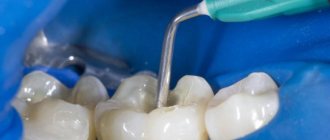
Material for temporary fillings Dentin paste is used to isolate the drug in a carious cavity and temporarily fill teeth.
Intended for use in a medical facility.
The material is a polymer-based zinc sulfate cement.
Dentin paste hardens under the influence of moisture for 2-3 hours; during the hardening process, the material expands, providing a tight marginal fit.
The material is highly resistant to stress and has excellent adhesion to hard dental tissues and does not cause irritation to oral tissues.
What materials are used for temporary filling?
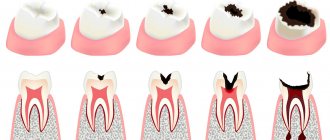
Temporary fillings are installed in cases where treatment requires several visits to the doctor. For example, to eliminate the inflammatory process or kill the nerve during pulpitis, the doctor places the appropriate medicinal substance and covers it with a special filling material on top. This ensures a hermetically sealed cavity, which prevents bacteria and infection from entering. But unlike permanent fillings, the material for temporary fillings may not be as durable. Read further in this article about what formulations are used for this.
"Vinoxol" and other cements based on zinc sulfate
This type of filling material for temporary fillings is based on zinc sulfate and zinc oxide. When in contact with water, they form substances that contribute to the rapid hardening of the mass. This category includes such drugs as “Dentin-paste”, “Vinoxol”, “Dentin for dressings” and others. Doctors use a dental excavator or probe to remove the cement filling. If the walls of the carious cavity are too thin and there is a high risk of damage, the material is removed using a drill.
Composition of “Dentin paste”
This material for temporary filling is produced in the form of a rather dense and thick mass. A preparation is being prepared based on zinc sulfate cement. To give it the appropriate consistency, a paste former is added. Additional ingredients included in the product are fragrances and dyes.
Thanks to additional additives, the drug is now available in several versions:
- without smell;
- with cherry aroma;
- with the smell of mint;
- clove;
- strawberry.
Artificial dentin and dentin paste
A white powdery substance based on zinc oxide and anhydrous zinc sulfate also contains dextrin and kaolin. Cement powder is mixed with water on a glass plate in a ratio of 2 to 1. Water is gradually added to the resulting mixture until a thick paste is obtained. Once ready, the material is transferred into the cavity using a trowel or spatula and compacted.
Dentin paste is similar in composition to artificial dentin
Dentin paste is similar in composition to artificial dentin, but it also contains white clay, peach oil and eugenol. The paste is available in ready-to-use form, in 50 g jars. It is a homogeneous white mass, may have a yellowish tint and a light clove aroma, and is intended for temporary covering of carious cavities. The material is applied using a spatula, and it hardens within 2-3 hours, while a humid environment and contact with saliva accelerates this process.
Instructions Dentin paste
Material stored or transported at low temperatures must be kept at room temperature for at least 1 hour before use.
Before filling with Dentin Paste material, the tooth cavity must be moistened. Using a spatula, select the required amount of paste corresponding to the size of the cavity to be filled, place the material on a glass plate or on a sheet of notepad for mixing. Immediately seal the jar of paste tightly to prevent surface hardening of the material! Introduce the required amount of material into the cavity and condense the paste into the tooth cavity using a plugger.
Attention! The filling material remaining on the glass plate must not be placed back into the jar with the Dentin paste material.
Surface hardening of the material begins within 20-30 minutes.
After 2-3 hours, the temporary filling is able to withstand chewing loads (the patient is not recommended to eat during this time).
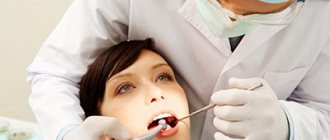
The material is easily removed from the cavity in large fragments using an excavator or probe. The remaining material is washed out of the cavity with water.
Zinc-eugenol materials and their features
Cements belonging to this group are based on zinc oxide and eugenol. There are three main types here:
- classic,
- reinforced with filler,
- based on EVA acid.
The first category includes mixtures of powder in the form of zinc oxide and liquid, for example, purified eugenol or clove oil. To make the hardening process faster, 1% ethyl alcohol, acetic acid or water in small quantities can be added. Upon contact with a humid environment, the material hardens in literally 10 minutes and reaches a strength value of 7 to 40 mPa. Currently, the Czech zinc-eugenol cement Cariosan is widely in demand in dental practice.
When in contact with a damp environment, the material hardens in 10 minutes
Strengthened zinc has better mechanical properties. The powder contains zinc oxide mixed with 10-40% crushed natural or synthetic resins. After hardening, the strength of the material reaches 35-55 MPa. To further improve the properties of cement, 50-66% EVA acid is also added to it, which increases the strength to 55-70 mPa. In some cases, this material is recommended for fixing elements of orthodontic structures1.
