Home page » Phraseologisms » The meaning and origin of the phraseological unit “Pip on your tongue”
Author: Maria Znobishcheva
Philologist, candidate of philological sciences, poet, member of the Union of Writers of Russia. Date of publication: 07/12/2019
The Russian language has always been great and powerful. If in Rus' they wanted to wish someone good or bad, they didn’t go to great lengths for words. Many figurative expressions were born from such wishes.
What did they mean when they said “Tip your tongue!” , and what does this phrase mean now? It's time to figure it out.
The meaning of phraseology
This phraseological unit is used when they are afraid that a frightening or unpleasant thought expressed by someone will come true.
Nowadays, of course, no one wants something to actually jump out of the speaker’s tongue, but in the not-too-distant past the expression had a very direct and specific meaning: “Let a sore appear in your mouth so that you don’t talk all sorts of things.” nonsense!
In what cases is it appropriate to use an idiom? Well, for example, when a neighbor makes unfavorable predictions about the future of your children: “Your children are so tame. Never mind, in ten years you’ll be running around looking for them all over the city.”
Or when an envious competitor predicts the collapse of a well-started business. Both the predictors want to say: “Tip your tongue! Keep quiet, don’t croak, otherwise it will really come true.”
Causes of pipuna in humans and its symptoms
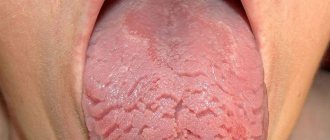
But in fact, tipun, or glossitis, are ulcers on the human tongue that appear due to poor oral hygiene. The main reason for the development of glossitis is the proliferation of bacteria that enter the mouth with dirty hands. In addition to poor hygiene, the reasons for the development of glossitis can be microtrauma of the tongue (cut, burn, injection), the presence of serious diseases (tuberculosis, stomatitis, candidiasis), lack of vitamins, and weakened immunity.
Symptoms of glossitis include burning pain and numbness of the tongue, and swallowing and chewing may be painful. There is a whitish coating on the tongue. If the disease is superficial, then taste buds are disrupted, talking becomes difficult and painful, and increased salivation appears. With a complicated course of the disease, the inflammatory process moves to the throat, it becomes painful to swallow, eat, chew, and talk.
It is necessary to treat pipun. If you do not take this problem seriously, the disease can develop into a chronic form, which is much more difficult to treat.
Origin of phraseology
Linguists have several assumptions about where the word “tipun” came from in our language. In the etymological dictionary of M. Vasmer we find a hypothesis according to which “pip” comes from the German “pips” (“disease”).
F. Milosic suggests that the common Slavic designation for a bump, a bulge (“pip”, “pipot”) is taken as a basis. In V. Dahl’s dictionary the verb “tip” is recorded - that is, “peck”, “pinch”. It is derived from the name of the hard part of a bird's tongue, with the help of which chickens and the like grind up swallowed grains.
A pip is an overgrown seal that can be regarded as a disease of poultry.
From the second half of the 16th century, purulent ulcers on the tongue began to be called pipunami. The reason for their appearance was considered to be foul language and any other verbal intemperance or impurity.
If a person gossips, slander, slander, wishes harm to others, lies and distorts other people’s statements, he cannot avoid sores in the mouth. Our ancestors firmly believed in this.
The wish for a tap on the tongue is of an abusive nature and comes from a pagan ritual of scaring away evil spirits. However, the idea of the material embodiment of everything bad and retribution for it was also reflected in the folk-Orthodox picture of the world.
From the point of view of ordinary people, bad lips and unclean tongue fully deserved momentary punishment “here and now.” So that it would be discouraging.
Nowadays, it is customary to interpret phenomena from a material point of view. The appearance of pips, medically called glossitis, is associated with poor oral care.
The cause of inflammation and suppuration can be dirty hands, unwashed fruits and vegetables, sunflower seeds, as well as mechanical damage to the palate, lips, tongue, gums, and mucous membranes.
Sometimes glossitis gives a person a signal about the presence of serious diseases in the body, so when pips appear, it is better to run not to a fortune teller, but to a doctor.
The seal on the tongue should be healed in a timely manner to prevent the infection from spreading and becoming chronic.
A clean mouth is the key to health. But it’s probably worth taking care of the cleanliness of your lips: spiritual health depends on it.
What is this - pip?
