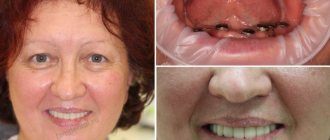
Basal or instant dental implantation is a procedure that allows you to restore the appearance and functionality of your teeth in just 2-3 visits to the dental clinic. The peculiarity of the method is that the implant is implanted into the deep basal layer of the jaw bone (into the cortical plate). This area does not atrophy over time. This type of implantation is indicated for patients with insufficient bone tissue for standard implantation.
In addition to basal implantation, classical and mini-dental implantation are common in modern dentistry. Instant implantation is the most controversial of these methods. To understand why, it is worth turning to the history of the method and its features.
What is basal implantation?
Let's try to give an analogy to make it clear what basal implantation is. If you place a stick in the ground using only the top loose layer, it will not hold well. But if you use deeper layers that are not washed out by water or exposed to other external influences, the stick can be secured much more firmly and will last longer. The same goes for basal dental implantation.
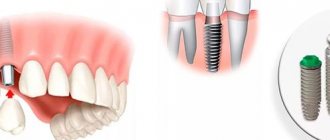
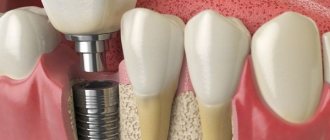
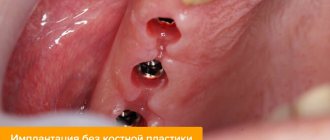
Basal complex is a type of implantation in one stage with immediate loading. The main difference between the basal implantation method and other protocols is that the installation of implants does not require the presence of alveolar cancellous bone, the most central part of the jaw bone tissue. It is used to install most classical implants. Basal implants work with fundamentally different sections: the cortical plate, basal bone, buttresses of the skull, nasal, zygomatic and sphenoid bone. To ensure that the bone and implant have a large contact surface, artificial roots are installed at a certain angle. Angling also helps to select the most suitable areas of bone and place implants bypassing the sinuses and nerve endings.
Unlike classic implants with a rough surface, basal implants are smooth and have a special antimicrobial coating. According to many studies, it is the absence of a rough surface in combination with the use of deep bone sections for implant installation that is an excellent prevention of peri-implantitis and, as a result, minimizes the risk of rejection in the long term. This is especially true in the presence of inflammatory processes in the oral cavity and periodontal tissues in particular.
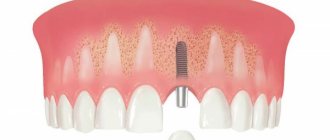
The method is ideal for patients with complete edentia and is not suitable if only one tooth needs to be restored. The minimum is three missing teeth.
Types of Basal Implants
There are two types of basal implants: disc and compression. Disc ones are not currently used, having given way to more modern compression ones.
Disc implants
During the era of basal dental implantation, disc implants, also called lateral basal implants, were developed and actively used. To install them, a rather traumatic operation was required, during which the gums were cut and the bone was sawed out. For this reason, disc basal implants were gradually replaced from clinical practice by more convenient compression ones.
Compression implants
The development of dental surgery has led to the emergence of a new generation of basal implants - compression or root-shaped. These implants are similar to conventional ones, but are larger in size, allowing them to “reach” the basal layer of bone.
Basal implants are produced in different countries and are represented on the market by a large number of manufacturers. Dental clinics usually use implants from 2-3 manufacturers - this is enough to cover the entire price range.
Basal method of dental implantation - indications and contraindications
The main restrictions on refusing basal implantation are the absence of 1–2 teeth, as well as general contraindications to any other surgical intervention. At the same time, Basal complex allows you to solve problems that classical implantation cannot solve.
Indications for basal implantation are complete or multiple absence of teeth, which is accompanied by the following problems and needs:
- advanced forms of periodontitis and other dental diseases, when the only way out is their removal, for example, with a high degree of mobility or loss, in the presence of strong cystic formations on the roots;
- acute and chronic forms of gum disease, accompanied by severe recession of the gingival contour and exposure of the roots;
- inflammation and acute atrophy of spongy bone tissue;
- desire to change dentures to implants;
- the need to speed up treatment;
- reluctance or inability to grow bone;
- advanced age of the patient;
- restoration of teeth in experienced smokers.
