the necks of the gums - this is running in circles. Over time, again all the restoration fillings are chipped, and again these patients come to have these fillings restored again. And this happens endlessly
:
And the diagnosis of “periodontal disease” does not go away. As Desna ran away, she continues to leave. The fillings increase, that is, the teeth increase in size, because the gums sag more and more, and nothing useful happens.
When such a patient gets an appointment with me, unwinding his entire tangle of ordeals during the consultation, it becomes clear that all previously performed gum treatment consists of 3
factors:
- Lost time,
- lost money
- shattered hopes.
The diagnosis was incorrect and the treatment was appropriate for the incorrect diagnosis. What went wrong?
Patients should always go for a consultation with such a diagnosis... to an orthodontist
.
Because periodontal disease is an occlusal injury
.
What I see in these patients with signs of periodontal disease is a completely different diagnosis. This is an occlusal injury that can only be corrected by an orthodontist.
Vitamins and minerals
To restore damaged tissues, the body needs a wide variety of nutrients, which are not always contained in the required quantities in the daily diet. That is why the drug treatment regimen for periodontal disease often includes taking vitamin complexes. The best effect can be achieved by taking special complexes, for example, the vitamin-mineral complex for teeth ASEPTA.
The ASEPTA complex includes a whole range of substances necessary to strengthen gums and teeth. Vitamin C strengthens the walls of capillaries and blood vessels, helping to improve blood circulation in the gums, disruption of which is one of the main causes of periodontal disease. Vitamins B3 and B6 help reduce gum sensitivity, strengthen bone tissue and promote healthy mucous membranes. Vitamin A is involved in all metabolic processes occurring inside the body and increases protection against inflammatory and infectious diseases that often accompany periodontal disease.
In addition to vitamins, the complex also contains green tea extract - a natural component that has an antimicrobial effect, eliminates unpleasant odors, and slows down the aging process of tissues. An equally important component of the complex is coenzyme Q10, a substance that is a rich source of energy for the growth and restoration of cellular structures. Taking coenzyme promotes accelerated regeneration of damaged gums.
The complex also includes substances intended to strengthen the hard parts of the tooth, which are subject to increased stress during periodontal disease - coral calcium, which is well absorbed by the body, and vitamin D3, necessary for the proper absorption of calcium and phosphorus.
What is occlusal injury
Occlusal trauma is when a tooth experiences excessive stress due to:
- the tooth is not in the dentition,
- the tooth is not in the correct position,
- the tooth has not grown physiologically,
- the tooth is tilted, at the wrong angle.
The occlusion of the teeth is impaired. That is, when chewing in a patient with impaired occlusion, a destructive force of chewing pressure is created, and the bone tissue in the area of these above teeth begins to decrease.
What is chewing from a physiological point of view?
It's teeth hitting teeth. The strongest blow, since the masticatory muscles are the strongest in the body.
In simple words, in a patient, from such a hyper-impact, hyper-contraction of the masticatory muscles, which develops during chewing, from this beating of teeth against each other, the bone begins to contract. Bone tissue shrinks. And after the bone, the gum also contracts, because the bone and gum are tightly connected. The gum descends, following the bone. And here we answered the main question - why gums recede.
Let's now begin to form an understanding of the answer to the next question: what to do if your gums have receded.
Remedies for reducing tooth sensitivity
Due to the exposure of the necks and roots, the teeth of patients with periodontal disease become much more sensitive to the effects of various irritants - thermal, chemical, mechanical. Patients experience significant discomfort when eating spicy or sour foods, drinking hot or cold foods and drinks. To eliminate this unpleasant symptom, various means are used, including calcium gluconate, which is administered by electrophoresis (medicine applications combined with a weak electric current).
To combat hyperesthesia and eliminate other symptoms, you can also use special toothpastes. In particular, the minerals potassium citrate and hydroxyapatite, as well as thermal mud, which are contained in ASEPTA Sensitive toothpaste for sensitive teeth, help reduce tooth sensitivity and strengthen enamel. It also contains extracts of medicinal plants that have anti-inflammatory and antimicrobial effects.