A pip is a hardening on the tip of a bird's tongue that helps it peck at grains. Its growth is a disease.
Hard pimples, ulcers on the human tongue, are also called pimples, by analogy with bird growths.
According to superstitious beliefs, tipuns appear in deceivers and liars or those who verbally offended an innocent person.
Synonyms
When we want to ask someone not to predict failure in advance, we can use one of the following expressions:
- don't croak;
- so that your tongue dries up (dries to the roof of your mouth);
- don’t worry, Emelya;
- shut up the fountain;
- stop talking nonsense.
Foreigners stop people who speak intemperately like this:
- bite your tongue (English) - bite your tongue;
- Halt Maul (German) – stop your face.
Rough, but very intelligible. Nobody wants to hear bad things addressed to them. Well, this just means that people have not stopped believing in the power of words.
Sometimes it’s better to keep your mouth shut than to feel the pain in your mouth of a pip that someone sent onto our tongue in indignation.
Types of glossitis
In order to get rid of pipun in a timely manner, the form of the disease should be determined. It is customary to distinguish 9 types of inflammation of the tongue:
- Candida. It occurs more often than other forms. It is formed against the background of a violation of the local immunity of the oral cavity due to infection with candida fungi.
- Diamond-shaped. A pathological focus resembling a tubercle, square or diamond is found in the middle of the tongue. Infection of the mucous membrane of the tongue occurs through microcracks. There are lumpy, smooth and papillomatous forms.
- Catarrhal. Characterized by swelling and hyperemia. Qatar takes over the entire tongue, causing an increase in its volume.
- Exfoliative. It is distinguished by structural and color changes in the area of the tip of the tongue and the back. The defeat resembles a geographical map. Glossitis develops against the background of blood disease and endocrine pathologies.
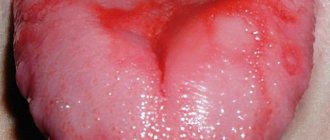
- Ulcerative. Develops due to dental problems. Small ulcers may appear on the mucous membrane, which quickly disappear after the cause is eliminated.
- Villous. This type of tip resembles hair on the tongue. These are overgrown filiform papillae of a dark brown color. It occurs mainly in men due to bad habits.
- Folded. Refers to an anomaly of language development. But with this form, the soft organ is susceptible to infection due to food debris and plaque in the folds.
- Phlegmonous. Distributed in the deep tissues of the tongue. It requires constant attention from a doctor, since over a long period of time the pipun can become malignant.
- Atrophic. The surface of the tongue becomes smooth and unnaturally red. Characterized by bad breath and grouped painful ulcers. The origin of glossitis is not completely known. A multifactorial ethological theory is proposed.
Candidal glossitis
Other phraseological units
hit or miss
All or nothing. Willingness to achieve what you want even at the cost of complete defeat.
Crocodile tears
Insincere expression of grief, regret, false suffering.
Pandora's Box
An object or phenomenon that contains a threat and can lead to irreversible consequences.
Sewn with white threads
The motives for action are obvious, and the goals lie on the surface.
All phraseological units
A book from the authors of this article!
Collection: “100 popular phraseological units of the Russian language”
More details
How to cure a pip on the tongue
The therapeutic course is determined by a dentist, therapist, and sometimes an endocrinologist, as with a gastroenterologist. Initially, the cause of the pip is identified and eliminated.
How to remove a pip on the tongue quickly and without consequences? If glossitis has formed due to dental problems, then the oral cavity is sanitized. In the presence of concomitant diseases, a general therapeutic course of treatment using antibacterial and antiviral drugs is required. Symptomatic effects are indicated in the oral cavity.
General principles of therapy
In medical practice, it is customary to treat pipun with the following methods:
- conservative;
- surgical;
- folk.
Conservative treatment of pipuna involves the use of certified medications both locally and in the form of tablets for oral or intramuscular injection.
Radical surgical treatment is rarely used. This treatment is indicated when the tongue hurts for a long time, and the growth has a pronounced outline. Basically, removal of overgrown papillae or neoplasms occurs by cryodestruction or diathermocoagulation.
Drug treatment depending on the form of glossitis
With timely treatment, the pip is quickly cured and does not occur again. The following drugs are used for therapy:
- Antiseptics. Chlorhexidine, Iodinol, Furacilin and potassium permanganate are mainly used. Suitable as a rinse for all forms of pipun.
