The most common form of jaw injury is a bruise. No one is immune from this. For example, with a strong blow to the jaw, soft tissues, blood vessels, and capillaries are affected, resulting in the formation of hematomas and swelling. This is accompanied by severe pain and discomfort.
To avoid complications, it is recommended to consult a doctor immediately after injury. The fact is that impaired jaw function entails a chain of negative consequences: difficulties while eating, deterioration in the quality of spoken speech, etc.
Symptoms of manifestation
Bruises on the face are difficult to ignore. It is characterized by knowledge of all standard symptoms, such as:
- Painful sensations in the facial area. And they are usually felt strongly because the ends of the facial nerves are among the most sensitive;
- Tissue swelling. This manifests itself as swelling of the skin, which may appear thickened upon palpation. The severity of edema depends not only on the severity of the injury, but also on the thickness of the skin and the internal structure of the tissues. Therefore, the area around the mouth and face is most susceptible to swelling;
- Bruises, bruises and hematomas. They arise as a result of damage to blood vessels and the accumulation of platelets in the damaged area. It’s worth saying right away that the deeper they are under the skin, the later the reaction will appear, but, unfortunately, the longer it will take. For this reason, many people start using ointments and gels for bruises even before visible signs appear;
- Feeling numb. This occurs in cases where the fibers of the facial nerve were directly affected during the injury. If nerve damage is very severe, there is a risk that reduced nerve activity may persist;
- Disruption of various areas of the face. Examples include: inability to see if the eye is swollen, difficulty breathing if the nose is injured, difficulty chewing food if the jaw is injured;
- Open bleeding. Observed when the skin is damaged at the site of the bruise and there is an open wound or deep scratch;
- Nausea, vomiting, loss of consciousness, convulsions. Such serious symptoms can occur if a bruise of the soft tissues of the face is accompanied by a traumatic brain injury and, as a consequence, impaired brain function.
Bruises and bruises are symptoms of contusion of the soft tissues of the face.
Of course, each of these symptoms may vary in severity in each individual case. Much depends on the individual characteristics of the body, such as the thickness of the skin or the elasticity of blood vessels. So, with one type of injury, one person may only have swelling, while another may have a severe hematoma.
Forehead and nose injuries
Surely many people remember how they hit something with their forehead so that “sparks flew.” Of course, after a while it seems that the blow was insignificant and not harmful to health. However, frontofacial injuries are among the most insidious and can have many negative consequences.
When the forehead and nose are injured, the bones that form the nasal cavity and paranasal sinuses become blocked. The result is swelling of the mucous membrane, slower mucus release and nasal congestion. Under such conditions, local immunity decreases, and the environment for the penetration of pathogenic microorganisms becomes ideal. Often the most common allergic rhinitis, which is manifested by copious mucus secretion upon contact with an allergen, is a consequence of a long-standing injury. The mucous membrane, overflowing with fluid due to chronic edema, reacts inadequately to the ingress of substances that are normally familiar and safe to us, and the protective reaction becomes overly pronounced.
After a blow to the forehead or face, the frontal bone moves out of place and can put pressure on the speech centers of the cerebral cortex. If this happens in a child, there may be delayed speech development or stuttering. This is especially evident against the background of the initial birth trauma. When struck, the bones of the nasal septum directly transmit the impact to the main (sphenoid) bone and to the sphenobasilar symphysis. The latter is the main mechanical center of the entire body. Therefore, severe injuries to the frontal-facial region affect the entire musculoskeletal system. Blockage of the symphysis limits the mobility of the sutures of the skull. As a result, the circulation of blood and cerebrospinal fluid is disrupted, and the brain does not receive proper nutrition. Therefore, adults and children who have received such trauma may experience outbursts of aggression, short temper, depression, and panic attacks.
It will heal until the wedding! How to properly care for a wound Read more
If we analyze the behavior of those who had a forehead and nose injury, we can draw a clear pattern: irritability and nervousness developed or worsened in them precisely after the injury. Of course, it also happens that such character traits are associated with upbringing, but still injuries to the frontal-facial region play a very important role.
Article on the topic
Hello from the infirmary. What injuries can you get while playing football? With severe injuries to the area between the eyebrows, usually after 4-8 years, obesity can develop, which is very difficult to combat. Women often suffer from menstrual irregularities and infertility of unknown origin. According to statistics, every third adult has a pathology of the pituitary gland. Considering the number of skull injuries, this is understandable.
