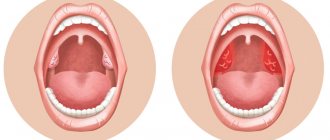
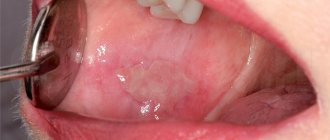
Plugs in the palatine tonsils (or tonsils) are purulent accumulations in the lacunae of the tonsils. In medicine you can find other names for this pathology: purulent plugs, caseous plugs.
Most corks are white, but can have a yellow, brown or gray tint, depending on their composition.
Tonsil plugs may be soft to the touch or harder if they contain a large amount of calcium. Their size varies from a few millimeters to a centimeter. Both men and women are equally susceptible to their appearance, regardless of age.
Some patients mistakenly think that this condition does not need to be treated. But this is fundamentally wrong! The presence of purulent accumulations in the palatine tonsils contributes to the development of complications (not only in the upper respiratory tract, but even in the joints, kidneys and heart!).
Why does an accumulation of pus occur in the tonsils? How to treat tonsil plugs? And is it possible to carry out treatment at home? You will find answers to all your questions in our new article.
Tonsil plugs: causes
To find out the etiology of the occurrence of purulent accumulations in the tonsils, you need to understand what role the palatine tonsils play in the body.
The tonsils are an important organ of the human immune system, which is the first to stand in the way of bacteria and viruses that enter the body through the mouth. As soon as “strangers” reach the surface of the tonsils, they begin to intensify the production of leukocytes, which enter into battle with pathogenic microorganisms. As a result of such “battle actions”, dead leukocytes, bacteria, and epithelial remains accumulate in the lacunae of the tonsils. Over time, minerals accumulate here, and the contents of the lacunae begin to harden, forming caseous plugs.
The main cause of traffic jams is chronic tonsillitis. But they can also form in the palatine tonsils for various reasons:
- accumulation of staphylococci, streptococci, pneumococci and other bacteria;
- in people who have a weak immune system;
- frequent sore throats;
- the presence of herpes virus and fungi in the body;
- dental problems (caries);
- viral infections (flu, ARVI).
Each of the above reasons can provoke inflammation of the tonsils. The risk of accumulation of caseous masses in the lacunae of the tonsils is increased by unhealthy diet, smoking, and alcohol consumption.
Traffic jams do not form just like that, for no reason. They are a consequence of another disease and signal that an inflammatory process is underway in the body.
Surgical intervention
If the disease is advanced, then the patient will have no choice but to lie on the operating table. This is an extreme measure that is used infrequently, but sometimes the degree of development of the disease is so severe that no antibiotic can cope.
Nowadays, there is an effective and safe method for removing ulcers in the throat. It is called laser lacunotomy. This is cauterization, due to which the bacteria are not able to develop further and the disease goes away. But this method of dealing with ulcers is very expensive, which makes it inaccessible to people with low incomes.
In cases where the tonsil damage is very extensive, tonsillectomy is performed. This surgical treatment method involves complete removal of the organ. The operation is performed under local anesthesia.
The procedure is quite painful and unpleasant, therefore, in order to prevent such developments, it is necessary to prevent the occurrence of ulcers. This should include, first of all, proper nutrition, outdoor sports and hardening. But you need to dress appropriately for the weather and avoid severe hypothermia. A person who does not want to face the appearance of tonsillitis, pharyngitis and other troubles should stay away from cigarettes, drink alcohol in extremely moderate quantities, or even better, give it up altogether.
Symptoms
Small accumulations, as a rule, do not cause significant symptoms. With large accumulations, the patient may experience the following symptoms of inflammation:
- bad breath;
- whitish dots are clearly visible on the surface of the tonsils;
- persistent sore throat;
- pain while swallowing;
- body temperature may be increased to 37-37.7 degrees;
- a feeling of discomfort at the site of accumulation of purulent masses;
- swollen tonsils;
- weakness, lethargy, general malaise;
- decreased performance;
- loss of appetite;
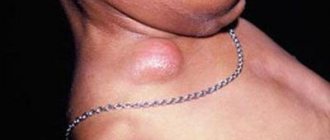
- enlarged lymph nodes;
- pain may radiate to the ears.
Traffic jams appear gradually, so in the early stages of the disease the patient experiences only discomfort when swallowing and a sore throat.
This condition is extremely dangerous for pregnant women! In addition to the fact that it has a detrimental effect on the general condition of the expectant mother, it can negatively affect the development of the fetus and, in the worst case, provoke a miscarriage. Therefore, it is extremely important to contact an otolaryngologist in time to receive competent recommendations on how to effectively treat tonsillitis during pregnancy and avoid complications.
