Malocclusion
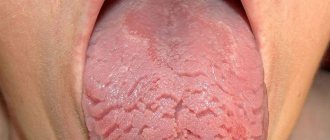
Incorrect bite formation leads to permanent injury to the mucous membranes of the mouth and tongue. As a result, the muscle organ swells and increases in size. Due to constant biting, teeth marks are left on the sides of the tongue.
The disease can be cured only after correcting the malocclusion. To do this, the doctor selects a design to straighten the dentition. For minor violations, patients are prescribed to wear orthodontic plates, trainers, and silicone trays. In case of more serious pathology, the defect is corrected using braces. The course of treatment can take from 3 months to 2 years.
Other dental problems
When teeth imprints constantly appear on the tongue and cheeks, while a person manages to bite and injure the mucous membrane, this can indicate not only malocclusions, but also other dental pathologies:
- incorrectly installed crowns, fillings and dentures,
- presence of chipped and damaged teeth,
- abnormal structure of the temporomandibular joint,
- bruxism,
- lack of teeth,
- anomalies in the growth and eruption of third molars: for example, “eights” can grow into the cheek, cause crowding of the row and provoke bite pathologies.
Folded tongue
This is a congenital anomaly in which the tongue is excised by longitudinal and transverse folds, wavy, uneven at the edges. As a rule, the disease is accompanied by an increase in the size of the organ and its thickening; teeth marks can be seen on the sides. Usually the pathology is asymptomatic and does not cause discomfort; pain and inflammation can appear after infectious diseases, with the development of stomatitis or glossitis.
The folded tongue requires good hygienic care, since bacterial plaque easily accumulates in the cracks and creates a convenient environment for the proliferation of pathogenic bacteria. Such a disease is incurable; therapeutic procedures are necessary only when stomatitis and glossalgia develop.
How do they look
Small cracks in the tongue can be completely invisible to the naked eye; only an experienced doctor can examine them using special instruments. The larger ones are clearly visible to the naked eye; they resemble longitudinal or transverse grooves on the tongue. Deep cracks look like crevices; sometimes the tongue appears to be cracked or split into two parts. If you notice such a problem, consult a doctor, even if nothing is bothering you at the moment. If an infection gets into the crack, the course of the disease may be complicated by the inflammatory process.
Liver diseases
In people suffering from serious liver diseases (viral hepatitis, cirrhosis of the liver), the tongue has a characteristic appearance - the mucous membranes are red, hyperemic, the surface is smooth, glossy, the papillae are smoothed. Often such symptoms are accompanied by swelling of the organ and an increase in its size, as a result of which the edges are constantly bitten by the teeth, forming wavy sides.
Among the additional external symptoms, patients note the appearance of spider veins, xanthomatous plaques, and erythema (redness) of the palms on the surface of the skin. Patients complain of pain in the right hypochondrium, nausea, vomiting, indigestion and stool disorders.
The disease must be treated by a general practitioner, infectious disease specialist, surgeon or oncologist.
Why does the problem occur in pregnant women?
Teeth imprints on the tongue during pregnancy may be associated with the pathologies that we listed earlier, but most often they appear for the following reasons:
- dehydration of the body against the background of severe toxicosis,
- iron deficiency anemia: the muscle organ becomes red, swollen and numb,
- candidal stomatitis: then the unpleasant symptom is accompanied by the appearance of a dense cheesy coating,
- lack of B vitamins and folic acid,
- physiological swelling of organs due to the accumulation of fluid in the body in late pregnancy.
“I constantly noticed this problem during pregnancy. Especially after I get nervous. It was very noticeable in the later stages, in the summer, in the very heat. I was also constantly thirsty, I always felt that my mouth was very dry, and my tongue was swollen as a result. And I drank water and drank... True, the doctor scolded me all the time, saying that my whole body and all my internal organs were swelling. As soon as I gave birth, everything returned to normal...”
Anastasia K., review from woman.ru
Vitamin deficiency
If there is a lack of vitamins B and D in the human body, the surface of the tongue dries out, cracks, becomes inflamed, becomes coated, and bad breath appears.
When an allergic reaction to vitamins occurs, the muscular organ swells, and dents from the teeth are clearly visible on its lateral surfaces. With a lack of vitamin B₃, the organ cracks, painful sensations appear, and a burning sensation occurs while eating. If an infection occurs, an acute inflammatory process develops, purulent ulcers form, and the person’s well-being worsens. To treat the disease, it is necessary to compensate for the lack of vitamins in the body.
Main non-dental causes
Tongue diseases
If you notice an enlarged tongue with teeth marks in yourself or your child, then you should look for the problem in inflammation of the muscle organ. Often the cause of the pathology is a disease such as glossitis. There are many types of glossitis: desquamative, allergic, herpetic, ulcerative, hypertrophic, folded - read in detail about all types and forms in the feature article on the website.
