Why do you need a tongue?
The uvula in the throat is a palatal process that resembles a small bell. Its main function at the junction of the larynx and palate is protective. It prevents bacteria, viruses and pathogenic microorganisms from entering the throat and lower respiratory tract. The tongue covers the throat from cold air when walking on a frosty day. It also distributes air flow.
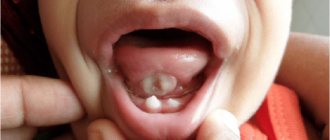
The tongue is located above the larynx, and when it enlarges, the functions of swallowing, breathing, and speech are impaired. The swollen organ can increase in size by 5 times. Because of this, it falls on the tongue, causing gag reflexes.
Solutions for inhalation
One of the most effective methods of therapy is therapeutic inhalations. It is necessary to make a decoction based on thyme, eucalyptus oil and pine buds. 20 grams of kidneys are poured into a glass of water and boiled for 30 minutes. Then mix 10 grams of thyme with a glass of boiling water and leave to infuse for 40 minutes. The decoction and infusion are combined in one container and 20 grams of eucalyptus oil are added. The resulting product is poured into a nebulizer and inhaled at home.
Inhalation with vasoconstrictor drugs is also good for relieving swelling.
Causes of swelling
Swelling of a small organ is a symptom indicating the development of an infection or other pathology. In 25% of cases, an inflammatory process develops on the uvula, even in this case the disease is a consequence of inflammatory reactions, for example, tonsillitis, pharyngitis, laryngitis.
Swelling is caused by the development of bacteria: streptococci, staphylococci. Viruses, especially influenza, parainfluenza and adenoviruses, are also causes. Only in 20% of cases can the uvula become swollen due to the spread of a fungal infection.
One of the reasons for swelling of the tongue is an allergic reaction. It can develop through contact with various substances or as a result of taking medications.
A tumor of the uvula develops from factors:
- pathologies of the oral cavity and nasopharynx;
- neoplasms, benign and malignant uvula or adjacent elements;
- surgery to remove tonsils;
- throat surgery;
- injuries, burns of the tongue;
- inhalation of toxic substances, dust;
- drinking hot drinks and food.
Inflammatory processes in the pharynx and pharyngeal ring develop due to dry mucous membranes, hormonal imbalances due to pregnancy, menopause, adolescence, or the use of hormonal medications. In this case, the greater damage occurs on the tongue.
Risk groups include smokers and people who drink alcohol excessively. If a person has reduced immunity due to chronic endocrine or systemic pathologies, a swollen uvula will be a consequence of illness.
Due to undeveloped immunity, children are primarily affected by swelling of the uvula. The symptoms are extremely severe. Elderly people are also susceptible to swelling of the uvula, but the signs are not obvious.
Poor treatment of respiratory diseases leads to tumors: if a person gargles with a concentrated soda solution and a decoction of medicinal herbs of various origins.
Treating uvulitis at home
Treatment at home is carried out for mild or uncomplicated disease. To do this, use medications prescribed by a doctor (antibiotics, for example), local preparations with an antiseptic, and decoctions for rinsing the mouth.
The following medications help with inflammation and sore throat:
- Hexoral (spray, lozenges). Standard course – 7 days.
- Lizobakt, Lizak (lozenges). They are allowed for children from 3 years old.
- Faringosept, Septefril, Decathylene (lozenges, tablets).
- Gevalex, Chlorophyllipt, Rotokan, Tantum Verde (solutions for frequent mouth rinsing).
It is impossible to quickly cure inflammation; it is important to regularly dissolve lozenges with an antiseptic or rinse the mouth.
The minimum course of such treatment should last at least 7 days. Antiseptic solutions are also available in the form of aerosols for irrigation of the mucous membranes of the mouth and throat (Ingalipt, Angistop), but they are prohibited for children under 3 years of age and persons prone to sudden laryngospasm and allergic reactions.
Inhalations and homeopathy are not effective in treating acute or chronic uvulitis.
It is highly not recommended to resort to this type of alternative medicine, especially when treating children.
On topic: Rotokan: instructions for use for gargling. Reviews. How to divorce?
Gargling with Chlorophyllipt: instructions. Reviews. How to use the product?
Symptoms
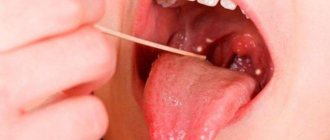
It is difficult to miss the swelling of the uvula: the feeling of a foreign body, gagging are unpleasant signs. Even a person who is far from medicine can visually examine the throat and find out that the appendage of the palate is swollen.
But if the tumor is not obvious, other symptoms may indicate a problem:
- increased salivation;
- speech disorder;
- labored breathing;
- pain and sore throat.
