Cheilitis is an inflammation of the red border, mucous membrane and skin of the lips. In common parlance, the disease is called jamming. The inflammatory process can be long-lasting and periodically worsen. In healthy young people it often goes away on its own, but in children, the elderly and people with chronic diseases it should be treated with medication. Elderly people have a high risk of leukoplakia and malignancy of the process.
Cheilitis is treated by a dentist, and if necessary, a therapist, pediatrician and other specialized specialists - an endocrinologist, an infectious disease specialist, etc. - are involved in drawing up a treatment plan.
Causes of cheilitis
Cheilitis can be an independent disease and a manifestation of other pathologies of the mucous membranes and internal organs. The most common causes of the disease include:
- Dermatoses. The mucous membranes and skin of the lips can be involved in the pathological process in lichen planus, psoriasis, erythematoses and other skin diseases.
- Unfavorable factors. Exposure to hot and cold air, wind, and excessive exposure to UV rays are especially common causes of cheilitis in people who work outdoors and under special weather conditions.
- Allergic reactions. Allergies can be triggered by chemical factors, ultraviolet rays, cosmetics, etc.;
- Other diseases. Secondary cheilitis often develops against the background of atopic dermatitis, eczema, neuritis of the facial nerve, etc.
Natural protective mechanisms are weakened by such factors as hypothermia, previous surgical interventions, long-term antibacterial therapy, hypovitaminosis, etc.
Ask a Question
Symptoms and types of disease
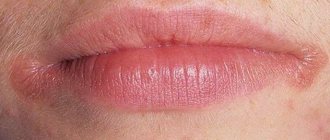
Cheilitis on the lips can manifest itself in different ways depending on the form of the disease. Thus, the exfoliative type of inflammation appears more often in women; its main symptom is peeling. The disease is based on neurological and endocrine disorders. Peeling occurs on the red border of the lips and does not affect the skin and mucous membranes. The disease rarely spreads to the entire red border, so part of it remains unchanged.
With severe dry skin, peeling is accompanied by symptoms such as:
- feeling of dry lips;
- burning;
- formation of easily detachable scales.
The disease is long-term and sluggish, with periods of exacerbation occurring from time to time. It rarely goes away on its own. With the exudative form, pain, swelling of the lips, and the formation of large crusts may occur.
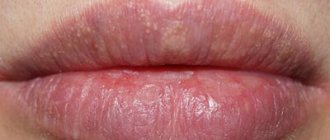
Glandular cheilitis develops against the background of the proliferation of minor salivary glands and their subsequent infection. With congenital pathologies, signs of such inflammation of the lips are present in almost all cases. Acquired overgrowth may be associated with chronic diseases of the periodontal tissues, tartar, multiple caries - diseases leading to infection of the dilated ducts. Lesions of the lower lip with this form of cheilitis are more common. The disease develops with the appearance of dry lips, which is initially easy to correct with the help of cosmetics. Subsequently, cracks begin to form, deepen and begin to bleed. The condition is aggravated by the constant desire to lick dry lips - cracks and ulcers can become weeping and become permanent due to the inelasticity of the skin of the lips.
Contact allergic cheilitis develops after exposure to an allergen - an irritant. The most common of them are components of lipsticks and other care products. Allergies can also be associated with bad habits, for example, constantly keeping pencils, pens and other foreign objects in the mouth. Musicians may develop occupational cheilitis due to constant contact of the mouthpieces of wind instruments with their lips. The main symptoms of the disease include:
- severe itching;
- burning;
- swelling of the lips;
- redness of the skin and mucous membranes.
Manifestations intensify upon contact with the allergen. Bubbles of different sizes may form; their spontaneous or accidental opening leads to the formation of ulcers and cracks. Chronic forms of allergic disease are accompanied by peeling, slight itching and the absence of other signs of inflammation.
Actinic cheilitis belongs to the category of diseases that are based on increased sensitivity to weather and other external factors. Usually occurs in response to sun exposure. Exudative forms of this disease are accompanied by the formation of crusts. Sometimes small blisters form, the opening of which leads to painful erosions. In the absence of exudate, the main symptoms are pain, dryness, and burning of the lips. Actinic cheilitis often degenerates into precancerous diseases.
In atopic cheilitis, the main cause of the disease is dermatitis of the same name, or neurodermatitis. It appears in people with an allergic predisposition, and the triggering factor can be medications, cosmetics, food products, as well as microorganisms and their waste products. The disease is accompanied by redness of the lips, itching and peeling of the red border, and damage to the corners of the mouth. After acute symptoms subside, peeling and thickening of the skin may occur. Dryness stimulates the formation of cracks.