Contraindications
Absolute and relative contraindications are noted. With the former, even the possibility of implantation is excluded. Such restrictions include systemic diseases for which any type of implantation is contraindicated. This:
- hematopoietic diseases;
- immunodeficiency;
- acute types of arthritis and rheumatism;
- severe stage of diabetes mellitus;
- mental disorders;
- dysfunction of the osteonal systems, in which bone remodeling becomes impossible;
- cancer, etc.
There is a group of contraindications related to the patient's condition, which may change over time.
- The length of the defect is less than 3 teeth.
- People treated with intravenous bisphosphonates.
- Inability to chew bilaterally (due to paralysis of the masticatory muscles, for example). This limitation is due to the overload to which the side on which they chew constantly is exposed.
- Pregnancy and lactation.
- Age under 18 years.
Features of the Basal complex
- No bone grafting is required.
- Basal implantation and tooth extraction are easily combined and are carried out in just one approach.
- Before the operation, a thorough 3D diagnosis is carried out, as well as three-dimensional modeling of the treatment process.
- At the surgical stage, templates are used to facilitate the process of implantation and allow their installation to be carried out as accurately as possible. During the implantation process, all manipulations are also monitored using 3D X-ray diagnostic technologies.
- Prosthetics take place within 3 days to ensure chewing load on the bone. Dentures can be fixed to implants using either cement or screws.
- When using zygomatic implants, they are fixed at an angle, bypassing the maxillary sinuses.
- For basal implantation, solid one-piece or one-component implants are used in an amount of at least 8 pieces.
Disc brands
Disk designs include the following modifications.
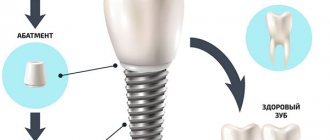
Basal Osseointegrated Implant (BOI). This is a lateral (side) implant, installed into the alveolar bone from the side. It is a rod, at one end of which there is an abutment, at the other - a plate perpendicular to the rod, placed in the basal bone. The number of plates varies from 1 to 3. There is a bending area near the abutment. The prosthesis is attached to the head using cement.
Transosseous implants (TOI – Trans-Osseous Implant). Designs of this type also refer to lateral ones, installed from the side. Usually placed in the canine area. The TOI abutment has a 2.7 mm external hexagon and internal threads for attaching the prosthesis.
The main difference between disc forms is installation on the side of the gum by detaching a flap and preparing the lateral bone of the alveolar process.
Why does the installation of basal implants take place without bone grafting?
Classic two-stage dental implantation is only possible if there is a sufficient amount of cancellous bone tissue. If there is a deficiency, bone augmentation is required before surgery. The basal method does not require this. Everything is explained simply:
- Other layers of bone are used, the density and hardness of which does not change due to the absence of teeth, since their chemical structure is different from the alveolar (spongy) layer.
- For the basal method, solid implants are used. They are often longer and thinner than the classic two-piece. This allows implants to be installed into the bone tissue at an angle with penetration into the deep layers.
- Basal implants are installed according to the principle of compression of bone tissue around its axis when screwed. That is, during implantation, the bone is not lost, but is compacted around the artificial roots. In this way, excellent primary stabilization is achieved with a force of up to 100 Newtons (for comparison: with the classical approach - no more than 30 - 40 Newtons). This approach has been used for more than 50 years for fractures and joint injuries. The principle of operation is also known by the name of the scientist-inventor G.A. Ilizarov.
- After fixing the implants in the bone, metabolic processes are immediately activated. The solution to this problem is taken over by the prosthesis. The patient chews food, improving blood supply to bone tissue. The cells are revived, replacing old and damaged ones, filling the space and increasing bone density around the artificial roots. Osseointegration occurs faster.
- The prosthesis has another important task - to fasten, connect or splint the implants with its frame, thus eliminating the risk of their mobility and displacement of the structure. The metal base connecting the implants to the prosthesis does not change its position even under heavy loads.
What types of implants are used?
For the basal implantation protocol, different implant options are used:
- disc (or lateral) - an outdated type, practically not used today due to high trauma, the need to cut the gums and saw out the bone;
- T-shaped disc (biocortical) - with a lower screw rod and a wide sharp thread for better stabilization in bone tissue;
- classic - their thread allows you to tightly fix the implants in the cortical layers of the bone and guarantee their reliable stability;
- compression (root-shaped) - have a microscopic thread on a titanium rod and a special abrasive coating for faster healing in both the cancellous and basal bone;
- combined - equipped with biocortical and compression threads at the same time, designed for implantation into the alveolar socket from an extracted tooth;
- zygomatic – placed in the upper jaw at an angle of 30-40 degrees.