Orthodontics comes to the fore
Today, a huge mistake is happening both in the search for the causes of periodontal disease and in making a diagnosis, as well as in the method of effective treatment. Instead of putting the tooth into occlusion, removing it from a traumatic bite, patients are offered all these manipulations that I have previously voiced, which are not at all aimed at getting rid of these complaints, but only at the fact that patients are wasting time, the processes are getting worse.
In the treatment of the so-called periodontal disease is a big problem in the loss of time for inadequate treatment, and the loss of time for the patient is a complication of the pathology of dental occlusion, and the transition of the stage of the disease to a more advanced form.
If a patient, for example, three years ago had a loss of bone tissue of two millimeters, then due to the “treatment of periodontal disease” he has already lost five millimeters, that is, we have lost time.
And if he came to the orthodontist with a loss of bone tissue of two millimeters, then it would be easier to stop the loss of gums, it would be easier to eliminate the development of gum pathology after orthodontic treatment, when the teeth become aligned with the dentition.
We can already talk about the fact that we close all exposed necks of gum recession, thereby treating the neck of the tooth. But when patients waste time on treatments that are inadequate for the disease, sometimes closing the recession is no longer possible. Because there are also strict indications and contraindications for the treatment of gum recession.
The main causes leading to periodontal disease
At the moment, experts have made serious breakthroughs in the study of this disease. But scientists still cannot say that they have studied periodontal disease 100%. At the moment, it is believed that the main reason for the development of this disease is heredity. If at least one of the patient’s parents had this problem, then most likely it will be passed on to the child.
The immediate cause of the development of periodontal disease is a violation of metabolic processes. Disruptions in the body associated with changes in hormonal levels often lead to a decrease in the flow of beneficial substances to the gums. Other reasons worth noting:
- Disease of the gastrointestinal tract.
- Poor nutrition and poor diet.
- Diseases of a neurological nature.
- Alcohol and tobacco abuse.
- Decreased protective functions of the body.
Indirectly, the development of periodontal disease is affected by bite pathologies and mechanical trauma to the periodontium. The formation of plaque and tartar often triggers the onset of processes that will subsequently lead to periodontal disease.
How to cure gum disease
The choice of treatment method for periodontal disease in Moscow is determined based on the stage of the disease, how many teeth need to be removed, and how many teeth have fallen out. When elements fall out, the load during chewing food goes to the remaining teeth. As a result, they become overloaded and the process of destruction begins to accelerate. The cost of treating periodontal disease and the therapeutic regimen are drawn up by the dentist after an examination and consultation. To get rid of periodontal disease, the clinic offers therapeutic, surgical, and orthopedic treatment.
Carrying out closed curettage
To eliminate pathologically altered tissue, a surgical method is used. Its purpose is to remove vegetative epithelium, subgingival tartar, decayed tissue, granulation, and damaged root cement. Closed curettage is used when periodontal disease has reached the moderate stage of severity. The condition for this is the depth of the periodontal pocket from 3 to 4 millimeters, the absence of a bone pocket, and a dense gum structure.
Before the procedure, the oral cavity is treated with an antiseptic and numbed. Using a scaler and curette, root cement and deposits on the teeth are removed. All dental surfaces are treated. The teeth are then polished with special periodontal burs. The pocket bottom is processed with a rasp or excavator. Next, the epithelium of the oral cavity, which has grown into the pocket, is scraped out.
It is prohibited to use the procedure in case of purulent secretion, suspicion or presence of an abscess, or a bone pocket whose depth exceeds five millimeters. It is not recommended for fibrotic, thinned gum tissues when tooth mobility has reached the third degree. The process of closed curettage can provoke a complication of an acute infectious disease of the oral cavity. How much it costs to treat periodontal disease using deep closed curettage on one tooth can be seen in the corresponding section of the site. The average price is 2 thousand rubles.
Carrying out open curettage
The procedure involves removing pathological tissue. The procedure is required for those patients whose periodontal pocket does not exceed five millimeters, granulations have grown, resulting in deformed interdental papillae, and the gum edge is not adjacent to the tooth. Open curettage is not performed for periodontal pockets whose depth exceeds five millimeters, thinned gum tissue, necrotic changes in the gum edge, or discharge of pus.