Advantages and disadvantages of the pus removal procedure
It is necessary to remove pus from the tonsils in severe cases of the disease in a medical facility. Ulcers are containers where there is a large accumulation of various bacteria. After two days of antibiotic therapy, pathogenic microorganisms are destroyed. When the infection is defeated, the pus stops secreting, and the plugs disappear after 3–4 days.
If you do not remove the inflammation from a purulent sore throat, but simply start fighting the traffic jams, the patient’s condition will only worsen. There is a risk of reappearance of purulent discharge on the tonsils, and irritation and inflammation of the mucous membrane will cause an increase in temperature.
The situation will lead to the spread of infection and damage to the mucous membrane. When you cleanse your throat with hard objects on your own, the pus seeps even deeper.
Help yourself?
The biggest mistake most patients make is overconfidence that caseous plugs can be removed at home using improvised means. They use a whole arsenal of objects that are absolutely not intended for this: spoons, forks, toothpicks... At best, such amateur activities simply will not bring results, at worst, they will cause injury to the surface of the tonsils and provoke severe bleeding, swelling and inflammation! This will most likely be followed by a sore throat! Plus, if you press incorrectly with a hard object on the accumulation of pus, you can push it even further into the thickness of the tonsil.
Some people try to gargle, believing that gargling will bring relief. Yes, the feeling of discomfort in the throat temporarily passes, but the accumulations of pustules do not disappear, because the rinsing solution comes into contact only with the surface of the tonsils, and getting inside it is extremely problematic, or rather, impossible. Therefore, this method is also not effective.
The best method to get rid of traffic jams is to consult an otolaryngologist!
Hexoral against purulent sore throat
For acute tonsillitis, all drugs from the HEXORAL® line can be used.
You can treat the throat with a sore throat (acute tonsillitis) using HEXORAL® spray based on hexethidine. It allows you to evenly cover the surface of the mucous membrane of the tonsils and pharynx, which contributes to a more effective fight against infection8. A solution of HEXORAL® with hexethidine and a combination of essential oils7 may be suitable for gargling.
The use of hexetidine preparations is prescribed in clinical guidelines for the treatment of acute tonsillopharyngitis2. Hexetidine is an antiseptic that is active against most bacteria, herpes simplex viruses type 1, influenza A, PC virus that affects the respiratory tract, and fungi. In addition, it has a mild analgesic effect7.
Both HEXORAL® spray and solution are approved for use for local treatment of tonsillitis in adults and children over three years of age7,8.
Lozenges with a neutral mint flavor HEXORAL® TABS based on chlorhexidine and benzocaine have antiseptic properties and analgesic properties. They are approved for use in adults and children aged 4 years and older9.
For adults and children over 6 years old, HEXORAL® TABS CLASSIC is available with the flavors of orange, black currant, lemon and honey. It is based on a combination of the antiseptics amylmetacresol and dichlorobenzyl alcohol, which help in the fight against tonsillitis pathogens10.
HEXORAL® TABS EXTRA may be suitable for children over 12 years of age and adults. In addition to the antiseptic component, it contains lidocaine, which can relieve even severe sore throat11.
The information in this article is for reference only and does not replace professional advice from a doctor. To make a diagnosis and prescribe treatment, consult a qualified specialist.
Up to contents
Literature
- Dergachev V. S. Angina. Clinic, diagnosis and treatment algorithm. Choice of local antibacterial therapy // Regular issues of “RMZh” / No. 18. – 2007. – P. 1350.
- Clinical recommendations Acute tonsillopharyngitis // National Medical Association of Otorhinolaryngologists / 2016.
- Kunelskaya N.L., Turovsky A.B., Kudryavtseva Yu.S. Sore throats: diagnosis and treatment // General Medicine / No. 3. – 2010. – P. 4-9.
- Krasnova E.I., Khokhlova N.I. Differential diagnosis and treatment tactics for acute tonsillitis (tonsillitis) at the present stage // Attending physician / No. 11. – 2022. – P. 58-63.
- Shcherbakova M. Yu., Belov B. S. A-streptococcal tonsillitis: modern aspects // Pediatrics / Volume 88. - No. 5. – 2009. – P. 127-135.