Pros and cons of basal implantation
- Time frame – prosthetics using this method will not take the patient much time. According to the protocol, implants should be “loaded” on day 3. Maximum taking into account the need to prepare for the operation, with all possible corrections of the prosthesis to suit the patient’s bite, compliance with the requirements for aesthetics and beauty of the smile, the entire treatment will take no more than 7 days.
- Appearance - the artificial gum is made of translucent acrylic, there is very little of it. When smiling and talking, no one will notice the border of the prosthesis. And the base will brilliantly cope with its task - it will protect the gums from injury in case of inflammation and hide existing cosmetic defects of the mucous membrane, if any.
- Rejuvenation is a pleasant “side” effect of prosthetics. Wrinkles around the mouth will be smoothed out due to the normalization of the functioning of the facial muscles.
- Pleasure from food - you can eat everything! Chewing food is welcome - it speeds up the process of bone tissue regeneration.
- Teeth can be restored even with a large deficiency of bone tissue.
- Contraindications - minimum. Even smoking, inflammation of bone tissue, periodontitis, and periodontal disease are not an obstacle to surgery. Implants work with deep parts of the bone, which are sterile and inflammation does not reach them.
- The implants are securely fixed - the fixation force is 2 - 3 times higher than that of classic models.
- Rehabilitation is very fast. Thanks to minimal trauma and the use of bio-membranes, which are created from the patient’s own blood plasma, tissues are quickly restored. There is only mild pain, comparable to the discomfort after tooth extraction. It goes away in 3 – 7 days. On an individual basis, the doctor prescribes antibacterial and painkillers that will reduce pain to “no”.
- The risk of implant rejection is minimal. Fixation in sterile parts of the bone tissue and preservation of the gums eliminate inflammation. An individually developed 3D plan for installing implants for each patient and the same control throughout the operation to install implants does not allow errors.
- The prosthesis is easy to care for.
- The prices are incredible. Basal implantation will cost less than classic two-stage implantation.
The main disadvantage of basal implantation is that Russia currently lacks qualified specialists. While implantation using the Basal complex method requires experience and knowledge. In one person, the doctor must be a surgeon with excellent knowledge of the anatomical structure of the maxillofacial system, an experienced orthopedist, an implantologist himself, as well as a competent user of software for modeling treatment results in 3D.
Summarizing
As mentioned earlier, the choice of basal or classic implantation should be left to the dentist, who will evaluate the overall picture, on the basis of which a decision will be made. But we can confidently say that when restoring one or two teeth, it makes sense to use classical implantation, and to restore three or more – basal. Both procedures, with properly selected therapy and selected materials, will not only provide the patient with full chewing function, but also restore the aesthetics of the smile.
Computer-aided treatment planning
It is impossible to prepare for basal implantation without 3D technologies. Bone tissue will not grow, so it is important to carefully and accurately plan treatment. The computer helps you select a model, calculate the angle of inclination of the implant, and choose the ideal location for it.
Computed tomography is also strictly required. From the images you can evaluate the quantity, quality and characteristics of bone tissue. Implants should not touch the sinuses or nerves. The examination results are processed through a computer, and by the time treatment begins, the doctor is very clear about the next steps. A detailed plan for the placement of implants and the developed parameters of the prosthesis helps you not to go astray.
In addition to computer technology, when creating individual orthopedic structures, special devices are used to measure the characteristics of the patient’s bite and occlusion.
Before installing the implants, again using virtual modeling, an individual template is prepared from elastic material for each specific patient. It is fixed on the gums - this stencil allows you to install the implant perfectly and without displacement in accordance with the chosen location.
Slab structures
Implants BOI-BAC and BOI-BAC2. They are installed on the upper jaw transsinusally using screws - vertical to the palatine bone, lateral - to the lateral cortical bone of the maxillary sinus.
Other types of implants
TPG Implant (Tuberopterygoid). There are four zones, three of which represent threads of different diameters and pitches. The polished neck of the implant is located at the top, where the rod contacts the soft gum tissue. The design and surface treatment of TPGs makes them highly resistant to bacterial contamination and peri-implantitis.
ZSI Implant (Zygoma Screw). Implants are designed specifically for installation in the cheekbone. Long (35-50 mm) rods have an aggressive thread at the end for screwing into dense bone tissue. There is a bending area near the abutment, which allows, when tilting the implant, to set the abutment in a normal position relative to the alveolar ridge.
