1983
In a healthy person, the color and appearance of the tongue are determined quite accurately - it is pale pink without any coating. However, there are diseases in which the tongue looks different.
One of the most unpleasant, although not health-threatening, diseases has the popular name “black hairy tongue,” which will be discussed.
How dangerous is the disease?
The name black hairy tongue (Lingua nigra pilosa) fully corresponds to how the tongue looks with this disease. Despite the menacing and intimidating name, in fact, the definition of “hairy” or, as they also say, “villous” should not be taken literally.
The medical name of this disease is glossophytia or chronic hyperplasia of filiform papillae with subsequent keratinization.
Black hairy tongue is recognized as a fairly rare disease. Moreover, it can occur at almost any age, both in adult patients and children. It is mainly diagnosed in elderly and middle-aged men.
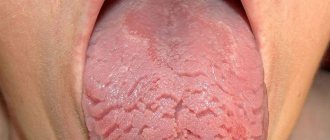
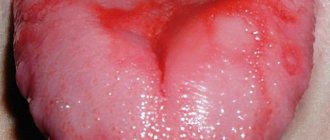
Photo: black hairy tongue
How is it going?
It is characterized by a long course and rather slow development.
Hyperplasia of the papillae of the tongue (an increase in their length and thickness) is usually observed only in one specific area - the posterior and middle thirds of the back of the tongue. The shape of the changed area can be oval or triangular.
In this case, the front and side surfaces usually do not undergo changes and look completely natural.
Due to the lack of desquamation, the filiform papillae located on the mucous membrane of the tongue begin to gradually increase in size. Later they can reach a fairly large size - about 2 cm in length and 2 mm in width.
The black color appears already in the later stages, when the process of keratinization occurs. Then the enlarged papillae, located tightly next to each other, begin at first glance to resemble dense hair, as if combed back, although in fact they are not.
In some cases, in the posterior third of the back, the growth of the papillae may become more pronounced . Cases are described when their length in this area reached almost 3 cm and thickness - 3 mm.
In the initial stages of the disease, the papillae have a normal or whitish tint. At this stage, differential diagnosis is carried out with similar conditions of the tongue that are observed when using medications.
Having reached their maximum length, the papillae become harder, and the process of keratinization begins, due to which such an unusual and unpleasant color appears that worries the patient.
Sometimes the horny masses can take on a different color - brown, dirty gray, yellowish or beige-brown, green, and other shades . This is due to the activity of chromatogenic bacteria.
Read how to treat oral stomatitis in adults in a separate publication.
In the next article we will discuss when it is advisable to prescribe myogymnastics.
Here https://www.vash-dentist.ru/lechenie/yazyik-l/zheltyiy-nalet-prichinyi-poyavleniya-i-sposobyi.html we will talk about the reasons for the appearance and methods of treating yellow plaque on the tongue.
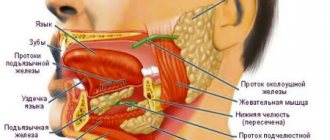
Language structure
To understand what is happening and why the papillae of the tongue hypertrophy, let us consider its structure. It is a muscular organ that is covered with a mucous membrane. The body of the tongue is covered with papillae of four types:
- leaf-shaped, they are located on the lateral surface of the tongue and contain taste buds and glands that produce a secretion resembling viscous saliva;
- grooved, they are located at the root of the tongue, the largest and fewest papillae of the tongue, contain taste buds;
- mushroom-shaped, they are randomly located over the entire surface of the tongue, also containing taste buds;
- thread-like, the most numerous, located on the back of the tongue, their function is to retain food and touch, they do not contain taste buds.
Thus, the anatomy of the tongue lacks hair follicles from which hair grows. Therefore, the name “hairy tongue” is conditional. The overgrown filiform papillae are very reminiscent of hair.
What factors provoke it?
The disease was first described back in 1835. However, its etiology has not yet been clarified, and scientists cannot come to a consensus about the causes of this problem.
At the same time, there are a number of factors that can provoke its development. These factors were determined by collecting and systematizing data from clinical analyzes of patients and anamnesis.
