Almost everyone has had to deal with toothache in one way or another. This symptom is a signal that there are inflammatory processes in the oral cavity that require the intervention of a professional dentist. However, when a toothache occurs, it is not always possible to immediately contact a specialist. Therefore, your first aid kit should always have products that will help relieve pain before visiting the dentist’s office. After all, these can arise quite suddenly, and getting rid of them without analgesics is not easy.
Tablets for toothache relief
Review of painkillers
Disadvantages of tablets
Painkillers for pregnant and nursing mothers
What not to do if your tooth suddenly hurts
In most cases, the first thing people do when pain occurs is take pills. This is the most common and accessible way to get rid of unpleasant sensations. Of course, the ideal solution would be to see a doctor, but there are different situations: there is no time, clinics are closed (tooth pain at night), financial situation, etc. We provide a list of the most effective remedies for toothache and we hope that you will use them only as a last resort case.
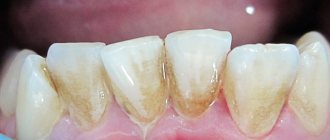
What causes aching pain in a tooth?
The main causes of pain are:
- Infectious lesions of dental units: caries, pulpitis, periodontitis. Even in the later stages, these diseases may not give a clearly defined clinical picture and may only manifest as persistent aching pain inside the tooth when exposed to any irritant.
- Too thin enamel layer, cracks and chips in the enamel.
- Periodontitis. In some cases, gum inflammation is accompanied by throbbing toothache.
- Treatment or tooth extraction. Aching pain often appears after the removal of a wisdom tooth or any other tooth - this is a normal reaction to the operation, and usually the painful sensations gradually go away on their own after a few days. Also, aching pain in the tooth often occurs after removal of the nerve - this is a common reaction of the body to treatment and does not require special therapy.
Review of painkillers
Table 1. Painkillers
| Drug name | Appearance | Characteristics and action |
| Nimesil | Available in the form of tablets, granules, suspensions. Recommended for mild to moderate toothache. | |
| Nise | Available in various forms. Suitable for mild to moderate pain. | |
| Ketorol | Available in the form of tablets and capsules for injection. Will help relieve moderate to severe pain. Maximum dose per day – 3 tablets | |
| Ibuklin | Available in tablet form. Recommended for mild to moderate pain. | |
| Tempalgin | Has anti-inflammatory and antipyretic effects. Does not irritate the gastric mucosa. | |
| Nurofen | Available in the form of tablets, suspension and gel (for external use). | |
| Took | Available in tablet form. Helps relieve moderate toothache. | |
| Analgin | Available in various forms. The maximum dose per day is 4 tablets. |
“Remember that the pill is a temporary way to relieve pain.
The effect of the drug will wear off, and the pain may return because the cause itself has not been eliminated. If after the first “bells” you do not go to the dentist, the disease will continue to progress. Each time the pain will get stronger and stronger" Irina Vinogradova, Dentist-therapist, endodontist, head of the department of therapy and periodontology, member of the medical council of the network of clinics "STOMPRAKTIKA.RF"
Antibiotics for gum inflammation -
The strategy for choosing an antibiotic for periodontitis, as well as the regimen of use, will be somewhat different. In most cases, antibiotics for gum inflammation are also prescribed “empirically”, i.e. without preliminary microbiological examination of the contents of periodontal pockets. But this may only be permissible for “mild severity” periodontitis. But with an aggressive course of periodontitis, as well as with moderate or severe periodontitis, we are obliged to refer the patient for microbiological examination.
The study will determine the composition of the microflora in periodontal pockets and determine its sensitivity to various antibiotics. For example, patients with moderate and severe periodontitis usually take antibiotics 2-3 times a year, which leads to the development of oral microflora resistance to them (i.e., many antibiotics will either not work at all or the effect will be negligible). It is also worth remembering that antibiotics can be used for gum inflammation only after preliminary removal of dental plaque.
Preparations "Tsiprolet-A" or "Tsifran-ST" -
If we do not send the patient for a microbiological study, then the 1st choice drugs will be 2nd generation fluoroquinolones. More precisely, these will be combination drugs that contain the combination “ciprofloxacin 500 mg + tinidazole 600 mg” (such combinations contain the drugs “Tsiprolet-A” and “Tsifran-ST”). Application regimen – 1 tablet. 2 times a day, for a total of 10 days.