What prostheses are used?
A model of the prosthesis is created before treatment using a computer program; the design is subsequently improved and verified using impressions, which are taken after the installation of basal implants. The mucous membranes need time to recover, so immediately after fixing the implants, the prostheses are not attached. It is recommended to wait 1 – 2 days.
For the first six months to a year, as a rule, an adaptive prosthesis with a metal frame and plastic crowns is installed (if desired, it can be left for its entire service life - up to 3 - 5 years). When the implants take root (and this will take a maximum of a year), the temporary prosthesis must be replaced with a permanent one. Crowns can be made of zirconium or metal ceramics.
But there is another option, which modern technologies allow: in 75% of cases, you can immediately install not a temporary, but a permanent prosthesis made of polymer materials. No need for re-prosthetics. Such a modern prosthesis lasts at least 10 years and is subject to adjustment to the bite directly in the patient’s mouth. The structure can be secured using cement or screw fastening.
Screw designs
Compression (KOS – Compression Screw Design). A special feature of KOS implants is a special compression thread, which, when the rod is screwed in, expands and compacts the bone tissue.
Bicortical (BCS – Bi-Cortical Screw Design). BCS implants have a screw-shaped thread at the end with developed sharp blades. This shape is optimal for attachment to the basal (cortical) bone. In the area of the cancellous bone of the alveolar ridge there is a smooth rod, which ends with a head (abutment) for attaching the prosthesis. Implants have bending points to give the head the position necessary to fix the prosthetic structure.
BCS are represented by a large number of modifications with threads of different diameters and different numbers of turns. The thread blades of some modifications have holes and grooves for better osseointegration. The diameter of the threaded part ranges from 3.5 to 12 mm, the length varies from 10 to 38 mm.
The surface of the rods from the head to the thread is polished to prevent the spread of bacteria down the rod into the osseointegration area.
A wide range of BCS sizes allows you to select a design suitable for a specific clinical case. In case of thin cortical bone, implants with a small number of wide turns are used. If the basal bone is of sufficient thickness, it is advisable to use implants with a small diameter but a large number of turns.
Combined (compression + bicortical) implants (KOS Plus Implants). KOS Plus have two types of threads at the same time - a compression thread, cut in the upper part of the rod and intended for fastening into the cancellous bone, and a screw-shaped thread, located at the end of the rod and intended for cutting into the basal bone.
What can be used instead of Basal complex?
One alternative solution is to install conventional removable dentures. However, the service life of orthopedic structures fixed only on the gums is short-lived, they are inconvenient to use, and they also lead to bone tissue atrophy, which requires frequent relining. An alternative may be solutions such as implantation of All-on-4 or All-on-6 - on four or six implants, respectively. These protocols are also used in cases of complete absence of teeth and involve implantation with immediate loading. But unlike basal implantation, they have certain limitations in the volume and quality of the jaw bone and are not used in cases of pronounced atrophic processes.
Dental implants: types and prices with photos
The quality of basal implants from all well-known manufacturers is approximately comparable - it is very difficult to identify the leader among them, since it is impossible to objectively compare the number of complications, service life and the presence of defects. In addition, to a certain extent, these indicators depend on the “straightforwardness” of the doctor installing the implant. Therefore, briefly about implants from well-known manufacturers:
- Nobel Biocare (Switzerland). The implants of this company are made of titanium, which has a high degree of biocompatibility. The external coating of Nobel implants is represented by TiUnit material, which is titanium oxide enriched with phosphorus and has a high degree of crystallization. This coating provides moderate surface roughness of the implant, which increases their survival rate and reduces adaptation time. Nobel Biocare is one of the leaders in the production of implants and equipment for implantology; the company provides a lifetime guarantee on its products. The quality of the product also corresponds to the price - the cost of an implant for basal dental implantation starts from 60,000 rubles.
- Straumann Roxolid (Switzerland). This company uses a special alloy in the production of its implants, which in some respects is not inferior to titanium. Dental implants from Straumann Roxolid are thin, short implants with a special coating that facilitates installation in patients with several concomitant diseases. The price of these implants is slightly lower than the prices of flagships from Nobel - the average cost of one Straumann Roxolid implant is 50,000 rubles.