Also, injuries to the forehead and nose can cause disturbances in sleep, appetite (hunger and satiety centers are located in the hypothalamus), decreased visual acuity, and vertical strabismus. Natural consequences of incidents in this area are headaches, migraines, and weather sensitivity.
First aid
First aid is recommended for injuries to the soft tissues of the face, regardless of the force of the blow. Here are three basic steps in this situation:
- Place something cold on the bruised area. This could be ice, snow, a compress soaked in cold water, or even a chilled metal spoon. Cold helps constrict blood vessels, reducing the risk of bruising under the skin. However, there are two things to keep in mind. Firstly, facial skin is quite thin and cannot be exposed to prolonged exposure. The optimal time is 15-20 minutes. The procedure can be repeated after 2 hours. Use material that protects the receptors from hypothermia. The second point is that the effectiveness of this method is available only in the first half hour after injury;
- If there are signs of skin trauma, be it wounds or abrasions, it is important to treat them with antiseptics. The most common of them are the well-known hydrogen peroxide, herbs, and a very weak solution of manganese solution. This must be done very carefully, since every touch to the wound can cause pain to the victim;
- Anesthesia. If the sensations are strong, you should turn to painkillers. Among them are Ketone, Ketorol, Ibuprofen. Before use, be sure to read the instructions.
First aid for bruised soft tissues of the face includes applying ice.
In most cases, the listed first aid measures for bruises are sufficient. However, if the injury is much more serious and the victim experiences heavy bleeding or convulsions, then the first step is to call an ambulance. When traveling, control bleeding with a tourniquet or position the person so that they do not risk swallowing their tongue.
It is important to remember that the method of providing first aid will affect the result of further treatment of facial bruises and the likelihood of developing complications.
How long does it take to heal a brain injury?
- The first stage of treatment
is pain and vascular therapy, which promotes the restoration of damaged brain cells. If necessary, medications are prescribed to normalize sleep and improve concentration of memory and attention. - The second stage
is recovery, which lasts one to two months. At this time, you should not visit the sauna, since temperature changes are dangerous due to the appearance of vasospasm, swim, dive under water, and run, since during running there is a strong impact on the blood vessels of the brain.
Diagnostics
A bruise is easy to diagnose, but only doctors can determine its severity and possible complications. Therefore, if for any reason the injured area is bothering you, it is better not to waste time and seek professional help. The diagnosis can be made:
- inspection;
- palpation;
- Assessment of symptoms and complaints;
- In some cases, an ultrasound or x-ray examination may be required.
Diagnosis consists of determining not only the presence of a bruise, but also its severity. There are four degrees:
- First degree. This is the easiest and least dangerous option, involving a slight change in the structure of the subcutaneous tissue. There is no bleeding or hematoma, but blue skin discoloration is quite possible. For the first degree of injury, visiting a doctor is usually not required. It is quite possible to limit yourself to home remedies, which, with the right approach, will help eliminate symptoms in 5-7 days;
- Second step. In this case, significant damage to the subcutaneous and muscle tissue occurs. Severe swelling, pain and even hematoma may appear. It is better to treat such a bruise with medications together with physiotherapeutic procedures;
- Third degree. It damages not only muscle tissue, but also tendons. In some cases, the integrity of the skin may be compromised. Since there is a risk of developing an infectious process, examination by a doctor is mandatory.
- Fourth degree. This is the most severe and dangerous degree of injury. It is always accompanied by injuries not only to soft tissue, but also to bone tissue. In this case, there is a high risk of developing various types of complications. It is imperative to seek qualified medical help.
Accordingly, the type of treatment will directly depend on the degree and nature of the bruise.
Tailbone injury
Injuries to the coccygeal-sacral region are characterized by pain in this place and the lower back, varicose veins in the lower extremities, in the rectum or pelvis. So-called “bones” will form on the legs, while the feet, knees and hip joints may hurt, and the legs will constantly swell. An injured tailbone can have a negative impact on pregnancy and childbirth. Sometimes it is impossible to completely eliminate the damage. But the treatment will definitely help a woman carry a child more easily and give birth by caesarean section.
