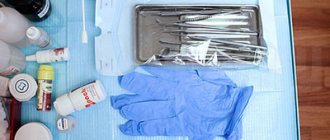
Rotary dental instruments include burs, cutters, discs, abrasive heads, and polishers used in dental practice for processing hard and, in some cases, soft tissues of the maxillofacial area.
Regardless of the functional purpose of rotating dental products, their design includes a so-called working part, with the help of which the material being processed is removed, and a shank, designed to secure the tool in the dental handpiece. The surface of the working part can be made of various materials, for example, steel, diamond chips, corundum, silicone, polymers, natural pile, artificial bristles. These circumstances must be taken into account when choosing methods and means of processing products before subsequent use.
In accordance with the provisions of Ch. V SanPiN 2.1.3.2630-10 “Sanitary and epidemiological requirements for organizations engaged in medical activities” all dental instruments that come into contact with the wound surface, blood or injectable drugs, as well as those that come into contact with the mucous membrane during operation and can cause its damage, must consistently undergo disinfection, pre-sterilization cleaning and sterilization.
General requirements for compliance with sanitary standards
Today, the main requirement in dentistry is the use of disposable materials for patient treatment. Before the appointment, all auxiliary materials must be replaced, including gloves and a doctor’s cap. Reusable instruments must be removed from special sterilization bags that indicate the date and time of their sterilization.
Some patients are so eager to see a doctor that they want to enter the office immediately after the previous patient has left. They do not think that after seeing a patient, medical workers disinfect the office. Therefore, after one patient leaves, all surfaces with which he came into contact or could hypothetically come into contact are wiped with a disinfectant solution. Disposable instruments are disposed of in accordance with all sanitary standards. During the entire reception, the bactericidal recirculator lamp should be running, which can operate in continuous mode (without stopping).
Types of sanitary cleaning in a medical facility
Wet cleaning of premises (floors, furniture, door handles, beds, medical equipment) is carried out twice a day, always using certified detergents and disinfectants.
General cleaning of health care facilities is carried out according to the established schedule:
- in operating rooms, delivery rooms, dental and dressing rooms at least once every 7 days;
- in the wards and corridors of infectious diseases departments - once every 10 days;
- in the wards and corridors of a regular department - once a month;
- in bathrooms, utility rooms - 2 times a month.
Walls, floors, furniture, and appliances are treated with rags soaked in a disinfectant solution. facilities. Disinfection of premises by irrigation from a hydraulic remote control is allowed (subject to compliance with personal protective measures). The equipment is wiped with rags and cleaned with brushes.
Disinfection and cleaning measures
Instruments that have come into contact with the patient's saliva are a source of increased danger. Therefore, immediately after use, the instrument is loaded into a container with a disinfectant and cleaning solution. Then, it is processed in a thermal disinfector.
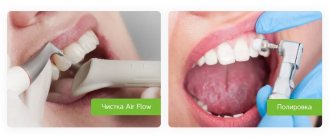
The next stage of processing is cleaning. It helps remove remnants of medications and fatty contaminants. The best method of cleaning is mechanical processing in special machines. This is the only method that allows complete removal of saliva and blood residues from the surfaces of instruments.
Disinfection of instruments used in therapeutic practice
When answering the question about what instruments are disinfected in dentistry, we should immediately say that in the doctor’s office all surfaces are treated at the beginning of the working day. Also, medical staff must clean the dental chair and other surfaces of the equipment used after each patient.
Therapeutic instruments must undergo appropriate multi-stage cleansing. The standard set includes a tray, a trowel, a spatula, an elevator, a probe and tweezers.
Sterilization
Sterilization is the final stage of processing medical instruments. There are two main methods - steam and air. Steam sterilization uses:
- autoclave;
- wet sterilizer;
- hot steam sterilizer.
This method works using steam from distilled water under high pressure at temperatures up to 135o.
Air sterilization is carried out using a dry-air sterilizer or a dry-heat oven. The air temperature in such devices reaches 180°.
Sterilization takes place in several stages:
- steam treatment;
- sterilization;
- drying.
The entire procedure takes approximately 1.5 hours. After this, each instrument is placed in a disposable sterilization bag, on which the date and time of packaging is written. Sterility in such bags is maintained for about six months.
Methods for sanitizing instruments in the Da Vinci aesthetic dentistry studio
Our clinic is a modern dental center. And we approach the issue of patient safety thoroughly. Therefore, cabinet processing necessarily includes the following steps:
- disinfection of all surfaces in the office before each patient;
- placing all instruments related to the patient in a special sterilization bag;
- issuing disposable “clothing” to those coming for treatment - a disposable napkin, a cap;
- the bactericidal lamp operates throughout the entire appointment;
- sterilization of instruments after each use;
- The doctor changes gloves and cap after each appointment; gloves are also changed if the doctor leaves the patient. In our clinic, it is customary to do this in front of the patient so that he has no doubts about the complete safety of the entire treatment.