Another option is that you can simultaneously take not a combination drug, but say, regular ciprofloxacin 500 mg 2 times a day, and in addition to it metronidazole or trichopolum - 500 mg 3 times a day (the course of treatment for each drug is only 10 days). Although this option is cheaper, it is worse. Metronidazole in this case will be a replacement for tinidazole. But in any case, you should not buy Russian-made antibiotics; for example, even Indian drugs are of much higher quality.
Important: the scientific work “Antimicrobial effectiveness of the systemic use of antibiotics of different groups in the complex treatment of patients with chronic generalized periodontitis” (Zorina O.A., Berkutova I.S.) shows that after the use of drugs such as “Tsiprolet-A” - in periodontal pockets 14 days after the end of antibiotic therapy, the lowest level of pathogenic bacteria is noted when compared with antibiotics of the macrolide group (azithromycin) and 3rd generation cephalosporins (Suprax).
Currently, the antibiotic ciprofloxacin is the only antibiotic in periodontal antibiotic therapy that suppresses absolutely all strains of A. actinomycetemcomitans (while it has minimal effect on the normal microflora of the oral cavity). In addition, when ciprofloxacin is administered orally, its concentration in periodontal pockets will be 8-10 times higher (compared to its concentration in blood plasma), and therefore ciprofloxacin is very effective against infection in periodontal pockets.
Combination of drugs “Amoxiclav + Metronidazole” –
We have already talked above about the antibiotics Amoxiclav and Augmentin, which contain a combination of amoxicillin and clavulanic acid. But if we need an antibiotic for gum inflammation, then we must combine one of these drugs - with metronidazole. Treatment regimen – Amoxiclav or Augmentin should be taken 1 tablet. 3 times a day (each tablet contains 500 mg of amoxicillin and 125 mg of clavulanic acid), as well as metronidazole - 500 mg 3 times a day. The course of treatment is 10 days.
Just do not buy cheap Russian metronidazole; it is better to take inexpensive metronidazole preparations from European manufacturers (for example, Trichopol or Flagyl). By the way, for patients who have gastrointestinal diseases associated with Helicobacter Pylori (peptic ulcer of the stomach and duodenum) - this scheme will also reduce the population of Helicobacter Pylori bacteria in the gastrointestinal tract.
Important: what to do if you need to choose between options - either the antibiotic Tsiprolet-A (Tsifran-ST) or the “Amoxiclav + Metronidazole” regimen. In principle, these 2 regimens are approximately equivalent - thanks to the addition of metronidazole to the drug Amoxiclav. But the “Amoxiclav + Metronidazole” regimen is still better, because in clinical studies it shows effectiveness against a significantly larger number of microbial associations in periodontal pockets.
Antibiotics for aggressive periodontitis –
Aggressive periodontitis means that the destruction of the bone tissue around the teeth, as well as the periodontal attachment of the teeth to the bone, will occur very, very quickly (24stoma.ru). Accordingly, tooth mobility develops in such patients many times faster than in patients with the usual course of chronic generalized periodontitis.
The development of aggressive periodontitis involves special types of anaerobic bacteria, which have the greatest destructive potential for the bone tissue around the teeth. We are talking about the “red triad” of anaerobic bacteria - these are Porphyromonas gingivalis, Tannerella forsythensis and Treponema denticola, the presence of which in a patient will mean a severe aggressive course of periodontitis. According to clinical studies, for aggressive periodontitis, one of the most effective antibiotics will be the antibiotic Moxifloxacin, which belongs to the 4th generation fluoroquinolones.
Important: in patients with aggressive periodontitis, it is fundamentally important to prescribe an antibiotic not empirically, but only after a microbiological examination of periodontal pockets (identifying the sensitivity of isolated microorganisms to different types of antibiotics).
Disadvantages of tablets
Painkillers also have a downside: almost all pills have side effects.
- Negatively affect the functioning of the digestive system. Erosion and ulcers can form on the walls of the stomach, so if there are problems with the gastrointestinal tract, it is better to choose a different method.
- Disturbs liver function.
- They can cause headache, shortness of breath, swelling, skin rashes, etc.
Most analgesics are prohibited for expectant and nursing mothers, young children and people with systemic diseases that are included in the list of contraindications. Therefore, it is recommended to consult a doctor before use.
Types of anesthesia in dentistry
Anesthesia in dentistry can be general or local. The first includes intravenous sedation, as well as general anesthesia. That is, the drugs do not act locally in the oral cavity, but throughout the entire body. Actually, this is ordinary general anesthesia, which is used everywhere in medicine - it’s just that certain types are used in dentistry. Local, as it is already becoming clear, includes the familiar “freezing”, which is administered by injection.