- Oneway Biomed (Switzerland). Biomed implants are recognized leaders around the world among all immediate loading implants. The Immediate Load implantation protocol developed by the company in addition to implants made the prosthetic procedure so convenient that many implantologists with conservative views began to introduce it into their practice. Biomed implants are distinguished by a super-smooth surface that prevents the absorption of microorganisms. These implants are suitable for prosthetics in the most advanced cases - in patients with severe atrophy of the jaw bone tissue and severe periodontitis. With the cost of one Biomed implant being 25-35 thousand rubles, basal dental implantation of one jaw will cost about 200,000 (all-in-6 or all-in-4 protocol).
- Noris Medical (Israel). The implants from this manufacturer are focused on zygomatic (zygomatic) implantation, so their length exceeds the length of all other implants. In more than half of cases, zygomatic implantation is associated with the need to compensate for bone tissue deficiency. In this regard, Noris Medical offers doctors complete systems that include all the necessary components. The price of basal dental implantation with upper jaw prosthetics using all-in-6 or all-in-4 protocols using implantation systems from Noris Medical can reach several hundred rubles (this is the cost of zygomatic implantation of the upper jaw).
- Ankylos (Germany). The popularity of this company's products is due to their lower price category. The design features of implants from this manufacturer reduce the likelihood of their loosening. In the manufacture of implants, the patented FIRADENT Plus technology is used, thanks to which, after installation, more active formation of bone tissue is observed in the peri-implant space.
- BioHorizons (USA). The fame of this American brand is due to some extent to the fact that the company has developed a special coating for its implants - Laser-Lok. Thanks to it, the fusion of the implant with the bone tissue is accelerated. The company also patented the TeethXpress technique, which is a modification of All-on-6 and is intended for complete jaw replacement. This technique has only one drawback - for high-quality prosthetics it requires absolute parallelism between the implants, which cannot always be ensured in case of severe atrophy of bone tissue.
- Osstem Implant (South Korea). The South Korean company is one of the top 5 manufacturers of dental implants and implantation systems, accounting for 80% of the South Korean market. The company's products are quite affordable - the cost of one implant is 20,000 rubles. Since 2006, Osstem has been producing implants at its plant in the USA and selling them under the HIOSSEN brand.
What is better – classic or basal implantation?
Basal implantation is indicated for complete or almost complete absence of teeth. It is carried out both in case of bone tissue deficiency and in the presence of acute forms of periodontal tissue diseases. Classic implantation will not work in this case - the operation requires bone tissue augmentation. And this is extremely difficult, expensive and will take a lot of time. Therefore, in such situations, patients often hear a refusal and a recommendation to stay with removable dentures. We can safely say that today there is no full-fledged alternative to the basal implantation technique, especially in complex clinical cases.
Possible consequences
Surgeons at some dental clinics lure people with promises of installing basal implants for existing inflammatory diseases, existing cancer, and type I diabetes. In all of these cases, a person’s immunity is sharply reduced, the survival of a foreign body is difficult and can have a number of undesirable consequences:
- peri-implantitis (infectious inflammation of soft tissues with a purulent nature) - often occurs with an untreated inflammatory process;
- bad breath coming from the implantation site;
- damage to blood vessels with hematoma and suture dehiscence;
- the presence of pain in the temporomandibular joint;
- complete resorption of tissue around polished discs;
- exposure of the necks of the implants, its cutting through the bone tissue and the mucous membrane of the intraosseous part - this is observed already in the first 1-5 years;
- loosening and mobility of the implant is a natural reaction of bone tissue to improper force load;
- implant rejection.
The reason for the rejection of the basal implant can be several reasons: from an incorrectly selected product to incomplete diagnosis and the doctor’s omission of inflammatory processes. The patient's body can also reject the implant if there is intolerance to the artificial root material. Banal non-compliance with hygiene rules for caring for the oral cavity after implantation, alcohol, smoking, and drugs also provoke rejection.
Patients easily buy into the “Fast and Cheap” advertising of basal implantation that seems optimal to them. As a result, they not only lose the implant, but also suffer destruction of the soft and bone tissue around it. Due to the loss of bone crest volume, correction of the consequences of basal implantation can take years for clients. Moreover, you will have to spend amounts tens of times higher than the cost of classical prosthetic technology.