- Ointments and gels. Cholisal, Levomikol and Kamistad are prescribed for severe forms of inflammation and to reduce the pain reaction of the tongue. If after examination a viral etiology of the disease is revealed, treatment with oxolinic ointment is recommended.
- Antibiotics. Required in the presence of bacterial flora of inflammation.
- Antifungal drugs. Prescribed in case of pip appears against the background of a fungal infection.
- Retinol acetate. Provides wound healing for folded, catarrhal and atrophic glossitis.
- Sprays. Lugol, Tantum Verde, Hexasprey are prescribed for local treatment of the tongue in the presence of a bacterial infection.
- Immunoglobulin and Viferon. It is an immunomodulator that is necessary for all forms of glossitis in case of severe chronic course. In addition, if pip has formed, it is necessary to take vitamin-mineral complexes, change the diet in favor of gentle food and at least temporarily give up bad habits.
How to treat pip at home
Folk remedies are always used to treat dental diseases. Today, official medicine uses natural ingredients as additional substances to eliminate oral pathology. Tipun on the tongue at home is affected by such means as:
- oil solutions of rose hips, peach and sea buckthorn as compresses;
- decoctions of chamomile, St. John's wort, calendula or nettle for rinsing the mouth for non-healing wounds;
- oak bark as an antiseptic and hemostatic agent;
- propolis as an application to the tip area;
- eucalyptus juice, which can be used to anoint wounds to heal and relieve pain;
- a decoction of horseradish leaves for the regeneration of ulcers;
- compress of raw potatoes and sunflower oil;
- rinsing with a baking soda solution to eliminate candidal glossitis;
- a decoction of coltsfoot and raspberry leaves as mouth baths for inflammation and open wounds.
Attention! It is strictly forbidden to cauterize the tipun with chemicals or using high temperature. Such exposure will cause extensive damage to the mucous membrane of the tongue and aggravate the presence of the underlying disease.
The use of phraseological units in fiction
The phraseological unit “Tip your tongue” was widely used in literature, for example:
- from Nekrasov N.A. in “Green Noise”: “She said it herself, stupid, Tip on her tongue!”;
- Vyazemsky P.A. in the work “Station”: “He should have hit his tongue!”
In Dahl V.’s Dictionary of the Living Great Russian Language there is the word “otipunet”, which means to get a pip or sore in the mouth.
There is such an interesting book called “Dictionary of the plays of Ostrovsky A. N.”, which provides an explanation of the expression “pip-mongrel” - this is a disparaging expression in relation to a capricious person for whom everything is wrong.
Kinds
The International Classification of Diseases defines the following types of glossitis:
- Wandering (desquamatous). The pathogenesis of the pathology is associated with focal destruction of the epithelium, forming red areas of a pronounced red color on the surface of the tongue and its sides.
- Atrophic. A characteristic feature is a reduction in the size of the tongue. The etiology of this form of the disease is associated with infection of the body of any etiology, as well as the development of oncology of the organ and its injury.
- Diamond-shaped. As it develops in the central part of the tongue, the papillae atrophy and visually form a small lesion. It has three forms: flat, tubercular, hyperplastic.
- Black tongue (villous tip). It manifests itself as the growth of papillae in the form of threads over the surface of the tongue, followed by their keratinization.
- Folded. These are congenital deviations from the norm in the structure of language. It is characterized by the presence of folds on the back of the muscular organ, of which the deepest is located longitudinally in the center.
- Gunterovsky. Refers to the consequences of pernicious anemia. A distinctive feature of this form of pathology is the complete absence of ulcers and pimples on the surface of the tongue. Its surface is smooth, shiny and has a rich crimson color.
Forms of manifestation and localization
In medical practice, glossitis is classified taking into account the etiology and clinical course of the disease. Depending on the type of pathology, the focus of inflammation in the form of a tip is located in different parts of the tongue (root, tip, etc.).
In primary localization, taste buds and tubercles are affected. As the tip progresses, it spreads over the entire surface of the tongue and can affect other mucous and soft tissues of the oral cavity.