The procedure begins with antiseptic treatment of the oral cavity and anesthesia. A horizontal incision is made at the apex of the interdental papilla. After this, the oral and vestibular portion of the gum, which is located between the teeth, is peeled off. Using a hoe, curette, or scaler, pathological tissue and deposits on the tooth are removed. The root surface is polished with a periodontal bur. After treating the dental tissue, the dentist excises the pathology of the soft tissue. Excision involves getting rid of ingrown oral epithelium and granulation.
Treatment of periodontal disease in dentistry using open curettage ends with rinsing with an antiseptic drug. The patient's interdental papillae are placed and secured with a catgut suture. The area where the operation was performed is covered with a protective gum bandage, which is impregnated with an anti-inflammatory agent. If excessive bleeding is present, do not apply a bandage to prevent a hematoma from forming.
Carrying out plastic surgery of the vestibule
This procedure is a corrective surgery that increases the space between the gums and the inside of the lip and cheek. If the vestibule is less than five millimeters, surgical correction is performed. If surgery is not performed, the risk of periodontal pathology increases.
Surgical intervention to deepen the vestibule of the oral cavity lasts no more than 60 minutes. The clinic’s dentists select a specific technique, which is based on a study of the soft tissue of the oral cavity. The administration of local anesthesia relieves the patient of pain. The wound heals after two weeks. Clients of the dental center undergo the operation without complications. An important condition is to follow the recommendations:
- Carry out oral hygiene regularly.
- Treat the surgical area with antiseptics.
- Avoid physical activity for a certain period of time.
- Use antibiotics and other drugs that promote rapid healing.
- Follow a diet that excludes foods that irritate the mucous membranes of the oral cavity.
Carrying out splinting of teeth
The procedure is indicated for patients who have loose teeth or one element. Treatment of periodontal disease in the clinic using splinting is carried out to strengthen and preserve natural teeth, which prevents their loss. The procedure is performed in cases of bleeding gums, deep periodontal pockets, exposed tooth roots, and also if dental plaque occurs pathologically quickly.
The method of splinting the dentition is divided into the following types:
- Temporary. Tires are installed for a period of one to three months. Dental treatment of periodontal disease in Moscow is indicated for the first stage of the disease. The process does not affect the soft tissue of the oral cavity.
- Long term. Tires are installed for up to 12 months. Therapeutic actions depend on the individual characteristics of the patient.
- Permanent. Tires are installed for a period of 12 months. There is no negative effect on the gums, a lasting effect is achieved.
During the procedure for splinting damaged teeth, fiberglass, armid thread, clasp prosthesis, and crown are used. The dental clinic provides removable and non-removable expanding structures. Which type to choose depends on the following factors:
- How many teeth are lost?
- What type of dental deformation does it belong to?
- How severe is the inflammation in the gums?
A removable splinting structure is indicated for lack of teeth, and a non-removable one is required to prevent overload of periodontal tissue. These types of installations can eliminate tooth mobility. Splinting structures do not interfere with hygienic or therapeutic procedures in the oral cavity, their use does not injure tissue, and also have a high aesthetic effect.
Completely curing periodontal disease is not an easy task. The dental clinic provides comprehensive treatment for the disease. After therapy, signs of the disease will decrease, tissue nutrition will improve, and atrophic processes will slow down. Comprehensive treatment of periodontal disease in Moscow includes the following measures:
- Use of medications. There are often cases when periodontal disease and periodontitis appear simultaneously. As a result, the client is prescribed an anti-inflammatory drug and a drug that improves tissue nutrition.
- Cure caries that occurs on the exposed neck of the tooth.
- Use of physiotherapy. All methods that improve periodontal tissue.
- Ultrasound treatment. Ultrasound affects teeth and tissues. The essence of the procedure is to clean the surface of the gums, teeth, and antiseptic treatment. When accompanied by periodontitis, ultrasound cleanses the periodontal pocket.