Cost of treatment
The final price of basal implantation in Moscow depends on the complexity of the case, the manufacturer of the implants, as well as the materials of the selected denture. However, the patient always has a choice. Thus, the cost of basal implantation on the upper or lower jaw is 265 thousand rubles with an adaptive prosthesis, the service life of which is 3–5 years. With the installation of a permanent polymer ceramic-composite prosthesis, the installation of basal implants will cost 350 thousand rubles. With the fixation of a metal-ceramic prosthesis, the entire procedure will cost 450 thousand rubles.
FAQ
1. Is it possible to immediately install a permanent prosthesis on basal implants? It is possible, the essence of basal implantation is the immediate loading of the implants with a denture.
2.Will there be pain after basal implantation, for how long? They will. Any surgical intervention is traumatic and painful. The duration of pain depends on the patient’s individual pain threshold and the number of implants. On the 14th day, the pain significantly decreases or stops.
3. Which technique should I choose to make the implants last longer: basal or endosseous?
Do not choose a technique on your own, consult with your dentists. Each technology has its own contraindications. In terms of the risk of implant rejection, the basal method shows much worse results. Moscow metro station Zvezdnaya, Danube Avenue, 23
Recommendations for choosing a clinic and implantologist
As mentioned above, basal implantation in the form in which it allows you to achieve high results is practiced today by very few specialists. In order not to run into a “fake” and not to become a victim of inexperienced doctors, but to get a guaranteed high result of the work done, I recommend paying attention to the following points.
The most important thing is that the doctor has a certificate issued by the International Implant Foundation. It is this association that has been actively studying and introducing into practice methods of one-stage implantation with immediate loading for many decades, including the basal complex. Currently, the foundation has introduced a five-step training that every specialist practicing these protocols must undergo. Naturally, the doctor must be accredited by the company that manufactures the basal implants.
Stages
Any dental implantation, including basal, involves 6 main stages:
- diagnosing;
- drawing up a treatment plan;
- sanitation of the oral cavity;
- implantation;
- prosthetics;
- rehabilitation.
The purpose of diagnosis is to obtain a complete picture of the dentofacial apparatus to draw up a treatment plan and determine contraindications. Diagnosis consists of interviewing the patient, examining the medical history, examining the oral cavity and fluoroscopy. If necessary (to clarify systemic diseases), laboratory tests are prescribed - blood tests, urine tests, etc.
During examination, the alveolar process is palpated to determine the configuration and volume of the bone. The presence of dental diseases and lesions of the oral mucosa is established.
Fluoroscopy in the form of orthopantomography, teleradiography and targeted images allows you to assess the condition of teeth and roots, and determine the presence of impacted teeth. Diseased units that cannot be treated should be removed.
A computed tomography scan is performed. Based on its data, three-dimensional virtual models of jaws and surgical templates are built. The use of 3D navigation allows you to determine a safe place to install the implant and avoid complications such as damage to the mandibular nerve, maxillary sinuses and arteries.
An obligatory point of any implantation is sanitation of the oral cavity: cure of acute pathologies and transfer of chronic ones into remission.
Local or general anesthesia is used. The latter is relevant when installing highly traumatic BOI/TOI.
Disadvantages and possible complications
The basal method of dental implantation can only be performed by experienced specialists who have undergone additional training in working with systems for immediate loading. In addition, fluency in the necessary 3D modeling computer programs is required. Also, the doctor must have deep knowledge not only in dental implantology, but also in maxillofacial surgery, orthopedics and other related areas of dentistry. In fact, this is the main disadvantage or shortcoming of the concept. In Russia there are not yet many experts capable of performing a high-quality operation without complications, and this is a problem in general with all immediate loading protocols.
Complications, as a rule, result from errors made by the doctor during the procedure, or poorly performed preparatory manipulations, which can result in contraindications being missed or the locations and implants themselves being selected incorrectly. It is worth understanding that nagging pain and slight swelling are a completely natural reaction of the body to tissue injury, so there is nothing to be afraid of. But complications that require medical intervention include damage to the nerves and maxillary sinuses, suture dehiscence and prolapse of structures - in such situations, the main thing is to consult a doctor in a timely manner, such problems are completely solvable.
The most serious complication after implantation is considered to be peri-implantitis - inflammatory processes that spread in the tissues holding the artificial root. This problem often arises due to non-compliance with basic rules of oral care and abuse of bad habits. If no measures are taken in a timely manner, implant failure may soon occur.