Recently, doctors and researchers increasingly share the same point of view. It lies in the assumption of organ sensitization that occurs under the influence of certain factors.
Sensitization is a sharp increase in tissue sensitivity, which provokes the development of an allergic reaction. In this case, it manifests itself exactly like this - specific tissue swelling with subsequent enlargement and keratinization of the papillae.
There are three groups of predisposing factors : trophic and physicochemical, as well as various general diseases.
- Trophic factors are a disruption of metabolic processes normal for the epithelium of the tongue.
- Physico-chemical factors mean the effects of tobacco, alcohol, medicinal and narcotic substances, and a significant change in the acidity of saliva.
Sometimes even the consumption of certain foods can lead to the appearance of this disease. A similar phenomenon was observed mainly in children.
Some researchers assign an important place among predisposing factors to the development of fungi of the genus Candida, since the majority of patients with hairy black tongue are also diagnosed with candidal stomatitis. However, this may be a consequence rather than a cause of the disease.
The occurrence of the disease in question is also very often associated with various disorders of the gastrointestinal tract and liver dysfunction. A fairly large number of patients had chronic colitis and gastritis.
To summarize, we can identify certain factors that can serve as an impetus for the development of hypoplasia and keratinization of the papillae.
- Poor or lack of oral hygiene.
- Smoking.
- Drug use.
- Taking (long-term) antibiotics and some other medications.
- Too little saliva production.
- Dehydration of the body.
- Radiation to the face and neck, for example during chemotherapy.
- Infectious diseases.
- Disorders of the gastrointestinal tract.
- Metabolic disease.
- Too frequent and active rinsing of the mouth with special liquids (balm-rinses), which can affect the change in acidity.
Symptoms
In many cases, the only symptoms are the external manifestations of the disease. The patients had no complaints of discomfort, pain or discomfort.
In this case, detection of hyperplasia and keratinization of the papillae occurs already in the last stages of the disease.
Some patients experience only psychological discomfort caused by the extremely unpleasant appearance of the tongue. Sometimes there is even a need to undergo a course of psychological rehabilitation.
How this disease manifests itself externally, watch the video:
Most often, patients are also bothered by the constant sensation of a foreign body in the mouth, which is extremely unpleasant. When talking, a gag reflex may occur. Taste sensitivity is also reduced due to an insufficient number of “working” receptors.
Less commonly, patients may complain of burning or itching. However, this is rather a manifestation of a concomitant dental disease – candidal stomatitis. Also, some patients may experience not only a gag reflex and nausea, but also vomiting.
An additional symptom is bad breath, which is caused by poor hygiene - it is caused by food particles that remain between the enlarged papillae.
Macroglossia
“Macroglossia” is an increase in the anatomical size of the tongue. It can also manifest itself in Down disease and cretinism. In this condition, the tongue is enlarged and does not fit in the oral cavity, as a result of which it becomes folded. But when the tongue is removed from the mouth, the folds straighten out. The tongue becomes inactive and speech becomes difficult. Treatment of this disease is mainly local, symptomatic. If macroglossia is a consequence of any other disease, then treatment is carried out primarily by an endocrinologist and therapist.
Diagnostics
It is necessary to distinguish hypoplasia of filiform papillae from diseases where a change in the appearance of the tongue is a symptom - cirrhosis and dysfunction of the liver, Addison's disease, problems in the thyroid gland, myocardial infarction, erosive gastritis, leukoplakia due to HIV infection and some others, as well as from pigmentation caused by the consumption of food pigments.
Treatment
Effective treatment can only be carried out by a specialist after research and diagnosis.
Which doctors should I contact?
The disease is classified as dental, but can be caused by various factors .
That is why, first of all, you should contact a dentist. After examination and initial diagnosis, the intervention of other specialists - a dental surgeon, psychotherapist, infectious disease specialist or gastroenterologist - may also be required, depending on the presence of general problems and diseases.
There is also a need to visit a dental hygienist.
Methods
Treatment of black hairy tongue can be carried out in two different directions - general and local.
General treatment is aimed mainly at eliminating provoking factors , as well as general strengthening of the body and normalization of the patient’s psychological state.
