Tooth extraction is carried out plannedly, as well as for emergency indications.
The main indications for planned tooth extraction: complete or severe destruction of the tooth crown and the inability to use it for prosthetics, chronic periodontitis that is not amenable to conservative treatment, grade III tooth mobility in periodontal diseases, and others.
Urgent tooth extraction is indicated for purulent periodontitis, acute osteomyelitis, periostitis, sinusitis, lymphadenitis (if the source is a diseased tooth), fracture of the tooth crown exposing the pulp and some other diseases and conditions.
Removing various teeth has some of its own characteristics, for example, removing teeth with a crown is somewhat simpler than removing tooth roots. The extraction technique for the teeth of the upper and lower jaws, incisors and molars is also slightly different.
Indications and contraindications for molar tooth extraction
Reasons for removing a molar tooth may be:
- purulent periostitis;
- abscess;
- phlegmon;
- large tumor in the tooth area;
- purulent periodontal disease;
- the presence of a cyst in the area of the diseased tooth;
- exposed pulp;
- longitudinal tooth fracture;
- critical tooth decay;
- critical tooth curvature;
- disease of the dental bone tissue;
- sinusitis.
The following reasons are contraindications to the removal of molars:
- acute heart diseases;
- acute viral diseases;
- flu;
- angina;
- renal failure;
- pancreatitis;
- hepatitis;
- acute diseases of the nervous system;
- oncological diseases
- initial and final stages of pregnancy;
- stomatitis;
- gingivitis
- general degeneration of the body;
- alcohol poisoning.
Alternatives
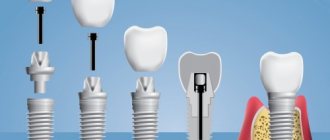
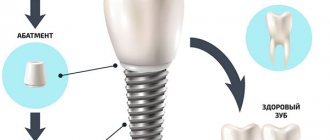
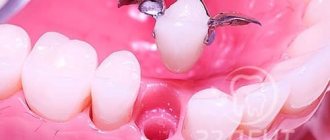
An alternative method for restoring sixes is a bridge prosthesis. This is a structure consisting of crowns tightly connected to each other. To restore one tooth, the bridge consists of 3 crowns. The two outer ones are fixed on the teeth on both sides of the defect. The supporting teeth are ground down to form the internal cavity of the outer crowns of the prosthesis. The middle crown is hinged and imitates the lost six.
This option is cheaper than implantation, but has disadvantages - grinding the enamel of living teeth leads to a reduction in their service life. Another important point is that the bone under the hinged crown does not receive stress during chewing, so bone tissue atrophy is inevitable.
Molar removal technology
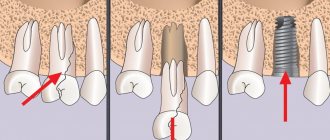
Before proceeding with the removal of a molar, the doctor must make sure that there is no curvature of the roots. For this, an x-ray is taken. If the roots are not bent, the patient is given an anesthetic injection. After 10 minutes, the tooth can be removed.
First, the dentist carefully separates the gum from the body of the tooth. Then he grabs the tooth with pliers and begins to swing it and rotate it at the same time. After several such manipulations, the doctor pulls the tooth out of the alveoli.
In this sequence, both the upper and lower root teeth are removed. However, it is somewhat more difficult to grasp the upper molars with forceps.
Sometimes, when removing a molar, the doctor must first cut it into two or three parts and then pull out each part separately. This usually happens when the roots are bent.
In case of severe curvature of the roots, when they intertwine with the roots of neighboring teeth, removal must be done in fragments and under general anesthesia. In this case, the doctor completely exposes the gum around the diseased tooth.
If there is a cyst in the area of a diseased molar, the doctor is required to be highly qualified. This removal is done under both local and general anesthesia.
Two days after the removal of a molar, the patient must visit the dentist again to take an x-ray. This is necessary to ensure that all tooth roots have been removed.
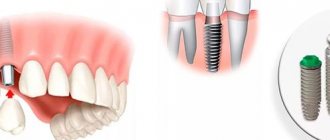
Is it worth getting an implant?
The absence of the sixth tooth threatens:
- displacement of neighboring units;
- advancement of antagonists on the opposite jaw.