- Instructions for use of the drug HEXORAL® solution // Reg. number P N014010/02 //
- Instructions for use of the drug HEXORAL® aerosol // Reg. number P N014010/01 //
- Instructions for use of the drug HEXORAL® TABS // Reg. number LSR-002626/07 //
- Instructions for use of the drug HEXORAL® TABS CLASSIC // Reg. number P N015976/01 //
- Instructions for use of the drug HEXORAL® TABS EXTRA // Reg. number LSR-004122/09 //
Up to contents
Possible complications
As already mentioned, the presence of clusters of caseous masses is not as harmless as it might seem at first glance. The danger of this condition is that pathogenic microflora from the lacunae of the tonsils can spread to other organs beyond the tonsils and provoke various kinds of complications:
- Peritonsillar abscess of tissue around the tonsils. A severe inflammatory process starts in the tissues around the tonsils. A patient with this condition experiences a sore throat. He can't help but feel like there's a foreign object stuck in his throat. There are difficulties with swallowing and wide opening of the mouth (trismus of the masticatory muscles). Periodically, the patient has a fever, and other unpleasant symptoms of intoxication of the body appear. In this case, only opening the peritonsillar abscess, sometimes with the simultaneous removal of the tonsils (abscessonsillectomy), will help improve the patient's condition.
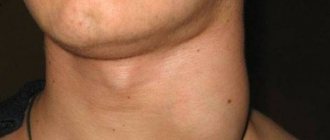
- Cervical phlegmon is an infection of the tissue of the neck. The patient experiences severe pain at the site of inflammation, and the body temperature rises to 40°C. The danger is that a purulent infection can enter the blood and cause sepsis and purulent damage to other organs. The abscess can also descend into the mediastinum - the case where our heart is located. This inflammation is called mediastinitis. This is a disease with an extremely high mortality rate!
- Sepsis (blood poisoning), caused by infection in the blood. This condition is extremely dangerous for humans and requires urgent hospitalization.
- Kidney diseases.
- Joint diseases.
- Heart diseases.
Types of disease
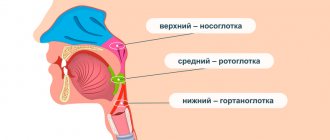
The inflammatory process can occur on the left or right in the pharynx. Such inflammation is called one-sided - respectively, a left-sided or right-sided abscess. If inflammation occurs on both the left and right at the same time, this is a bilateral type of inflammation.
If we take the location of the purulent “pocket” as the basis for the classification, the following types of disease are distinguished:
- anterior - the most common type of diagnosis; the tissues above the tonsils become inflamed;
- posterior, when purulent inflammation occurs between the posterior palatine arch and the tonsil; such inflammation can spread to the larynx;
- lower, when inflammation is located at the lower pole of the tonsil, while the anterior palatine arch moves forward and downward;
- external (lateral) - a less common, but most severe type, in which a suppurating cavity appears between the edge of the tonsil and the wall of the pharynx. With this form of the disease, pus can break into healthy tissue in the neck.
Treatment of tonsil plugs
When contacting an ENT doctor, the patient is offered conservative treatment, which includes washing the tonsils, physiotherapeutic procedures and drug therapy.
There are two methods of rinsing: removing pus with a syringe and hardware rinsing. The method using a syringe is used much less frequently if the patient has a strong gag reflex. The most effective method is to wash the tonsils using a vacuum method using the Tonsillor apparatus. In our ENT clinic, we use a special vacuum attachment for this, which has no analogues today! With the help of this attachment, it is possible to effectively and painlessly wash the entire contents of the lacunae of the tonsils, and improve the patient’s condition after the first session.
How to treat peritonsillar abscess?
Treatment is carried out in two stages:
- Surgical.
- Conservative.
First of all, it is necessary to evacuate the pus from the peritonsillar space.
This can be done in the following ways:
A) Tonsillectomy - removal of the tonsils.
B) Puncture (puncture) and aspiration.
B) Opening (incision) and dividing the paratonsillar space.
After draining the pus, the patient should receive antibacterial and anti-inflammatory therapy.
Schemes for preparing antiseptic solutions
Self-production of Furacilin, medicinal decoctions, saline solution and a number of other disinfecting liquids is allowed. Cooking methods are listed in the table below.
| Solution | Way | Proportions |
| Saline | Sea or table salt is combined with warm water. | 1 teaspoon of substance per 200 ml of liquid |
| Furacilin | The drug tablet dissolves in boiled water; the solution is infused for up to half an hour. | 2 pills per glass of water |
| Chlorophylliptate | The medicine is mixed with water. | 1 part drug to 5 parts liquid |
| From propolis | The alcohol (aqueous) tincture is diluted with water. | Alcohol: 1 tsp. medical product for half a glass of liquid. Water: 1:3 |
| From medicinal herbs | Medicinal infusions (oak bark, sage, chamomile, calendula) are poured with boiling water, infused for 30 minutes, and filtered. | 1 tablespoon per 200 ml of boiling water. |
When using solutions for the treatment procedure, you must remember the main rule: if you have an individual intolerance to the components of the product (this is often manifested by allergic reactions), the use of disinfectant liquids is prohibited.