The table shows the forms and description:
| Form | Description |
| Catarrhal | A characteristic feature is the absence of inflammation in the deep layers of the tongue. It develops against the background of many dental, hematological and gastroenterological pathologies. Catarrhal form can also be provoked by bacterial, viral infections, helminthic infestation and injury to the tongue. It manifests itself as a intense feeling of burning and discomfort. The back of the tongue swells, the color of the organ becomes bright red, salivation increases and taste is dulled, and the mobility of the tongue is limited. White or gray spots may appear. |
| Ulcerative | It develops against the background of complications of the catarrhal form of glossitis or is the result of advanced stages of pathologies of internal organs or the oral cavity. Clinical manifestations are caused by the localization of single or multiple ulcers on the surface of the tongue. Their development is accompanied by pronounced pain, bleeding and severe swelling. There is often a deterioration in general health. |
| Purulent-phlegmous | Defined as the most severe form of pathology. When it develops, it affects: the deep layer of the tongue, tissues of the oral cavity, and nearby lymph nodes. Manifests itself as intoxication, hyperthermia, and severe malaise. Surgery and antibacterial drugs are recommended as effective therapy. |
Catarrhal
Purulent-phlegmonous
Ulcerative
Diagnostics
A dentist can determine the presence of glossitis. At the initial appointment, he determines the presence of pathology and prescribes a comprehensive examination in order to establish an accurate diagnosis and etiology of the disease.
This complex includes:
- At the initial appointment, the doctor determines the presence of pathology and prescribes a comprehensive examination in order to establish an accurate diagnosis and etiology of the disease
Physical examination by the dentist.
- Clinical blood test.
- General urine analysis.
- Blood chemistry.
- Examination of stool for helminths.
- Oral smear for microflora.
- Examination of tissues for the presence of pathogenic microflora in the oral cavity.
- Histological examination of tissues.
- PCR diagnostics.
If indicated, the diagnostic complex can be supplemented by other studies, such as ultrasound of internal organs, fluorography of the lungs, fibrogastroscopy, bacteriological blood test, blood donation for torchinosis and syphilis.
Important! The primary diagnosis of glossitis is carried out by a dentist. An examination by specialized specialists is necessary to differentiate glossitis and prescribe appropriate treatment for the pathology.
Origin of the word "tipun"
Fesmer Max Friedrich (a German linguist of Russian origin) suggested that the name “tipun” came from the name of the disease in German “pips”. Miklosic France (Slovenian and Austrian linguist) compared the word with the Ukrainian "pipot" and the Bulgarian "pipka", which mean "bump".
There is another version of the origin of the word - from the verb “tipat”, which means “to pinch” or “peck”.
Since the 16th century, in the Russian language, sores in the human language, which were considered signs of deceit or slander, began to be called tipunami.
Symptoms
The symptoms of glossitis are directly related to the degree of development of the pathology.
At the initial stage, the presence of pip is accompanied by the following external manifestations:
- In addition to the external manifestations of the pathology, discomfort, burning and pain are felt when eating or talking.
The surface of the tongue is covered with single or numerous pimples.
- The area around the tip is inflamed and red.
- Swelling is observed in the affected area of the muscular organ.
- Salivation increases.
- The surface of the tongue may become covered with a whitish coating.
In addition to the external manifestations of the pathology, discomfort, burning and pain are felt when eating or talking. The patient's sense of taste becomes dull or completely disappears.
The advanced stage of the disease is characterized by the following symptoms:
- Persistent and dense swelling of the tongue.
- Hyperplastic changes in the structure of the organ.
- The presence of mushroom-shaped growths.
- With a viral etiology of the pip, erosion subsequently forms in its place.
- A local increase in temperature is observed.
Important! When the first symptoms appear, treatment should be started immediately. The advanced stage of glossitis is complicated by abscesses, and when the pathology becomes more complicated, phlegmon of the soft tissues of the mouth and neck develops.
Main symptoms
With glossitis, a person may experience the following symptoms:
- Hyperemia and swelling appear.
- A large amount of plaque is formed.
- Itching, burning, pain.
- There is discomfort in the mouth.
- Bubbles and rashes appear.
- There is a repulsive odor from the mouth.
- Tactile and taste functions are impaired.
- Large and small ulcers, cracks, abscesses, and phlegmons appear.
- Salivation is disrupted, the structure of the membranes is modified.
If the pip jumps up due to an exacerbation of systemic pathologies, the person’s body temperature rises - the thermometer can reach 39 °C.