- During X-ray procedures, the device’s sensor is placed in a disposable bag, which is immediately thrown away after use.
We care about the health of our patients and strive to ensure that treatment is as safe as possible.
Add a comment
Leave your comment
Pre-sterilization cleaning of dental instruments
Stage II processing of medical products pre-sterilization cleaning - carried out to remove protein, fat and mechanical contaminants from products, as well as residues and medications.Pre-sterilization cleaning of dental products is carried out after their disinfection and subsequent washing of disinfectant residues with running drinking water.
Pre-sterilization cleaning is carried out using cleaning agents and modes regulated by OST 42-21-2-85 , as well as new generation drugs, according to the instructions for use.
Can be carried out:
- manually;
- in a mechanized way.
When manually cleaning, the process includes a number of operations:
- Soaking in a washing solution while completely immersing the disassembled product with mandatory filling of all channels and cavities for 15-60 minutes, depending on the product used.
- Wash each product in a washing solution using a brush or a cotton-gauze swab or cloth for 0.5–1 minute. Monitor the temperature if this condition is specified in the guidelines. Rubbing rubber products is not allowed.
- Rinse under running water (0.5–10 minutes). It is carried out in containers (bathtub, sink) using devices for jet water supply, for the time specified in the instructions for the product used. The instrument rinsing sink should not be used for washing the hands of medical personnel.
- Rinse with distilled water for 0.5 minutes.
- Drying with hot air at a temperature of 85°C until moisture completely disappears in the air sterilizer with the ventilation hole open; in a sterilization drying cabinet - with the door not tightly closed.
If the product, along with detergents, also has disinfecting properties, pre-sterilization cleaning can be combined with disinfection (“Alaminol” (SSC RF NIOPIK, Russia) 5.0% or 8% - 60 minutes, “Veltolen” (AOZT Velt, Russia) 2.5% - 60 minutes, "Deconex Dental BB" (Bohrer Chemi AG, Switzerland) - 30 minutes, "ID-212" (Dürr Dental-Orohim, Germany) 4% - 30-60 minutes, etc.) .
Improving the pre-sterilization cleaning process, instead of the previously used manual method of processing using a washing solution, is possible through the development and implementation of installations in which the cleaning process is carried out by treating products with detergents or detergent-disinfectants in combination with ultrasound. Allowed for these purposes is only equipment that is authorized in the prescribed manner for industrial production and use, and in the case of imported equipment, permitted for use on the territory of the Russian Federation.
In dentistry, ultrasound treatment makes it possible to achieve complete cleaning of burs, endodontic and other instruments from dentin residues, blood, oral fluid, and filling materials, which cannot be achieved by manual washing with brushes even after prolonged soaking in a cleaning solution.
The use of ultrasonic baths for pre-sterilization cleaning allows you to:
- reduce the tactile contact of medical personnel's chickens with the instruments being processed, which guarantees a reduction in the risk of infection and the spread of nosocomial infections;
- prevent damage to expensive medical instruments and products and increase their service life;
- significantly improve the quality of cleaning medical instruments and products of complex configuration;
- significantly reduce processing time for large volumes of tools and products.
Sterilization is carried out to ensure that cross-infection does not occur during dental procedures. To achieve complete sterility, it is very important that all organic matter is first removed from the instruments.
If the instrument has not been cleaned first, the sterilization process may not be effective. Hand washing of tools can cause the organic substrate to become shredded and contaminants can get into even more inaccessible areas (jagged edges, nicks on handles, screw threads, fine scratches, etc.)
For pre-sterilization cleaning, the following products can be used: "Alaminol" (SSC RF NIOPIK, Russia) - 8%, "Deconex-50 FF" (Bohrer Chemie AG, Switzerland) - 1.5%, "Veltolen" (AOZT Velt, Russia) - 1.0% or 1.5%, "Deconex Dental BB" (Bohrer Chemie AG, Switzerland), "ID-212" (Dürr Dental-Orohim, Germany) - 2.0% or 4.0%, "Septabic" "(Abik, Israel) 0.15% or 0.2%, "Septodor" (Darvet LTD, Israel) 0.4%, etc., according to the requirements of the guidelines for the use of these drugs.