Gums are bleeding - contact a periodontist
If you notice the slightest symptoms of periodontitis, immediately go to the doctor. The first sign is regular bleeding of the gums after mechanical impact.
If there is a single bleeding, there is no reason for serious concern: to strengthen the gums, you can change the toothpaste to a special product for the treatment and prevention of periodontitis, or use a strengthening gel or balm. But if bleeding becomes regular, you need to see a specialist.
If the disease progresses, some teeth may need to be removed. Therefore, the earlier the diagnosis is made and treatment is started, the greater the chances of completely getting rid of periodontitis without negative consequences.
Asepta Parodontal - specialized products for the treatment of periodontitis
has developed a whole range of drugs for the treatment and prevention of gum disease. It includes:
- Asepta therapeutic and prophylactic toothpaste, which helps eliminate inflammation and bleeding of the gums. Contains a unique complex of medicinal extracts and active ingredients;
- Asepta Sensitive toothpaste for sensitive teeth. Provides gentle care for sensitive enamel and gums prone to inflammatory processes. Thermal mud in the paste helps heal damaged tissue and relieve irritation;
- Asepta mouthwash is intended to relieve symptoms of gingivitis, periodontitis, stomatitis and toothache caused by infection. The antimicrobial components of the drug help relieve inflammation and pain, and also have an antiseptic effect;
- Asepta Fresh mouthwash eliminates inflammation and bleeding of gums, prevents the formation of dental plaque, and also gets rid of pathogenic bacteria that cause bad breath;
- Asepta gel with propolis has an intense anti-inflammatory effect, reducing the sensitivity of enamel and promoting the healing of trophic ulcers. Effectively strengthens periodontal tissues and is suitable for patients of all ages.
- The adhesive balm in this series eliminates the causes and symptoms of inflammatory diseases of the mouth. The sticky base ensures a longer and more effective effect of the drug, allowing it to remain on the gums for a long time;
- Asepta vitamin and mineral complex contains all the necessary substances and active components for healthy teeth and gums.
Take care of your health with professional hygiene products!
Symptoms and signs of periodontal disease
There are no specific symptoms of periodontal disease, but there are signs that indicate problems have arisen and may indicate damage to the bone tissue of the tooth. But there are a number of basic symptoms that indicate the beginning of problems and the need to visit a doctor. Such signs include mobility and gaps between teeth, the appearance of bacterial plaque, periodontal pockets, pus, swelling and swelling of the gums. It should also be remembered that the oral cavity requires constant care, but if an unpleasant odor and the listed symptoms occur during regular cleaning, this indicates a developing disease.
Symptoms of periodontal disease include the following:
- the gums appear pale, and in the early stages there are no obvious inflammatory processes;
- Retraction of the gums appears, the neck is exposed, visually the length of the tooth seems longer;
- there is no bleeding in the early stages, but purulent pockets, enamel erosion, wedge-shaped defects and tooth abrasion may appear;
- At the same time, problems with the endocrine system, diseases of the cardiovascular system, and metabolic disorders can be diagnosed.
Main features
It is important to remember that at the initial stage there are no specific signs; alveolar pyorrhea often develops asymptomatically. Therefore, the first signs are already indicators of degenerative processes and require urgent intervention from a specialist. Pain, atypical plaque, softening of the gums - all this indicates the need to see a dentist and undergo examination with subsequent treatment.
The main signs of periodontal disease are:
- the appearance of atypical plaque in large quantities (this is not a specific sign, but already indicates the presence of problems);
- the appearance of tartar;
- discomfort when eating cold/hot, spicy food;
- itchy gums;
- the appearance of pulsation in the gum area;
- purulent discharge;
- bleeding in the gum area when chewing or other mechanical impact on their surface;
- the appearance of defects such as cavities, pockets or crevices in which food begins to accumulate;
- the gums begin to become covered with a whitish coating;
- teeth become weak, gaps appear between them, abrasion and other defects appear on the surface;
- the necks are exposed, the teeth visually appear longer;
- There is a phenomenon called retraction (destruction, resorption) of the gums.