When glossitis appears, other characteristic symptoms usually occur, in addition to the fact that tooth marks remain on the tongue:
- burning and itching of the muscle organ,
- redness, the appearance of plaque of different shades,
- pain and discomfort when eating food, when communicating with others,
- change in relief and structure: formation of cracks, ulcers, grooves, spots, erosions.
The causes of glossitis are very diverse: injuries, weak immunity, active reproduction of viruses and bacteria in the oral cavity, allergic reactions to personal hygiene products, medications and food.
Xerostomia (dry mouth)
A swollen tongue with teeth marks is often noticed by people who have impaired normal salivation. Xerostomia can occur in older people, as well as in those who take various medications for a long time. In some cases, the pathology is associated with dysfunction and inflammation of the salivary glands, autoimmune diseases (for example, Sjogren's syndrome), and hormonal disorders.
Another reason is dehydration after diseases accompanied by intoxication and high body temperature (poisoning, sore throat, influenza, ARVI and many others). Xerostomia affects people with diabetes, as well as those who frequently smoke and drink alcohol.
On a note! Sometimes dry mouth is normal. For example, the rate of salivation naturally decreases at night, which is why many people notice bad breath and teeth marks on the tongue after sleep. The problem can also appear after exhausting physical activity, sports, prolonged stay in stuffy rooms and in the open sun.
With a lack of saliva, the muscular organ becomes dry, may turn red, swell and increase in size, after which imprints appear on it and cracks appear. There are other signs of xerostomia:
- halitosis: bad breath,
- viscous and thick saliva,
- difficulty chewing and swallowing dry food,
- thirst.
If the problem of chronic xerostomia is not addressed, caries will progress, as well as other dental diseases (erosions, gingivitis and periodontitis, candidiasis). After all, the lack of a sufficient amount of saliva leads to the active proliferation of bacteria in the oral cavity and increased accumulation of plaque on the enamel, gums, and also under the gums.
Nervous disorders and stress
Teeth imprints on the sides of the tongue may indicate excessive nervous excitability and that the person has recently been in a stressful or conflict situation, experienced severe psycho-emotional shock, or is in a depressed state. Under nervous overload, you can involuntarily clench your jaws, squeeze the muscular organ between the lower and upper jaws, bite it, after which marks appear on its surface.
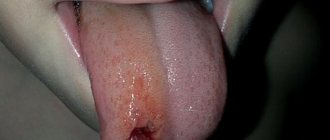
In rare cases, the problem indicates neurological disorders and neuroses, epileptic seizures in which a person cannot control himself. But then the patient not only bites a muscle organ, but can severely injure it, disrupt the integrity of the mucous membrane and tissue covering it, and cause bleeding.
Malfunction of the hypoglossal nerve
When an organ is displaced and occupies an unusual location for it, then teeth marks appear on it, as in the photo. Such an unpleasant phenomenon may be associated with pathological damage to the hypoglossal nerve resulting from a massive stroke or multiple sclerosis.
Pathologies of the gastrointestinal tract
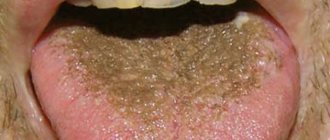
A dense plaque of white, yellow or brown color appears, and after closing the jaws, tooth marks remain on the tongue if there is any disease of the gastrointestinal tract: gastritis, ulcers, colitis, pancreatitis, dysbacteriosis, acidity disorders.
Usually, with these pathologies, the patient is accompanied by halitosis, and plaque cannot be permanently removed with a brush and paste, since it constantly accumulates again. There are other characteristic symptoms of gastrointestinal pathologies: bloating, pain, stool disturbances, nausea, heaviness in the abdomen.
Endocrine system dysfunction
If a muscular organ has increased in size and swollen, and there are imprints of chewing teeth on it, then what does this mean? Perhaps an advanced stage of hypothyroidism, when the thyroid gland does not secrete enough hormones. Patients with this disease usually notice not only swelling of the muscle organ, but also swelling of the face and neck. Their hair begins to grow and fall out, their nails peel, their diction is impaired, their blood pressure and pulse rise, arrhythmia occurs, and their voice becomes hoarse.
Acute deficiency of vitamin B3 and nicotinic acid
Due to the lack of these substances in the body, a rare form of vitamin deficiency develops, which doctors call pellagra. The disease is quite rare, because vitamin B3, as well as nicotinic acid, are contained in almost all products that we, one way or another, consume: eggs, milk, all types of meat, liver, fish, carrots, potatoes, tomatoes, wheat. Experts believe that the pathology mainly occurs in people from disadvantaged environments and those who abuse alcohol.
With pellagra, the muscle organ swells, and therefore teeth marks periodically appear on the tip of the tongue or on its sides. There is a feeling of discomfort and burning in the mouth, the mucous membranes and gums itch, hurt, and itch. This disease brings with it many others: dementia, dermatitis, nervous disorders, paralysis of the limbs, dysfunction of the cardiovascular system.