Separately, we can also distinguish xenon sedation or xenon therapy - the second name will be even more correct, since such anesthesia is used to prepare for local or general anesthesia. It allows you to reduce the level of anxiety and stress, saturates the body's cells with oxygen, due to which it has a general healing and even rejuvenating effect! It is not an independent type of pain relief, but is used in combination with other approaches.
Diagnostics
Diagnosis of pulpitis takes place in several stages. The first is an examination of the oral cavity by a dentist. The patient's complaints about acute pain, the presence of injury or a carious cavity are taken into account. All this points to pulpitis. But it is impossible to determine the acute and chronic forms of the disease by one visual examination.
To determine the stage and type of pathology, the patient is prescribed an examination:
- X-ray.
- EDI or electroodontodiagnosis. This method allows us to identify the reaction of the pulp to the influence of electric current.
- Rheodentography. It is carried out to assess the blood supply to the dental pulp.
- Thermal test.
To make an accurate diagnosis, differential diagnosis of acute pulpitis is important. This is important so as not to confuse it with other diseases that have similar manifestations.
What is local anesthesia?
Local anesthesia allows you to numb the specific area where the intervention is planned. The patient is conscious. And this is actually more than enough even for complex surgical operations.
For local administration of all types of anesthetics, special reusable syringes are used, which have a recess for inserting a carpule - this is a hermetically sealed ampoule with an anesthetic. Unlike disposable ones, carpule syringes have a thinner needle, which allows you to administer the drug slowly and thus eliminate pain. All syringes for reusable use must undergo antiseptic treatment and sterilization using modern ultrasonic and temperature sterilization equipment.
Bottom line
If you have a slight toothache (aching), you can do the following:
- take an aspirin capsule and drink a glass of water;
- give an injection of aspirin solution;
- light candles (for a child);
- drop drops (infant).
In case of severe pain and significant destruction of the tooth crown, crush the tablet into powder, dilute with a drop of water and place in a hollow. If there is an inflammatory process in the gum, place it on the swollen area. In addition to this, you need to take the capsule orally. Then you need to make an appointment at the dental office for treatment.
Painkillers provide only temporary relief, masking the pain syndrome. While taking analgesics, a person does not feel pain, however, pathological processes continue to develop. With repeated use of painkillers, the processes of destruction in tissues can become irreversible, and a person can expect long-term, expensive treatment.
The principle of action of analgesics is based on the relief of pain signals from the site of inflammation to the brain. However, the temporary disappearance of pain does not mean that the body is healing: it needs targeted therapy.
It should be remembered that the simultaneous use of the drug with other analgesics is prohibited: this will increase the toxicity of analgin. This combination of drugs is especially dangerous when treating infants: unforeseen complications may arise.
Sources used:
- Therapeutic dentistry. National leadership / L.A. Dmitrieva. - M.: GEOTAR-Media, 2015.
- Medicines in dentistry. Directory / L.N. Maksimovskaya, P.I. Roshchina. - M.: Medicine, 2001.
- Drugs.com Drugs.com international listings for Metamizole
Side effects
Symptoms of a drug overdose may include the following:
- attacks of nausea and headache;
- decreased appetite and tone;
- overexcitation of the nervous system;
- sometimes drowsiness and apathy;
- gastrointestinal disorders in various forms;
- interruptions in the heart;
- bronchospasm;
- noise in ears;
- allergic rashes;
- kidney disorder - anuria;
- leukopenia;
- convulsions.
If you find the listed symptoms of a drug overdose, you should immediately rinse your stomach, take activated charcoal, drink plenty of fluids and contact an ambulance.
Analogs of analgin
What can replace aggressive analgin? The reason for refusing this drug is life-threatening reactions of the body - agranulocytosis and allergies. The following medications are used to relieve toothache:
- ketorol;
- ketanov;
- ketorolac;
- naproxen;
- dolak;
- nimesil.
The listed drugs have a more gentle effect on the body when relieving pain. The disadvantage of these drugs is their high price and prescription. However, ketorol can be purchased without a prescription if the patient has severe pain.
Causes
The reasons for the development of pathology may be the following:
- Tooth injury, mechanical or chemical. Violation of the integrity of enamel and dentin makes the pulp extremely vulnerable to the effects of the external environment and pathogenic bacteria.
- Gum diseases. In this case, there is a high risk of infection entering through open periodontal pockets.
- Complications of caries. Uncured caries or its advanced form contribute to the entry of pathogenic microorganisms - streptococci - into the pulp through the dentin tubules.
- Incorrectly performed dental treatment - damage to dental tissue, opening of a tooth performed in violation of technique, burn of dental tissue by arsenic, etc.