%akc67%
Prices
The price includes:
anesthesia, computed tomography, installation of implants, fixed bridge prosthesis made of milled plastic using CAD/CAM technology.
| Name | Price, rub) |
| Jaw implantation on 4 Osstem implants (South Korea) with a fixed plastic prosthesis | 225 000 |
| Jaw implantation on 6 Osstem implants (South Korea) with a fixed plastic prosthesis | 275 000 |
| Jaw implantation on 4 Straumann (Switzerland) or Nobel (USA/Sweden) implants with a fixed plastic prosthesis | 290 000 |
| Jaw implantation on 6 Straumann (Switzerland) or Nobel (USA/Sweden) implants with a fixed plastic prosthesis | 350 000 |
How is the implant fixation procedure performed?
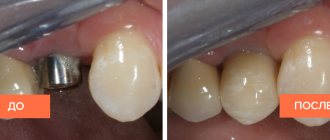
First, anesthesia injections are given (in general, local “freezing” is sufficient, but intravenous sedation can also be used), after which the diseased teeth are removed (if they remain). Surgical templates, previously created using 3D modeling programs, are then placed on the gums. Essentially, these are elastic stencils through the holes in which the implants are screwed - this allows you to avoid even the slightest deviations from pre-selected points for implantation. The concept involves minimal tissue damage - the surgeon does not need to cut the gum and peel off part of it. Small holes are formed in the bone, exactly corresponding to the diameter of the implants, after which they are screwed into the thickness of the bone tissue, which, in turn, is compacted and thereby increases the degree of primary fixation of the structure.
“By the age of 40, the teeth on the upper jaw had completely deteriorated, began to decay and fall out. Many had to be removed and a conventional prosthesis installed. To be honest, it was very difficult to bear, both physically and psychologically. And only recently I decided to get implants. There were few options, the doctor recommended surgery using basal technology, since it turned out that my bone tissue was very thin, and in some places there was even inflammation. I was very worried about the operation, but everything went better than ever! And after the operation I didn’t suffer much, everything somehow healed quickly. But the best part is that I got new teeth in 4 days! More beautiful than they were in their youth! The doctors did a brilliant job, for which I am very grateful to them!”
Potapova Lyudmila D., 53 years old, Moscow, review from the website of one of the dental clinics in Moscow
This method is called minimally invasive; it does not involve incisions, deep bone drilling or sutures. Due to this, postoperative rehabilitation is quick and less painful for the patient than in the case, for example, with the classical technique. Recovery takes literally a couple of days, and complete rehabilitation takes about a week.
(implantation with instantaneous loading)
The loss of one or more teeth is an absolutely solvable problem in modern dentistry, which has an effective method of restoring teeth using various types of implantation. Currently, due to aggressive advertising, basal implantation (also called implantation with instant loading) is of particular interest among patients.
If you believe the advertising, then thanks to this method you can quickly and reliably restore lost teeth, fully restore the chewing function and the beauty of your smile.
What is the difference with other solutions?
The basal implantation technique can be reduced to the main 5 points:
- Treatment is available to all patients wishing to receive implants, regardless of the degree of bone loss or the presence or absence of residual teeth.
- Only one operation is required. Basal implants are placed and splinted in an immediate or early loading protocol when using long-term temporary bridges. The final orthopedic design is installed after 8-50 weeks. In some cases, the final prosthesis can be placed immediately.
- Fewer surgeries and other treatment steps reduce overall costs. If complications arise, quick and effective measures can be taken.
- Basal implants practically do not disrupt the blood flow in the bone. In any case, they do this to a significantly lesser extent than comparable classical implants.
- Thanks to the possibility of immediate exercise, patients can immediately return to their normal lifestyle.
Before basal implants were available, all patients with insufficient bone to immediately place implants were required to undergo the following major procedures::
- Removal of all teeth (if necessary), removal of granulation tissue, cysts and other unwanted formations from the bone.
- Bone augmentation after approximately 2 months (problems may arise at the site of bone harvesting) followed by a 6-month waiting period.
- Introduction of axial implants (screw implants).
- Finally, after another 6 months, installation of a bridge or other orthopedic structure.
In addition to this already difficult treatment plan, soft tissue correction procedures often had to be performed. Throughout these four stages of treatment, surgical risks accumulate: despite all efforts, and contrary to published statements, the fewer surgical interventions, the lower the risk of rejection and complications.
In addition, the features of the technique make it possible to install basal implants in patients with HIV and hepatitis (due to the non-traumatic operation of installing the implant, the process of tissue rehabilitation is several times faster than with flap surgery for installing two-component implants).