Important! Teeth imprints on the tongue may indicate various diseases: hemolytic anemia[1], scarlet fever, cancer, tuberculosis, HIV. A swollen muscle organ on which imprints remain is sometimes a consequence of acute allergic reactions and Quincke's edema.
Hypothyroidism
This disease is caused by a malfunction of the thyroid gland. The pathology is manifested by swelling of the tongue with characteristic marks of teeth on its surface. Patients are inactive and find it difficult to talk due to dry mouth. There is a sensation of a foreign object in the mouth, the tongue becomes tangled.
External symptoms of the disease include a yellow tint to the skin, swelling of the face, increased hair loss, deterioration of memory and intellectual abilities, disruption of the digestive tract, and disorders of the genitourinary system. Hypothyroidism is treated by an endocrinologist.
Why do teeth marks appear on the tongue and what to do about it?
If you notice teeth marks on your tongue, then this symptom should alert you. We must not forget that the tongue is a mirror of the body. It is through this organ that signals about various pathologies and diseases that require treatment can be received. We will talk about the most common of them in our article today.
Gastrointestinal diseases
The oral cavity and digestive organs are in direct communication. Diseases of the stomach and intestines cause acidity in the mouth, creating a convenient environment for the proliferation of bacteria. A persistent white or yellow bacterial coating appears on the surface of the tongue and mucous membranes, spots or erosions may form, the organ becomes inflamed and increases in size.
A symptom of the development of gastrointestinal diseases is the root of the tongue coated with plaque.
Peptic ulcers of the stomach, duodenum, duodenitis, dysbacteriosis, gastritis with high acidity, and colitis can cause such symptoms. Additionally, patients are bothered by abdominal pain, nausea, vomiting, heartburn, stool disorders, and flatulence.
To treat the pathology and eliminate plaque on the root of the tongue, you need to consult a gastroenterologist. During therapy, plaque and swelling disappear. If erosions have formed on the mucous membranes, it is necessary to do regular antiseptic mouth rinses with Chlorhexidine, Miramistin or Chlorophyllipt.
Treatment
The main question that worries patients with glossalgia is how to cure cracks in the tongue. In fact, everything is not so difficult. The treatment method depends on the cause of glossalgia.
- First, it is necessary to eliminate the dental causes of tongue cracks - correct an incorrect bite, replace defective fillings, and adjust the prosthesis. Next, the patient should be carefully examined by a therapist, neurologist, and, if necessary, by an endocrinologist and gastroenterologist. And only after this should treatment for glossalgia be prescribed.
- Typically, treatment for fissures consists of drug therapy and physiotherapeutic procedures. Treatment with medications is to improve blood circulation in the tissues of the oral cavity, as well as to improve general cerebral circulation. For this purpose, drugs such as trental, cavinton, nicotinic acid, and vitamin C are prescribed.
- The tone of the autonomic nervous system should also be improved; for this purpose, sedatives are prescribed - tincture of valerian, motherwort, persen.
- Additionally, the doctor may prescribe procedures such as hirudotherapy or electrical neurostimulation using a TENS device. A good effect is achieved by using electrophoresis, as well as iontophoresis of novocaine.
- If the tongue is severely painful, the doctor may prescribe local painkillers - lidocaine, dicaine.
- If the patient has cracks in the tongue, plaque and burning, it is necessary to adjust the diet. During treatment, you should completely exclude from the diet foods that irritate the surface of the tongue - such as sour juices, vegetables, pickles and marinades. You should not consume large amounts of spices, especially pepper and salt. It is advisable to quit smoking.
- After each meal, be sure to brush your teeth and rinse your mouth with salted water or a decoction of medicinal herbs. Oak bark, sage, propolis, and honey have a healing effect.
Nervous system diseases
With disorders of the nervous system, unpleasant painful sensations occur, tingling in the tongue, a disturbing feeling of dry mucous membranes, hyperesthesia, burning, disturbances of taste, diction, swelling and the appearance of bacterial plaque. This disease is called stomalgia, most often it affects women during menopause or after suffering shocks. Symptoms of the disease decrease with eating, especially when eating spicy foods. Unpleasant sensations are localized on the tip and sides of the swollen tongue, its edges are wavy, and dents from the teeth are visible.
The main causes of pathology are recently experienced tragic events in life: the death of relatives, cancer of loved ones, personal problems. Patients are easily excitable, constantly look at their tongue in the mirror, and are pathologically afraid of developing cancer.
Treatment of stomalgia is carried out comprehensively. It includes medication, psychotherapy, physiotherapy, acupuncture, and oral sanitation.
Uneven, wavy edges of the tongue may indicate the development of a serious illness. Therefore, if such a symptom appears, you should consult a dentist and therapist. Timely treatment will help avoid the development of severe complications.