Treatment
Treatment methods for bruises can be divided into two large groups: traditional in the form of drugs and treatment methods, and non-traditional in the form of traditional medicine. Ideally, you can combine techniques from both groups. This solution will help you get rid of bruises in less time.
Medication
If the situation does not require hospitalization, the bruise is treated using standard methods. Namely:
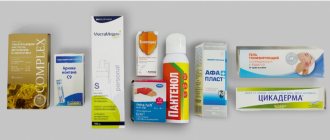
- Preparations for external use: gels, ointments, creams;
- Physiotherapeutic procedures. These include electrophoresis, heating, laser therapy. All these procedures are aimed at eliminating subcutaneous clots and stimulating skin regeneration.
Creams, ointments, and other treatments for bruises are widely available.
In every pharmacy you can find a huge selection of such products. But when choosing, it is important to pay attention to the composition, influence and age restrictions. Not all products are suitable for children.
With regular and correct use of the ointment, you can get rid of bruises and swelling within a few days. And if you supplement your treatment with physical therapy, you can expect results even faster.
Traditional methods
Bruises and bruises can also be treated with traditional medicine. The only rule is that you can start using them a few days after the injury.
Among the folk recipes for bruises and bruises on the face it is worth mentioning:
- Cabbage leaf or raw potato. They should be applied to the damaged area. Thanks to this, swelling quickly decreases;
- Honey. Has a good laxative and anti-inflammatory effect. You can even not limit yourself to the area of the bruise, but apply honey all over your face, creating the appearance of a mask;
- Camphor oil. To obtain the effect, it must be applied with light rubbing movements;
- Compresses. It is best to cook them with onions or salt;
- Alcohol-based compresses. In this case, the rosemary plant can be the basis. Has a warming and antiseptic effect;
- Arnica decoction. This measure is applied not externally, but internally. It not only strengthens the immune system, but also stimulates regenerative processes.
Applications with honey are a folk method for treating bruises of the soft tissues of the face.
And, of course, one should not underestimate the influence of standard massage measures in the form of light stroking and rubbing.
How long does it take for a bruise under the eye to last?
How long does it take? If after the blow you do not provide first aid and subsequently do not engage in treatment, a moderate or severe hematoma will disappear within a maximum of two weeks (plus or minus two to three days, taking into account individual physiological characteristics).
The speed of bruise resorption also depends on the time of year .
In hot weather, bruises take longer to heal. If a person immediately takes action and then treats the injury site with special ointments, the healing process takes from several days to a week .
Occasional mild hematomas, regardless of whether medications were used or not, usually resolve within three days.
Consequences
Complications with bruises are quite possible. It all depends on the nature of the injury and which area of the face was damaged. Possible consequences include:
- Nerve damage. completion. This is quite dangerous, since it is not always possible to fully restore their functionality. This means that the affected part of the face may stop moving;
- Deterioration of vision. If the area around the eyes is bruised, there is also the possibility of damage to the nerve responsible for visual functions. Again, the outcome depends on the nature of the injuries. Both partial and complete loss of vision is possible, which is much less common;
- suppuration at the site of the bruise in the form of an abscess;
- bleeding that, if not treated immediately, may lead to fainting or shock;
- Cyst formation in the presence of hematomas.
In case of serious injuries, the bruise may be accompanied by a concussion, deformation of the bones of the nose or jaw. As a result, a person may later suffer from conditions such as sinusitis or sinusitis.
Symptoms after hitting your head
Some symptoms after an impact may indicate serious brain damage - a hematoma or hemorrhage. An alarming signal is also a headache after a blow, which does not go away the next day, and increases significantly when tilting the head. With hemorrhage, the headache cannot be relieved by anything.
Hitting your head can have different consequences:
- The appearance of nausea and vomiting;
- Double vision;
- Dizziness;
- Unsteadiness when walking;
- Noise in ears;
Prevention
Almost all of us have had bruises on the soft tissues of our faces in our lives. Unfortunately, this cannot be completely prevented. However, in order to at least minimize the risk, it is necessary to take basic precautions and safety measures. When it comes to children, it is important to teach them from an early age how to avoid traumatic situations.
If facial bruises do occur, do not leave it unattended and take appropriate measures. You can do this yourself or seek medical help.