Neighboring and antagonist teeth will slowly shift, which threatens to expose the roots, the appearance of wedge-shaped defects at the gum itself, exposure of the neck, which is sensitive to changes in temperature of water and food, and pain. In addition, there will be a change in the bite, since the teeth will be out of place. Therefore, it is necessary to place an implant to maintain healthy teeth and correct bite.
Is it painful to remove molars?
Today, only older people remember the terrible pain during the removal of molars. Nowadays, the quality of painkillers is so high that the patient does not feel pain at all, even with difficult removal. At the same time, after the anesthesia wears off, pain, of course, occurs, but it is quite tolerable and depends on how much the gum under the tooth was disturbed.
If the pain is still severe, then the dentist recommends taking a painkiller tablet. The same analgin successfully dulls pain for a long time.
In rare cases, the patient may experience throbbing and increasing pain. This annoying phenomenon occurs due to inflammation of the socket. If measures are not taken quickly, the tissue begins to fester in the hole. This process can be suppressed with drug treatment, but sometimes you have to open the gum and clean the hole from pus.
Price
Our Center has a case payment system, which means that the case includes all materials and necessary manipulations.
The cost of implant installation includes:
- implant and superstructures;
- work of an implantologist;
- anesthesia;
- basic bone building complex;
- primary and repeat CT.
The price of implants varies depending on the type of bone. Nobel Biocare PMC (cheaper) is intended for weak tissue, and Nobel Biocare Conical Parallel CC (more expensive) is intended for dense tissue.
The cost of the crown includes:
- production of a prosthesis by a technician;
- taking impressions;
- installation of a crown.
Tooth extraction (for simultaneous implantation), bone grafting or sinus lifting are paid separately. Prices for services can be found here.
Removal of molars during pregnancy
Let us say right away that any surgical intervention during pregnancy is extremely undesirable. If a molar tooth hurts at this time, then ideally it would be best to simply heal it. Unfortunately, sometimes this is no longer possible and the diseased tooth has to be removed.
It is highly undesirable to remove molars in the first and last months of pregnancy. It is at this time that the fetus is most vulnerable.
If it is possible to postpone the removal of a molar until the birth of the child, then this is exactly what should be done.
Under no circumstances should you hide your pregnancy from your dentist. On the contrary, this should be said immediately. In this case, the doctor will select a harmless anesthetic that will not cross the placental barrier.
If a pregnant woman is facing a complex molar tooth extraction, then this should only be done in a hospital setting. After removal, the patient should be under medical supervision for at least two to three days. This is due to the fact that very often, after the removal of a molar, pregnant women experience a sharp increase in body temperature, and this is extremely harmful for the fetus.
What is the difference between implantation on the upper and lower jaw?
Features of the operation from below
Implantation of the 6th tooth from below is performed using a two-stage method with delayed loading. The implant is implanted using the patchwork method. The crown is installed on the abutment after the artificial root has healed (after 2-4 months). Features of implantation are associated with the anatomical structure of the mandibular structures:
- high jaw bone density - the implant takes root faster, its good primary stability is achieved;
- bone tissue is stronger, therefore it decreases more slowly than in the upper jaw;
- the volume of the mandibular bone is anatomically higher - there are more opportunities to replace the lower tooth without tissue expansion;
- absence of sinuses - there is no risk of injuring the membrane of the maxillary sinus during implantation.
But the trigeminal nerve passes through the base of the lower jaw; if the bone atrophies, it can be damaged (if the technology of the implantation protocol is violated).
Installation of the implant from above
Implantation of the first molars of the upper jaw also has features associated with the anatomy of the jaw structures. The upper teeth are located close to the sinuses (maxillary sinuses), damage to which is accompanied by serious consequences. The maxillary bone is looser and thinner, so it decreases very quickly, and implants take 1-2 months longer to take root than in the lower jaw.
- The choice of method for implanting first molars is a two-stage protocol with a break for osseointegration of the titanium root. The average healing time for upper jaw implants is 4.5 months.
- Since the classical protocol requires sufficient volume and good quality of bone tissue, treatment is often complemented by osteoplastic surgery (sinus lift).