Macrocheilitis is part of the Rossolimo–Melkersson–Rosenthal syndrome. Appears against the background of neuritis of the facial nerve and the symptom of a folded tongue. Develops due to infectious-allergic effects against the background of genetic predisposition. Manifests itself with the following symptoms:
- lip enlargement;
- severe itching;
- swelling of other parts of the face;
- bluish-pink color of swollen areas of the lips.
One or both lips, cheeks, and upper parts of the face may be affected. Neuritis leads to facial asymmetry, and the nasolabial fold is smoothed out.
Hypovitaminous cheilitis of the lips develops against the background of a deficiency of B vitamins. Burning and dryness of the oral mucosa and lips appear. The mucous membranes become swollen and red, peeling occurs on the red border, and cracks appear. They are prone to bleeding, which is also associated with a lack of vitamins. The tongue may become enlarged and can easily become imprinted with teeth.
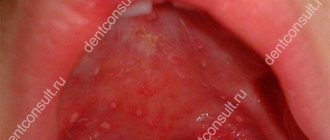
With candidal cheilitis, the inflammatory process is accompanied by the formation of white plaque on the mucous membranes. The cause of this disease is the proliferation of a fungus of the genus Candida; it often affects infants, people after radiation and chemotherapy, as well as patients with immunodeficiencies. Cheilitis develops with long-term use of antibiotics and immunosuppressants.
When should parents take their child to the doctor for seizures?
There are clear criteria by which atopic dermatitis can be suspected. First of all, the child should be bothered by itching and flaking of the skin over the past 12 months, plus at least 3 signs from the list below:
- age - signs of atopy usually appear before the age of 2 years, a little less often - up to 4 years and in adolescence;
- noticeable redness of the skin in its folds - for example, on the inside of the elbows, outside of the knees, on the cheeks or the front of the legs;
- constant irritation - itching, peeling - in the areas indicated above;
- constant dry skin;
- the child has close relatives with asthma - these could be parents, brothers or sisters.
If you have counted all the signs in your child, then he probably has atopic dermatitis. To confirm the diagnosis, you need to contact your local pediatrician. Usually, examination of the child’s skin is sufficient, but the doctor may also prescribe additional examinations.
These are usually allergy tests to check if there is something triggering the flare-up. To do this, they perform a prick test - in which a tiny amount of allergen is applied pointwise to the skin and the reaction is monitored. The appearance of redness and irritation is a signal that there is an allergy to the substance.
Diagnostic features
If inflammation appears on the lip, it is advisable to visit a therapist, for children a pediatrician, if indicated, an infectious disease specialist, a dentist, or other specialized specialists. Diagnosing cheilitis is usually not difficult - a specialist will conduct an examination, listen to complaints and prescribe a series of tests. If the allergic nature of the disease is suspected, allergy tests may be recommended, and if plaque appears, it is advisable to take a scraping. To detect endocrine and other disorders that may cause the disease, biochemical blood tests and other diagnostic methods are often prescribed. In rare cases, a biopsy is required to differentiate cheilitis from other pathologies. This will help to exclude the malignant or precancerous nature of inflammatory formations and prescribe the correct treatment.
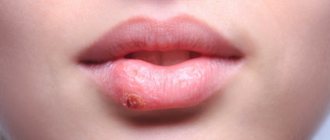
Angulitis: clinical manifestations
The symptoms of angulitis are very similar to the manifestations of herpes, so it is extremely important to promptly contact a specialist who will make the correct diagnosis and tell you how to quickly cure angulitis.
Symptoms of seizure:
- redness in the corners of the mouth;
- cracks;
- multiple blisters with purulent contents;
- slight bleeding (not always);
- purulent crusts.
Treatment of lip jams in adults depends on the etiology and form (acute or chronic). It is very important to start treatment on time, because without it, the affected area can increase, causing significant discomfort to the patient.
Treatment methods
The treatment plan for cheilitis is developed individually, depending on the form of the disease, the severity of symptoms, and the characteristics of the health condition. Thus, in the treatment of the exfoliative form of the disease, the key element of effective treatment is the impact on the psycho-emotional sphere: you will need to contact a neurologist or psychoneurologist to prescribe sedatives and antidepressants according to indications. Consultation with an endocrinologist may be required.