Summary:
For the following groups of patients, basal implantation will be one of the most preferred techniques...
- if you smoke,
- there is a lack of bone volume at the implantation site (and you do not want to undergo bone grafting and especially sinus lift surgery),
- elderly age,
- for women during menopause,
- for osteoporosis,
- if you have hypertension,
- compensated diabetes mellitus.
We have identified patients in a special group who, due to various diseases of the nose, mouth and throat, will have an increased number of pathogenic bacteria in the oral cavity, which sharply increases the risk of inflammation around the installed implants and their rejection. For these groups of patients, the basal implantation technique is also more suitable -
- for chronic gum inflammation,
- for chronic tonsillitis,
- with irregular oral hygiene,
- dryness of the oral mucosa,
- mouth breathing (chronic nasal congestion).
In what cases is complex implantation indicated and contraindicated?
The technology under consideration is indicated in the absence of all teeth in the upper or lower jaw or in the presence of a small number of teeth in a row, but rotten and destroyed, that is, requiring immediate extraction. Other indications include pronounced resorption of the alveolar ridge, and therefore the inability to reliably fix implants of classical models. Basal Complex becomes a real salvation if for some reason the patient cannot undergo a bone grafting procedure or, for example, continue to wear a removable denture, or suffers from periodontitis or periodontal disease, inflammation of the bone tissue. The technology is recommended for smokers and elderly people.
As for contraindications, basal implantation has very few. For example, surgery is not performed for diabetes mellitus (but only if there is a decompensated form), serious problems with the heart and blood vessels, nervous and immune systems, in the presence of malignant neoplasms, infectious diseases, which include tuberculosis and HIV. This protocol is not recommended for increased tone of the masticatory muscles. However, like any other implantation. In general, there are much fewer contraindications for this method due to the wider range of problems being solved.
Prosthetics on basal implants (with complete absence of teeth) –
Thus, during the 1st stage of basal implantation (surgical stage), from 8 to 12 implants will be installed in your jaw. The difference in the number of implants depends on many parameters: the size of the jaw, the bone density, as well as the diameter and length of the implants that we can use in a particular patient. The number of implants does not affect the cost of basal implantation, and you will have exactly as many of them installed as needed.
And the next stage is prosthetics. But you will need to choose the option of prosthetics (a type of fixed denture) before the operation. In most cases, prosthetics are carried out in 2 stages. At the first stage, only a temporary fixed denture will be made for you, which very often can also be called “adaptive”. It will be fixed to your implants already 2-3 days after the operation. You can use this temporary prosthesis for about 2 years, after which it will need to be replaced with a permanent one.
Options for temporary (adaptive) fixed prostheses:
- Metal-plastic prosthesis (with cement fixation) - such a prosthesis will be made of acrylic plastic and have a simple metal frame inside. Such a prosthesis will only be cement-retained, which will mean that it cannot be removed from the implants without damage and the need for complete replacement. Together with the installation of 8-12 basal or compression implants, such a prosthesis will cost only 265,000 rubles.
- A prosthesis on a titanium frame (with cement fixation) - in fact, it will also be metal-plastic, but the metal frame of the prosthesis will be made of titanium.
The titanium frame makes your denture much stronger, which is very important for patients with well-defined masticatory muscles and large jaws, patients with bruxism (hypertonicity of the masticatory muscles), who have an increased risk of breaking dentures on a conventional metal frame. In addition, thanks to the titanium frame, the prosthesis will be much lighter than when the frame is made of ordinary metal, for example, a nickel-chromium alloy. In turn, this will make it much easier for you to get used to the prosthesis. The price for basal dental implantation (including the installation of 8-12 implants and a temporary fixed prosthesis on a titanium frame) will be 295,000 rubles. - A prosthesis on a titanium frame (with screw fixation) is exactly the case when Roott implants of the Compressive M and MS series, having non-removable Multi-unit abutments, will be used. This type of abutment provides screw fixation of a fixed dental prosthesis to the implants, and the prosthesis itself will be made on a durable and lightweight titanium frame. The cost of a prosthesis and installation of 8-12 implants will be 325,000 rubles.
Important: the prices listed include the full cost of the turnkey work, including all necessary x-rays, anesthesia, post-operative examinations, prosthesis correction procedures, as well as a guarantee. The warranty for any type of temporary fixed prosthesis is 1 year, but their service life is usually 2 years (up to a maximum of 3 years).