- When making prosthetics, the increased mesiodistal space and the distribution of occlusal forces are taken into account.
Molar tooth extraction in children
Unfortunately, young children often develop diseases in both their primary and permanent molars. Worse, it is not always possible to heal them. Dentists remove permanent teeth for children only when there is no way to save them.
Primary molars are both treated and removed. If a permanent tooth begins to grow under a baby molar, then the baby tooth is always removed, since it interferes with the normal formation of the permanent tooth.
At the same time, dentists never agree to premature removal of baby molars. Such teeth are sure to heal. If you remove a baby tooth ahead of schedule, then the baby will develop a crooked bite.
There are situations when a child’s molar tooth must be removed. Such situations include:
- molar root cyst;
- presence of granuloma;
- inflammation of the tooth root;
- inflammation of the nerve of the lower jaw;
- severe destruction of the integrity of the tooth.
Advantages of contacting ROOTT
Tooth extraction is a serious surgical procedure; we advise you to entrust this to the professional doctors of the ROOTT clinic.
An anamnesis will be collected: complaints, an x-ray to specify the topography of the element, root system, and degree of damage. The type of anesthesia is specified, whether there are any allergic reactions, what medications are taken (may affect blood clotting). At the appointed time, you will need to try to relax (we understand, this is difficult, but necessary), we will then act.
Vast experience, qualified doctors, innovative equipment, sterile rooms, instruments. Modern pain management and constant monitoring both during and after surgery guarantee a favorable outcome of the operation.
Our dentists always take an individual approach to each patient and their problem; removal occurs as gently and quickly as possible. Afterwards they will give recommendations or select treatment for speedy rehabilitation.
Is it possible to remove a molar tooth yourself?
Trying to remove a molar tooth yourself is extremely dangerous. The only exception is very severe tooth looseness. It should be borne in mind that complete removal even in this situation will not work. You will simply break off the body of the tooth from the root, and nothing more. In any case, after such an independent removal, you need to visit a dentist, who will determine what should be done next. Sometimes an artificial tooth is installed at the root, and it can last for more than one year. If the root has defects, then it has to be removed.
There are situations when you have to remove a child’s very loose baby tooth at home. In this case, you should thoroughly brush the baby’s teeth and disinfect the oral cavity. Then you should wrap your fingers in sterile gauze, loosen the tooth thoroughly, and only then try to pull it out. If this was not possible on the second attempt, then the child must be taken to the dental clinic in any case.
If you have successfully removed the tooth from the socket, then you must firmly place a gauze swab in the socket and leave it there for 30 - 40 minutes. In the next two hours, the child should not be allowed to eat or drink.
Even if the removal was successful, the baby still needs to be shown to the dentist. This is the only way to protect your child from possible complications.
When is surgery indicated?
Indications can be called urgent and planned. The difference between them is that with an urgent operation, the clinical picture in the oral cavity and the general condition of the patient does not require delay. Delay may result in complications not only in the maxillofacial area, but the patient’s general condition may worsen.
Urgent indications include:
- A situation where dental tissues are severely destroyed and do not provide any functional benefit, but only aggravate purulent inflammatory processes in the oral cavity and soft tissues of the face. Usually these processes come from this jaw structure, due to the constant accumulation of pathogenic microflora there. Untimely treatment can cause the following purulent-inflammatory processes: periodontitis, periostitis, sinusitis, phlegmon or abscess.
- Diagnosed osteomyelitis in the projection of a destroyed, diseased dental unit.
- Longitudinal dental fracture.
- Transverse fracture of the dental crown with opening of the pulp chamber, but due to curvature or resorption of the roots, the tooth cannot be treated endodontically.
What to do if the bleeding does not stop
Immediately after removing a molar, the surgeon places a tampon on the socket to stop capillary bleeding. The patient needs to clench his jaw and not remove the tampon for 20 minutes. During this time, the blood coagulates and a clot forms in the hole, protecting the fresh wound from the penetration of bacteria into it.
If the patient has high blood pressure or poor blood clotting, the tampon should be kept in place for 40-60 minutes.
When a person strictly adheres to medical recommendations, but the bleeding does not stop, he should contact a dentist for help.