Local treatment may involve the use of laser or ultrasound physiotherapy, local anti-inflammatory drugs, and less commonly, radiation therapy. Elimination of excessive dryness is possible with the help of hygienic lipsticks. To speed up recovery, the doctor may prescribe vitamin therapy, UVOC and other methods of maintaining the body's defenses.
Therapy for glandular cheilitis consists of using local anti-inflammatory agents. Antibacterial, antiviral, and hormonal ointments can be used. A radical method of therapy is electrocoagulation of the salivary glands or their surgical removal, as well as laser ablation. These methods are used when conservative methods are ineffective. After the main course, the doctor will prescribe medications to prevent relapses - they will eliminate dry or weeping skin. It is important to sanitize the oral cavity in a timely manner and undergo professional teeth cleaning.
Treatment of atopic cheilitis consists of eliminating irritating factors. Drugs with antipruritic and anti-inflammatory effects can be used locally, and therapy with antihistamines with a systemic effect is also carried out. The use of glucocorticosteroids allows you to get quick relief, but it is important to strictly adhere to medical prescriptions - they can only be used for a short time. It is important to follow a hypoallergenic diet and remove allergenic foods from the diet.
Therapy for meteorological cheilitis begins with limiting harmful effects, for example, insolation. Local treatment is usually carried out - the doctor prescribes hormonal agents and protective creams, including those with SPF. The course of treatment is supplemented with vitamins - vitamin-mineral complexes or individual preparations (B, PP, C, etc.).
In the treatment of macrocheilitis, immunocorrective and antiviral therapy is of particular importance. The doctor may prescribe:
- hormonal anti-inflammatory drugs of systemic action;
- novocaine blockades;
- antihistamines, etc.
Laser therapy can have a positive effect on the correction of the entire triad of symptoms. Other physical therapy methods have been successful in treating facial neuritis.
How to care for children's skin with jams?
Regardless of the cause of the appearance of seizing, skin care is based on the same principles.
Avoid flare-up triggers.
Try to protect your child from anything that could cause seizures. These could be certain products, hygiene products or decorative cosmetics.
Wash your baby in warm (not hot) water for no longer than 10 minutes.
Hot water evaporates moisture from the skin and makes it dry and defenseless. Therefore, dermatologists advise children and adults to wash themselves in warm water for no longer than 5-10 minutes to protect the skin’s protective barrier from drying out.
Opt for gentle cleansers.
Pay attention to drugstore brands for baby skin care and the labels “for sensitive/atopic skin.” These products usually do not contain harsh cleansers and do not cause irritation or redness.
Moisturize your baby's skin regularly.
Caring for any skin is based on hydration, and if it is dry and prone to inflammation, then this stage should not be skipped under any circumstances. Apply moisturizer to your baby's skin after each wash, and cover your hands and lips several times a day to prevent dryness.
To prevent seizures and relieve discomfort when they occur, smear your child’s lips with Morozko® hygiene lipstick - it was developed specifically for children’s skin.
It protects the skin from the elements and prevents dryness, cracking and seizing. The lipstick contains a complex of healing oils, vitamins A and E, as well as chamomile extract. Together they soften and restore dry lips. Apply lipstick to children's lips before and during a walk.
Possible complications
Failure to see a doctor in a timely manner often causes serious complications. The disease itself often does not pose a serious health risk. But only an experienced specialist can tell you how to treat cheilitis. Self-medication can lead to unpleasant consequences and provoke the occurrence of a chronic form of the disease. In addition, cheilitis is dangerous because its symptoms can mask malignant tumor processes. It is important to remember that some forms are prone to malignancy - cheilitis may be followed by precancerous conditions.
Prognosis and prevention
With timely treatment and the absence of malignancy processes, the prognosis is almost always favorable. If the therapy has caused noticeable cosmetic defects, you can resort to methods for correcting the appearance of the lips.
To prevent complications, it is important to understand whether you are at risk. The presence of allergic diseases and dermatoses, chronic endocrine diseases, and wearing dentures increase the risk of developing pathology. To prevent the appearance of cheilitis, it is important to adhere to several rules:
- regularly visit the dentist, sanitize the oral cavity, remove tartar;
- promptly replace outdated fillings and orthopedic structures, contact after chipped teeth and injuries to prevent lip injury from the sharp edges of fillings and enamel;
- For the manufacture of prostheses, contact only professionals;
- eat properly and nutritiously to prevent hypovitaminosis;
- try to avoid prolonged exposure to the sun and use products with SPF, including for lips;
- be attentive to your health and promptly treat diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, endocrine, nervous system, and internal organs.