Depending on the pathology, severe fever, cough, and runny nose may occur. If a person suffers from allergies, a rash, itching, redness of the skin and swelling of the lips and tongue are possible.
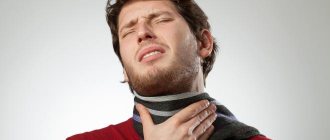
Painful swallowing of saliva during a long conversation or after sleep may indicate a problem. An unpleasant symptom may subside within half an hour. Discomfort may occur when eating, drinking, or sneezing and coughing.
Complications
If the uvula on the roof of your mouth is swollen, you must urgently seek medical help, otherwise there will be a rapid development of edema, asphyxia and death.
If the swelling is insignificant, a person may experience difficulty speaking or eating: the feeling of a foreign body causes nausea, as a result the patient refuses to eat and does not receive microelements for the body.
Difficulty breathing slowly but surely leads to dysfunction of internal organs and tissues. The respiratory and cardiovascular systems and meninges are affected.
What is uvulitis?
What is uvulitis? This is an inflammation of the conical process (uvula) on the posterior edge of the palate. It always occurs rapidly and very acutely, accompanied by pain, difficulty breathing and a lump in the throat.
The function of the uvula is to form sounds and protect the nasopharynx from food entering it. This anatomical element is important for the body, so it should be treated.
According to the form of uvulitis, the following are distinguished:
- Acute – the appearance of the disease;
- Chronic – periodic occurrence of the disease.
Based on the causes (causative agents) of occurrence, they are divided into types:
- Infectious: bacterial and viral.
- Allergic.
- Drug.
- Traumatic.
go to top
Diagnostics
If signs appear, you should consult a doctor: a therapist or an otolaryngologist. If hypersensitivity to one of the components is indicated, the patient will be referred to an immunologist or allergist. If a reactive tumor of the uvula is suspected due to the development of an infection, an infectious disease specialist is also involved in the study.
Visual diagnosis is not enough. It is important to identify the degree of swelling and symptoms, and determine the condition of the body. Therefore they carry out:
- laryngoscopy;
- pharyngoscopy;
- Ultrasound;
- radiography.
It is necessary to prescribe laboratory tests of blood, urine, and scraping of the mucous membrane. If purulent ulcers are visible on the uvula, their contents are examined.
Select equipment
Treatment
If the uvula is swollen, you cannot self-medicate: incorrect actions will lead to a sharp deterioration of the condition. If swelling develops quickly, you should call emergency medical care, the paramedic will give injections with antihistamines and anti-inflammatory drugs and refer the patient to the intensive care unit.
If the tumor of the palatine process is insignificant, you can consult an otolaryngologist yourself. After the examination, the doctor will determine the cause of the pathology and develop a treatment program.
Conservative therapy
Conservative treatment methods are chosen if the patient's condition does not cause concern. If the inflammation is caused by a bacterial infection, the first-line drug is an antibiotic. If the disease began due to the development of a viral or fungal infection, choose the appropriate medication.
A group of medications will help relieve symptoms:
- Antihistamines. If the swelling is not caused by contact with an allergen, medications help relieve swelling.
- Anti-inflammatory. Help eliminate swelling, redness, and pain. At the initial stage, non-steroidal drugs are prescribed; in difficult situations, steroids (hormones) are used.
- Diuretics. They are aimed at relieving puffiness, but the drugs must be taken carefully.
Antiseptics will help eliminate pathogenic microbes. In difficult situations, doctors prescribe injections of antihistamine and anti-inflammatory solutions. For small and moderate tumors, tablets and capsules are used. If swallowing is inconvenient, sprays, gels, solutions, syrups and suspensions are used.
Inhalations with different compositions are remedies for the treatment of uvula swelling. But the compositions for the devices must be chosen by an otolaryngologist.
Physiotherapy
Physiotherapeutic procedures are prescribed to strengthen the body when the main symptoms have already been reduced. To normalize metabolism the following is prescribed:
- magnetic therapy;
- ultrasound therapy;
- UHF;
- electrophoresis;
- phonophoresis;
- applications.
Usually choose one or two courses of 10 days.
Diet
Proper nutrition during treatment of any disease is the key to success. It is necessary to exclude allergens that caused the tumor, and also exclude:
- hot/cold food and drinks;
- spicy;
- pickled;
- sour.
Alcohol and carbonated drinks are prohibited. It is important for the patient to eat foods rich in vitamins, fiber, and carbohydrates.
Surgery
Otolaryngologists and surgeons are doing everything to delay surgery for partial or total removal of the uvula; this will lead to voice impairment. If a person’s life is at risk or the risk of developing disability is increased, then they resort to surgery.
Excision of the swelling is carried out using minimally invasive methods: laser, cryotherapy, ultrasonic scissors (scalpel). With these methods, stitches are usually not required because the edges of the wound are sealed using laser light or ultrasound. But if necessary, self-absorbing sutures are applied.
How to treat uvulitis with medications?
In the treatment of acute inflammation of the uvula, antibiotics, antifungals, and local antiseptic drugs can be used. Surgical intervention is resorted to extremely rarely - in the case of suppuration, the presence of phlegmon or abscess of the peripharyngeal fatty tissue, and in case of tumor diseases.
Treatment with antibiotics is indicated only if the bacterial origin of the disease is confirmed.
Such an infection is supported by long-term persistence of fever (more than 3 days), characteristic changes in the oral mucosa, clinical blood test (high level of leukocytes, neutrophilia, accelerated ESR).
In order to understand which antibiotic will help, it is recommended to undergo a bacteriological analysis of a smear from the throat and nose. It allows you to determine the source of infection (type and name of bacteria), sensitivity to various antibacterial drugs.
The most commonly used groups of antibacterial agents are:
1
Semi-synthetic, protected penicillins (“Flemoxin”, “Amoxicillin”, “Augmentin”, “Amoxiclav”). They have a wide range of effects and are available in the form of tablets and suspensions, approved for children. A common contraindication is the presence of an allergic reaction to penicillins.
2
Azalides, macrolides (Sumamed, azithromycin, clarithromycin, hemomycin). They have a bactericidal effect on a large number of pathogenic microbes and rarely cause adverse reactions. Available in syrups and tablets.
3
2nd or 3rd generation cephalosporins (“Zinnat”, “Pancef”, “Zinacef”). To treat uvulitis, a tablet or liquid form of these antibiotics is usually prescribed.
Note: only a doctor can prescribe any antibacterial drugs, preferably based on the results of a clinical blood test. It is also not recommended to interrupt the prescribed course, even if you feel better.
Remember
During pregnancy, antibiotics are used only if their expected positive effect significantly outweighs the potential risks.
If the disease is of an allergic nature, antihistamines are used (Suprastin, Loratadine, Cetrin, for children - Fenistil, Zodak drops). In this case, it is not recommended to use throat sprays or inhalations.
How to treat candidal uvulitis?
If fungal flora is detected, it is advisable to use local and systemic antifungal drugs for treatment: Fluconazole, Nystatin, Miramistin. The course of therapy is selected only by a doctor, taking into account the type of fungus and its sensitivity to drugs. [ads-pc-1][ads-mob-1]
Prevention
To prevent the development of a tumor of the uvula, otolaryngologists and other specialist doctors recommend:
- Treat acute respiratory diseases. Follow doctors' recommendations for chronic pathologies.
- Avoid contact with allergens.
- Do not take medications uncontrollably.
- Lead a healthy lifestyle.
- Strengthen the immune system (hardening, moderate physical activity, walks in the fresh air, taking vitamin complexes).
Do not consume hot food or drinks, and avoid long-term consumption of cold foods (for example, ice cream).
- Premium Clinic Medical Center. Uvulitis. // [electronic resource]. Access date 06/23/2021
- Luchikhin L. A. Otorhinolaryngology. — 2012
- Blotsky A.A. Inflammatory diseases of the pharynx. — 2015.
- Head and Neck Institute. Uvula. // [electronic resource]. Access date: 05/22/2021
Author: Lyudmila Fedorova Pulmonologist, immunologist, therapist
How to gargle with uvulitis?
Rinsing with folk remedies and medications helps reduce signs of inflammation, relieve pain, and locally fight infection. A banal soda and furatsilin solution has proven effectiveness.
The first is prepared by adding half a small spoon of baking soda to 250 ml of warm water, the second by dissolving 2 furatsilin tablets in 200 ml of water. It is recommended to rinse your mouth every 3-4 hours for at least a week.
Read more: How to gargle with soda? Proportions. Salt and iodine. Full description
How to gargle with Furacilin? How to properly dilute? Instructions and reviews
You can also use the following folk remedies for rinsing:
- solution from onion peels (a large spoon of the raw material is poured with 500 ml of water, boiled, infused for 5 hours and filtered);
- decoctions of sage, thyme, viburnum, St. John's wort;
- chamomile infusion, garlic infusion.
Rinsing with medications (Chlorophyllipt, Gevalex, Miramistin) is highly effective. The treatment regimen is drawn up by the attending physician: as a rule, 4-5 rinses per day after meals, for 7-10 days.
Prevention
In order to prevent the disease, you should avoid contact with infectious patients, observe the rules of personal hygiene, and regularly sanitize the oral cavity. To increase the body's resistance, you should eat a balanced diet rich in vitamins and exercise.