- Incomplete removal of carious tissue during treatment. The infection persists in the dental cavity and continues to develop.
- Poor quality filling installation. It is dangerous because there is a gap between the tooth wall and the filling material. Through it, pathogenic microorganisms penetrate into the pulp.
Are there any disadvantages to local anesthesia?
Local anesthesia has virtually no disadvantages. Unlike drugs that were used previously, modern anesthetics are absolutely safe, have a minimum of contraindications, are quickly eliminated from the body, and do not have a negative effect on the heart, kidneys and liver. With professional administration, the patient will not feel any pain even during long surgical procedures.
“Our clinic uses a strictly individual approach. We have selected several of the most effective and safe drugs - for each patient we select our own method, drug and its concentration, based on individual characteristics. Therefore, everyone who undergoes treatment, implantation or prosthetics at the Smile-at-Once clinic can feel completely safe.”
Zhilenko Evgeniy Aleksandrovich, Implant surgeon, periodontist, orthopedist Work experience over 18 years make an appointment
General anesthesia in dentistry
With general anesthesia, the patient falls asleep for 1-2 hours or more, i.e. for the entire duration of treatment. The drug is administered intravenously, less often by inhalation. If possible, general anesthesia should still be avoided, since its effect on many organs is quite toxic. Even despite the fact that dentistry uses “lighter” drugs than during complex surgical operations. This is a fairly large load on the body, especially on the heart, nervous and cardiovascular systems.
Treatment of acute pulpitis
Treatment goals:
- stop a pain attack;
- eliminate inflammation and stop the infectious process;
- restore the anatomical shape of the tooth.
When dealing with acute pain, the patient is prescribed painkillers to reduce pain until the dental appointment.
The disease is treated in two main ways - conservative or biological and surgical. In both, therapy is carried out with preliminary anesthesia. The injection is given approximately 30 minutes before the start of treatment. For anesthesia, a solution of lidocaine or trimecaine is most often used.
Conservative method of treating acute pulpitis
The main goal is pulp preservation. The doctor conducts step-by-step treatment:
- gives an injection for pain relief;
- removes necrotic dentin;
- opens the tooth cavity;
- treats with antimicrobial agents;
- lays down medicine;
- puts a filling.
Conservative therapy is carried out mainly in young patients. This method requires mandatory consideration of the presence of diseases of the oral mucosa, as well as the localization of caries.
During treatment, anti-inflammatory drugs are used - Calcidont, Dical. Preparations containing calcium hydroxide are necessary to stimulate dentin formation. Proteolytic enzymes are necessary for tissue regeneration and swelling removal. After placing the medicine, the dentist closes the tooth cavity for several days - from 3 to 5. Next, if there is no reaction of the pulp, a permanent filling is placed.
Operative or surgical method
The doctor carries out the following stages of treatment:
- Provides first aid for acute pain.
- Gives an injection for pain relief.
- Opens the dental cavity.
- Removes pulp.
- Treats the cavity with an antiseptic.
- Puts in medicine.
- Installs a seal.
This method is used to treat acute diffuse pulpitis. If acute focal pulpitis is diagnosed, treatment involves removing the ostial and coronal pulp, while preserving the root pulp.
Surgical treatment is carried out in one or two visits.
For surgical treatment in one visit, the order is as follows:
- The doctor administers anesthesia and removes necrotic tissue.
- Using instruments, the tooth is filled with a non-toxic material.
When undergoing surgical treatment in two rooms, the procedure has a different procedure:
- First, the dentist applies arsenic or a devitalizing paste containing arsenic to the affected area of the tooth. This is necessary to kill the inflamed nerve. The duration of installation of arsenic on a diseased tooth is 24 hours on a single-root tooth, up to 48 hours on a multi-root tooth. Some types of pastes can be left for a long time - up to 7 - 15 days.
- A tampon with an anesthetic is placed in the canal and a temporary filling is placed. The patient is sent home.
- At the second visit to the dentist, the doctor extracts the arsenic or paste, completely removes the pulp and fills the tooth cavity.
The surgical treatment process is always monitored by radiography.
In what cases is analgin prohibited?
This drug has a solid list of contraindications. Always keep the package insert in the medicine package so that you do not lose these important notes about taking the medicine. Some problems may appear over the years, and you need to check every time whether you can take this medicine given your current state of health.
Analgin has a number of contraindications
For whom analgin is contraindicated:
- children under one year old;
- people diagnosed with aspirin-induced asthma;
- people with bronchial diseases;
- people with digestive disorders;
- patients with anemia and leukemia;
- people suffering from peptic ulcers;
- people with kidney and liver diseases.