- Treatment of somatic general diseases - gastritis, infections of various kinds, and much more.
- Sanitation of the oral cavity and professional hygiene.
- The use of sedatives (motherwort, valerian, tranquilizers), psychotherapy sessions.
- Multivitamin complexes that also contain microelements.
- Vitamin B5 (calcium pantothenate) is used to normalize metabolism. The course lasts about a month (from 0.3 to 0.6 g daily in three doses).
- Desensitizing agents are prescribed in cases where the disease occurs against the background of general sensitization. They allow you to reduce specific reactions to irritating factors.
- Antifungal therapy in the diagnosis of fungal stomatitis.
If the root of the tongue is enlarged, what does this mean?
In the next review we will talk about further actions after cutting the child’s frenulum.
Follow the link to talk about the reasons for the appearance of a green coating on the tongue.
Local treatment involves eliminating the external manifestations of the disease . Depending on the body’s reactions and various indicators, different techniques can be used.
- The use of keratolytic agents to eliminate keratinization (resoruin, salicylic alcohol).
- Cryodestruction (liquid nitrogen) to remove altered papillae.
- Keratoplasty applications for healing and restoration.
- Daily tongue cleansing.
Sequence
First of all, it is necessary to carry out sanitation of the oral cavity, since this measure is mandatory for any cause of the disease.
Simultaneously with local therapy, general therapy is carried out, which can last much longer than simply eliminating the symptoms and changes that have occurred in the tissues of the tongue.
Complications
Lack of timely treatment for glossophitis can lead to the development of complications affecting the condition of the oral cavity:
- periodontal inflammation;
- extensive damage to dental caries;
- partial loss of taste perception;
- decrease in the amount of saliva produced;
- changes in microbiological flora;
- dry mucous membranes.
In addition to such “local” consequences, glossophytia negatively affects the general condition. Pathogenic bacteria from the papillae spread throughout the body, causing:
- ENT diseases: sinusitis, tonsillitis and sore throat.
- Dysfunction of the digestive organs.
- Respiratory pathology: pneumonia, bronchitis.
We will find out in the next publication whether there are analogues of Solcoseryl dental adhesive paste. And here we will tell you whether it is possible to sanitize the oral cavity yourself, at home.
By clicking on the following link: you can see a photo of gingival fibromatosis.
To prevent the development of such complications, it is important to seek help from specialists in a timely manner.
How to prevent development?
It is difficult to completely exclude the development of this disease, since all the factors that cause it are not clear. However, doctors recommend high-quality oral hygiene, including its professional variety.
In addition, it is necessary to promptly treat gastrointestinal diseases and other general pathologies that can provoke the disease. It is also important to give up bad habits (smoking, drugs).
If you notice any signs of this disease or simply unusual changes in the appearance of the tongue, it is better to immediately consult a doctor. Only a specialist can diagnose the disease and offer the best solution to the problem.
If you find an error, please select a piece of text and press Ctrl+Enter.
Tags hyperplasia tongue
Did you like the article? stay tuned
Previous article
ROCS cream for fixing dentures: what problems does it solve?
Next article
Oral cancer: how effective is treatment and when?
Prevention
To prevent the manifestation of the disease, you must adhere to the usual standard recommendations:
- Daily proper hygiene procedures not only for the oral cavity, but also for the tongue.
- Eat more solid foods to help remove plaque.
- Regularly (at least 2 times a year) have your oral cavity examined by a dentist.
- Monitor your general well-being and body condition. If health problems arise, do not delay treatment.
- The use of rinses, the action of which is aimed at eliminating bacterial flora and reducing inflammation. Important: change rinse aids twice a month.
Herbal decoctions can be used as rinses:
- 1 tsp. herbs (linden flowers, oregano or plantain) pour 1 tbsp. boiling water, infused for 2 hours, filtered and used for its intended purpose.
- sage, chamomile and mint (in equal quantities) are poured with water and boiled over low heat for 15 minutes. After cooling, the broth is filtered.
Attention to your health, proper and balanced nutrition, quitting smoking and alcohol will also help prevent hyperplasia.
In the next video we will be told about what language changes should be alarming: