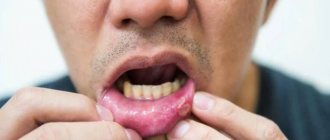
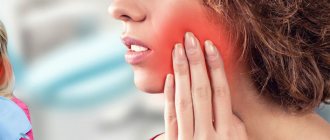
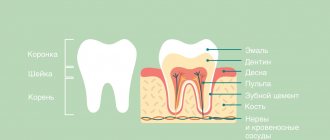
Why do my gums or cheeks swell?
In most cases, swelling of the gums or cheeks is caused by purely dental reasons:
- Flux
During gumboil, the gums become swollen and painful, and the temperature rises. The development of a tumor begins with an ordinary carious cavity. It gets infected, which eventually leads to tooth decay. Pus accumulates and begins to look for a way out. The cheek swells greatly and a white spot appears on its surface. Without treatment, a fistula forms in this place, and the cheek turns into a huge purulent wound. If you do not seek help from a doctor in time, blood poisoning may occur.
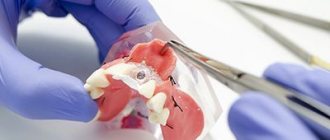
- Removal of a tooth
This operation inevitably involves damage to soft tissue, and swelling is a natural phenomenon. After a while it subsides. If this does not happen, and the gums swell more and more, then you need to urgently visit a doctor. Causes of severe swelling can be:
- a large accumulation of pus,
- incipient periostitis (inflammation of the periosteum),
- infection in the wound.
If you notice swelling of the cheeks and gums, or tissues of the oral cavity, then you need to consult a dentist.
The doctor will determine the exact cause, begin treatment or refer you to another specialist.
Leave your phone number. The clinic administrator will call you back.
By leaving a request on the site, you consent to the processing of personal data
Make an appointment
Initial consultation with a dentist
For free!
- Inflammatory infiltrate
It usually occurs against the background of pulpitis or periodontitis. Pus begins to accumulate in the soft tissues, which causes the appearance of phlegmons and abscesses. It is considered a very dangerous disease because it can lead to big troubles.
- Periodontal disease
Swelling is accompanied by aching or sharp pain. There is no conservative treatment; surgical intervention is necessary. Often it is necessary to remove some teeth and install dentures.
- Teeth chips
The sharp edges of a destroyed tooth begin to scratch the inner walls of the cheek, which leads to inflammation and severe swelling.
- Wisdom tooth growth, pericoronitis
The eruption of the figure eight often leads to inflammation of the gingival hood. Swelling, as a rule, extends to both the cheek and gum.
- Carious teeth
Advanced caries often causes not only the gums to swell, but also the tonsils and cheeks. After eliminating the cause, the swelling gradually goes away. Folk remedies are useless here; urgent medical help is needed.
- Cyst
Depending on the type of cyst, its shape, and location, the doctor decides on conservative or surgical treatment. In some cases, a consultation with an oncologist may be required.
- Gum disease
Swelling is one of the main signs of inflammation of periodontal tissue. Without treatment, the disease quickly becomes chronic and difficult to treat. There is a high chance of losing a tooth.
In addition to the reasons listed, swelling of the gums and cheeks can be caused by:
- inflammation of the facial nerves;
- pathologies of the maxillofacial skeleton;
- allergies;
- disruption of the immune system;
- inflammation of the submandibular and parotid lymph nodes as a result of an infectious disease;
- malignant neoplasm;
- facial injury;
- diseases of internal organs, such as the heart;
- eye diseases;
- blood pathologies.
Treatment
Pre-hospital assistance
The vast majority of causes of cheek swelling require medical intervention and cannot be eliminated through self-medication. The exception is minor injuries: bruises, small hematomas of the cheek, to which cold should be applied in the first days, and then dry heat. In case of intense pain, increasing swelling, or signs of general intoxication, you should consult a doctor as an emergency.
Conservative therapy
Treatment tactics are determined by the characteristics of the disease. In case of dental pathologies, complex treatment of periodontitis or pulpitis is performed. Patients may be prescribed the following medications:
- NSAIDs
. Medicines containing nimesulide are effective for toothache, injuries, and inflammatory processes. Reduce pain, swelling, inflammation. They are symptomatic remedies and do not eliminate the cause of the disease. - Analgesics
. Recommended for severe pain. They should be taken only as prescribed by a doctor, since they can, to a certain extent, neutralize the manifestations of the purulent process. - Antihistamines
. Block the production of histamine, eliminating the manifestations of allergic reactions. 2nd generation drugs and their active metabolites have the fewest side effects. - Antiseptics
. They are used as rinses on their own or after surgery. - Antibiotics
. Indicated for purulent and non-purulent inflammatory processes caused by bacterial microflora.
Along with drug therapy, physiotherapeutic procedures are carried out according to indications. Laser therapy, medicinal electrophoresis, UHF, and other techniques are used.
Surgery
Taking into account the characteristics of the pathological process, the following surgical interventions can be performed:
- Dental diseases
: tooth extraction, opening of a submucosal or subperiosteal abscess, removal of a salivary gland tumor, opening, drainage for purulent mumps. - Traumatic injuries
: osteosynthesis of the zygomatic bone, upper or lower jaw, splinting of the jaw, ligature binding of teeth. - Ophthalmological pathologies
: dacryocystorhinostomy, extirpation of the lacrimal sac. - Nervous diseases
: thrombectomy, decompression hemicraniotomy for cavernous sinus thrombosis. - Infectious processes
: opening of a boil. - ENT diseases
: open or endoscopic maxillary sinusotomy, micromaxillary sinusotomy, excision of maxillary sinus cyst.
What can you do before visiting the clinic?
Our dentists' recommendations will help you temporarily reduce discomfort.
- Wet a terry towel with cold water and apply it to the swollen cheek for 10-15 minutes. This compress will reduce pain and swelling.
- Do not heat the sore spot under any circumstances. Do not sleep on this side, do not tie it with a scarf, or apply a heating pad. Is it dangerous!
- Take a small dose of pain reliever. If it doesn't help, drink again after a few hours.
- Regular rinsing with warm infusions of sage, elecampane or valerian helps a lot.
- If your temperature rises, you can take an antipyretic. The medicine didn’t help, but the swelling and fever are increasing? Call an ambulance immediately!
Causes
Most often, a tooth hurts due to inflammation of the neurovascular bundle (pulp) and surrounding tissues. Pain can also be caused by injury or tooth extraction.
Sometimes exposure to mechanical, thermal and chemical stimuli is required for acute pain to occur. For example, a tooth may hurt when biting or when exposed to hot food.
Pain sensations can be localized in one tooth or spread to neighboring ones, which is called secondary hyperalgesia. In addition, acute toothache can radiate to the ear, temple or throat.
That is why, when making a diagnosis, the doctor must focus not only on the patient’s subjective feelings, but also on the results of the examination. Radiovisiography, CT and radiography of the affected area will help to identify the cause of the pain.
Pre-medical measures
If your cheek hurts, before visiting the dentist you can take some measures to alleviate the condition:
- Apply ice, a cold compress, or a bandage to the affected area;
- Take an analgesic;
- Rinse your mouth 3-4 times a day with a warm solution of antiseptic drugs, a salt solution or a decoction of herbs that have an anti-inflammatory effect.
Under no circumstances should you apply warm compresses to the painful area, as this may trigger the onset of a purulent process. You should also not take antibiotics without a doctor's prescription.
To prevent cheek pain, you should practice good oral hygiene. During the cold season, it is important to keep your face warm, as hypothermia can cause sinusitis and other inflammatory diseases of the ear, nose and throat.
Video from YouTube on the topic of the article:
Swelling of the cheek
Most often, pain in the cheek is associated with teeth, but situations are also possible when the cheek is swollen, but the tooth does not hurt. The cause may be an ear disease or inflammation of the parotid gland, so you may need to consult with several specialists to determine the true cause of the swollen cheek.
It should be remembered that swelling of the cheek, even if there is no pain, is a reason to consult a doctor. Inflammatory processes in the body can develop very slowly, but when the disease is advanced, it is much more difficult to cope with its consequences.
Why do my cheeks hurt?
There are several reasons why your cheek may hurt:
- Sinusitis - the pain is less pronounced in the morning and intensifies in the evening. Unpleasant sensations are not concentrated in one place and are perceived by the patient as a general headache;
- Trigeminal neuralgia (trigeminal neuralgia) is a chronic disease that affects the trigeminal nerve, which is manifested by intense paroxysmal pain in the areas of innervation of the branches of the trigeminal nerve. This disease most often affects women over 40 years of age. In this case, the cheek usually hurts severely on only one side; rarely, the disease affects both halves of the face. The pain is very strong, shooting, the duration of the attack is usually 10-15 seconds, but can reach two minutes and is accompanied by uncontrollable lacrimation and increased salivation;
- Ernest's syndrome - this disease has symptoms similar to trigeminal neuralgia. It is observed when the stylomandibular ligament, which connects the base of the skull with the lower jaw, is damaged. At the same time, the cheek, neck, face, head hurt;
- Temporal tendonitis - this disease is accompanied by unpleasant sensations that affect the teeth, cheek and neck area;
- Dental diseases - advanced caries, pulpitis or periodontitis often lead to severe pain in the cheek on the side of the damaged tooth.
What to do when your cheek hurts
To find out why your cheeks hurt, you first need to see a dentist. If the causes of discomfort are not related to teeth, he will refer you for examination to an otolaryngologist or neurologist.
Treatment for cheek pain depends on the cause that caused it. If the cheek is swollen as a result of gumboil, surgical intervention will be required. To treat inflammatory diseases, doctors prescribe antibacterial drugs, painkillers, as well as local therapy: cold compresses, rinses, etc.
Treatment options
As you can see, most often cheek swelling is caused by dental problems. A visit to the dentist will allow you to assess the clinical picture and provide timely treatment. Paying attention to your health will help you avoid serious consequences and restore your face to its original appearance. If necessary, assistance from other specialists may be required.
In order to temporarily alleviate the situation, you can resort to traditional medicine, including the following recipes:
- A glass of boiled water with salt or soda diluted in it. They need to rinse their mouth. The procedure should be repeated three times a day until the problem is eliminated.
- Honey and chamomile decoction. These components have strong antiseptic properties. For this, 1 tbsp. l. liquid honey should be mixed in 1 liter of healing chamomile decoction. This product allows you to eliminate harmful bacteria, heal existing wounds, ulcers and other diseases. At the same time, you can moisten gauze in chamomile infusion, apply it to the swollen area for a quarter of an hour and do not wash it off.
- A decoction of oak bark, St. John's wort and sage will also eliminate swelling. To prepare it, mix all the components in equal proportions (their total weight should not exceed 150 g), pour in 1 liter of boiled water and leave to infuse for an hour.
Saline and soda solutions are effective
In order for the body to cope with infection and hidden inflammatory processes, it is necessary to strengthen the immune system. To do this, you can take a course of multivitamins and include as many fresh fruits and vegetables in your diet as possible. Traditional medicine also recommends using rosehip syrup.
The problem of swollen cheeks due to dental diseases or any other pathologies is very common. It can be easily dealt with; the main thing is not to ignore this condition and seek qualified help in a timely manner.
The article was prepared under the editorship of doctors - dental implantation center ICDI ROOTT