It should be emphasized that analgin is a prohibited drug for pregnant women. Neither analgin nor aspirin can be taken for the entire 9 months. Some components of the drug may adversely affect the development of the baby. In the same way, analgin is prohibited during the lactation period, because the aggressive components of the medicine will reach the baby through milk.
Analgin is prohibited during pregnancy
The use of anesthesia for health pathologies
- diabetes mellitus, bronchial asthma, allergic reactions: anesthetics without preservatives and with a minimal amount of epinephrine are used. For these problems, medications are selected strictly individually, most often based on the results of additional tests,
- high blood pressure, heart disease: with minimal or no epinephrine. It is also important that anesthetics do not contain adrenaline. For these pathologies, intravenous or xenon sedation can be used,
- pregnancy and lactation: drugs with a low content of epinephrine - in minimal dosages, the active substance does not cross the placenta and practically does not enter breast milk (only in small quantities, but this does not have any negative effect, so after dental treatment you can not skip feeding and no need to express milk). It is important that the drugs cannot be used without the addition of the vasoconstrictor epinephrine - in this case, the vessels remain open and the active substance will quickly spread throughout the body, which increases the risk of its transmission to the fetus or child through breast milk.
Modern technologies for administering anesthesia
The pain of the anesthesia itself, as well as its effectiveness, depend 90% on the skill of the dentist. A professional doctor will make every effort and use various techniques to make the patient feel comfortable. However, all people are different, each has their own pain threshold, and that is why an individual approach not only to the concentration of drugs, but also to premedication before the direct administration of anesthesia is very important.
Today, special anesthesia devices have been developed to help doctors. Naturally, they work under the supervision of a specialist. The electronic system is equipped with special pressure sensors - to avoid pain, the anesthetic must be injected very slowly and immediately after puncturing the tissue. The device is equipped with special needles with a very thin double tip, which again reduces pain.
In addition, by administering a small dose of anesthetic, a kind of allergy test is performed - the doctor assesses the condition of the soft mucous membranes (swelling, redness, rash) and the patient’s general reaction, and the pressure force is controlled by the device.
Safe, painless and effective treatment without pain! Treatment is carried out under the supervision of anesthesiologists capable of providing first aid. Special equipment monitors indicators of the general condition of the body.
If there is any threat, the ambulance station is 800 meters from the clinics! You are under the reliable protection of professionals.
Enroll now
Osteotropic antibiotics: what they are and what they are used for
Osteotropic antibiotics are often used in dental practice. An antibacterial drug (ABP) is prescribed:
- to eliminate the inflammatory-purulent process (chronic and acute) with peristitis, abscess, odontogenic sepsis, pericoronitis;
- as a prophylaxis against infectious complications after implantation and surgery;
- patients at risk (patients with diabetes, cardiovascular problems).
Antibacterial therapy is contraindicated for surgical interventions on bone tissue, bleeding, and large-area wounds in the oral cavity.
Sedation and anesthesia - is it safe?
Yes, if they are carried out by professional doctors who have extensive experience and have undergone appropriate training (and a license is also required to perform general anesthesia - this requires an anesthesiologist-resuscitator), then the procedure will be completely safe. In addition, for complex and long-term implantation, the use of sedation is even preferable - you are less tired, you do not need to focus on keeping your mouth open for several hours and fixing your head in a certain position. For you, 3-4 hours of surgery passes in an instant. You will be under the supervision of specialists, and before the operation you will undergo a fairly extensive list of tests for high-quality preparation for treatment and selection of the most suitable, safe drug.
1 Zoryan E.V. Errors and complications when performing local anesthesia in dentistry, 2007.
Medicines for prevention
Prevention with antibacterial agents is a common technique in oral surgery and dentistry. Antibiotic therapy before and after surgery reduces complications.
It is advisable to use products with high bioavailability and minimal side effects. Requirements for medications used for preventive purposes:
- increased activity against pathogenic bacteria, more often found in ondontogenic inflammatory lesions;
- correspondence of the spectrum of action to representatives of the microflora located in the oral cavity;
- good penetration into tissue, especially during operations to open phlegmon and abscess.
An antibiotic when implanted in dentistry minimizes the risk of side effects. Actively fight against foci of infections and bacteria. Selected based on weight and age. Common drugs are penicillins and cephalosporins.
The prescription of drugs depends on the complexity of the surgical intervention and possible complications. Prevention is mandatory in case of prolonged surgery or unfavorable treatment.