↑ Top Products for pre-sterilization cleaning >>
Methods for disinfecting dental instruments
| Disinfection method | Disinfectant agent | Solution concentration % | Disinfection time (min) | Application |
| Physical - boiling. | A) Distilled water. B) Distilled water with sodium carbonate. | 2,0 | 30 15 | Recommended for glass products, metal, heat-resistant polymers. |
| Chemical. | A) Chloramine. | 3,0 | 60 | Products made of glass, corrosion-resistant metal, polymer materials. |
| B) Hydrogen peroxide. | 6,0 | 60 | Products made of glass, corrosion-resistant metal. | |
| B) Neutral calcium hypochlorite | 4,5 | 60 | Products made of glass, polymer materials. | |
| D) Glutaraldehyde. | 2,5 | 60 | Products made of glass, corrosion-resistant metal | |
| D) Formalin. | 4,0 | 60 | Products made of glass, polymer materials. | |
| E) Neutral anolyte. | 0,05 | 180 | Rubber products. | |
| Neutral anolyte. | 0,05 | 60 | Products made of plastic. | |
| Neutral anolyte. | 0,05 | 30 | Glass products. |
Disinfection of dental instruments
Disinfection of dental instruments is carried out by immersing them in a disinfectant solution. For products and their parts that are not in direct contact with the patient’s oral mucosa (tips, light guides of photopolymerizers), the method of wiping twice with an interval of 15 minutes can be used.
Wash water is disinfected by boiling for 30 minutes or covered with dry bleach at the rate of 200 grams per 1 liter, mixed and kept for 60 minutes.
After use, single-use plastic products are immersed in a specially marked container with a 5% solution of chloramine or a 1.5% solution of neutral calcium hypochlorite.
The tips, after each patient’s use, are removed and the outer surfaces and the boron channel are thoroughly wiped with a sterile swab twice, after 15 minutes, followed by an exposure of 45 minutes, with a swab moistened with a 3% chloramine solution or 70° alcohol.
The working surface of tables for sterile instruments and the wall along their length are wiped with a special rag moistened with a 1% chloramine solution.
After each patient, the dentist’s table is disinfected with a napkin soaked in a 1% solution of chloramine or 3% hydrogen peroxide or disinfectant wipes “Hexidis Plus”, “Diaseptic-30C”, “Avansept” and others.
Dentists should work in rubber (latex) gloves, which, after seeing a patient (without contamination with blood), are washed under running water with soap twice, followed by treating them with 70° alcohol for 2 minutes before seeing the next patient. If gloves are contaminated with blood, disinfection is carried out using 6% hydrogen peroxide or 3% chloramine for 60 minutes in a marked container. To work with another patient, take a new pair of gloves.
Features of working with endodontic instruments
The vast majority of instruments used in endodontic treatment today are disposable. When using them, specialists are guided by two basic rules:
- after use, the product must be properly disinfected,
- after that it must be sent for disposal.
As for reusable items, after each patient they are immediately sent to a disinfectant solution and usually left there for half an hour. After this, ultrasonic cleaning can be carried out, followed by treatment in an autoclave or oven. The method is chosen based on the type of tool used. After the full cycle, the processed items are sent for storage to specialized equipment, which is available in any modern clinic today.
Sterilization methods
| Sterilization methods | Means and conditions | Tools |
| 1. Dry heat method. | Dry oven -180 degrees 60 minutes. | Small dental instruments, trays with a set of dental instruments. |
| 2. Cold (chemical) sterilization. | Before sterilization, instruments are treated with a mixture of 0.5% hydrogen peroxide solution and Lotus detergent. The instruments are placed in a tray with an antiseptic solution for 40-45 minutes. 6% hydrogen peroxide 6% hydrogen peroxide 1% dezoxon-1 solution 2.5% glutaraldehyde solution 8% lysoformin-3000 solution | Dental mirrors, sharp cutting objects, plastic spatula. at 18-20°C - 6 hours at 50°C - 3 hours at 18°C - 45 min at 20°C - 6 hours at 50°C - 1 hour. |
| 3.Boiling method in normal or alkaline water. | 30-40 minutes. Sodium bicarbonate (baking soda) 10-20 g per liter of water is added to the water (to prevent oxidation). | Syringe, needles, burs, instruments for filling teeth. |
| 4. Boiling in Vaseline oil followed by centrifugation. | Method for performing surgical operations. | Dental handpieces. |
| 5. Disinfection (instruction of the USSR Ministry of Health dated March 1, 1977). | Wipe twice with a sterile cotton-gauze swab with a solution of chloramine, 3% formaldehyde solution (optional with an interval between wipes of 10-15 minutes). | Dental handpieces. |
| 6. Boiling brushes. | Place in a disinfectant solution for 2 - 3 hours, then boil for 40 minutes. | Brushes for washing hands. |