Filling materials with medicinal properties
Nowadays, dental practice widely uses filling materials with various medicinal additives. Auxiliary components in such compositions provide analgesic, anti-inflammatory, and plastic-stimulating effects. However, more often they are used as linings for other filling materials as part of the treatment of deep caries and pulpitis.
Such fillings are used in the treatment of pulpitis
They provide reliable protection of dentin and pulp from external factors, including mechanical and temperature stimuli. This is also an excellent option for ensuring a tight, airtight seal for a permanent filling. Materials with medicinal properties can be divided into 3 large groups:
- with calcium hydroxide in the composition,
- zinc-eugenol cements, which were already mentioned above,
- combined medicinal pastes.
Materials belonging to the first group most fully meet the requirements described above. When calcium hydroxide comes into contact with carious dentin, sclerosis of the dentinal tubules occurs, which, in turn, contributes to the formation of secondary dentin.
Currently, manufacturers offer a fairly wide range of various drugs created on the basis of calcium hydroxide. The materials are available in the market in various forms, including powder and liquid or two pastes. The two components are mixed on a paper or glass plate and brought to the state of a dense, uniform slurry, after which, using a special tool, they are transferred to a previously cleaned and prepared cavity in the tooth, and the composition is evenly distributed along its bottom.
There are also compositions with calcium hydroxide, which instantly harden under the light of a polymerization lamp. Such preparations are also used as spacers when filling with modern light composites.
Compositions with calcium hydroxide harden under the light of a polymerization lamp
“When I had deep caries, the doctor put in a special medicine and put a healing filling. I remember it was very painful at first, but after the procedure everything went away. He explained to me that this temporary filling contains calcium and some other useful microelements. That is, it not only covers the tooth, but also heals...”
Nelly23, from correspondence on the forum www.32top.ru
As for zinc-eugenol cements, they, as we already know, often have pronounced antibacterial and analgesic properties, effectively relieve inflammation and help stop the pathological process. Such drugs are often used in the treatment of deep caries and pulpitis.
"Dentin paste": instructions
Before using the drug, every dentist should read the instructions for use. Temporary material “Dentin paste” should be applied using a special trowel. This is done after the tooth cavity has been prepared. It must be cleaned of carious formations and then thoroughly dried. The paste layer should not exceed 1-2 mm.
The material hardens within 2 hours. During this time, the patient should not take any food. Otherwise, there is a chance that the temporary filling will break.
“Dentin paste” is easily removed from the dental cavity. This will require either a probe or a dental excavator. It is enough to pick up the filling with a smooth lever-like movement, and it will easily come away from the dental tissue.
After applying the paste is completed, you should carefully close the jar with the drug with a lid. This will protect the contents from moisture getting inside. Accordingly, the paste will not harden and will last a long time.
“Dentin paste” is produced in containers of 50 grams. To treat one tooth, no more than 0.5 grams of product is required. Thus, one jar is enough to form approximately 100 temporary fillings.
Combined medicinal pastes and their composition
Here we are talking about non-hardening preparations that are prepared from various drugs immediately before filling the carious cavity. Such pastes may contain antibiotics, sulfa drugs, vitamins, corticosteroids and other medicinal components. On site, the therapeutic lining prepared and placed on the bottom of the cavity is covered with artificial dentin or other material suitable for temporary filling. At the next appointment, the doctor will remove any remaining medication, assess the condition of the pulp, and if there are no signs of inflammation, perform a permanent filling.
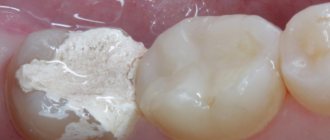
The photo shows the process of removing a temporary filling.
As can be seen from all of the above, today in dentistry there is a fairly wide selection of materials for temporary fillings with different properties and indications for use. The choice of a particular drug is at the discretion of the attending physician and largely depends on the individual characteristics of the clinical picture.
1Abakarov, S.I. Protection of exposed dentin after odontopreparation at the stages of prosthetics, 2003.
Peculiarities
The main feature of “Dentin paste” is its disinfecting effect. Dentists choose this material for its other characteristics:
- "Dentin paste" is easy to use.
- No mixing is required, the product is already ready for use.
- This is a fairly durable material - it can even be applied for up to 14 days.
- The drug hardens when exposed to moisture. This happens after 2 hours.
- The material hermetically seals the tooth cavity.
- “Dentin paste” does not dissolve over time.
- All the necessary manufacturability is present in this material.
- The drug protects the tooth from staining. This is especially important if filling is done with amalgams.
“Dentin paste” is used to cover the drug, which is placed in the tooth cavity to eliminate the consequences of uncomplicated caries.