What determines the speed of recovery?
With timely consultation with a doctor and proper treatment, the acute form of stomatitis can be cured in 3-7 days.
Optimistic forecasts are not always justified: too many factors influence the duration of the disease. Among them:
- reasons that caused the disease. So, for careless handling of the fork you will have to pay with 2-3 days of discomfort. But allergic stomatitis will not go away until the doctor identifies the allergen;
- correct diagnosis . Treatment of viral stomatitis is fundamentally different from fungal stomatitis, and prescriptions for the catarrhal variety have nothing to do with the list of measures necessary to treat the nicotine form;
- treatment literacy . And here only the professionalism and experience of the doctor will help;
- accuracy of compliance with recommendations . An interrupted course of antibiotic therapy, ignoring the need for further examination by other specialists, omissions in taking medications - all this prolongs the course of the disease;
- state of immunity . The lower the body’s protective function, the higher the likelihood of developing stomatitis and the longer the recovery period.
At the first symptoms: burning of the mucous membranes, unpleasant itching, the appearance of small but painful ulcers on the palate, inner surface of the lips or cheeks, you need to consult a dentist as soon as possible. After all, the main danger of stomatitis is its transition to an advanced form. And then treatment will take a long time and not always successfully. The risk factors here are:
- taking medications
that reduce immunity and disrupt intestinal microflora, for example, antibiotics; - vitamin deficiency
, including seasonal; - weakened immunity
. That is why it is absolutely impossible to let stomatitis take its course in infants, elderly people and pregnant women; - disruptions and restructuring of the hormonal system
. And again, expectant mothers are targeted, and along with them, teenagers in the transition period; - chronic diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, oral cavity, endocrine system
.
Even constant stress at work or misunderstandings in the family can cause stomatitis and its transition to a chronic form. Moreover, to completely cure the disease in this case, the efforts of the patient and the dentist are not enough. You will need to completely change your habits, diet, establish sleep and rest patterns, and even consult a psychologist.
Symptoms
The development of the disease occurs in several stages.
At the initial stage, the symptoms are very similar to the manifestations of acute respiratory infections: there is an increase in body temperature to 40 degrees, enlarged lymph nodes, the person experiences general malaise, weakness and loss of appetite. Already at this stage, the patient begins to experience unpleasant painful sensations in the mouth, which intensify while eating or talking. When examining the oral cavity, you may notice redness.
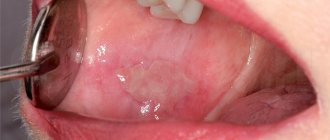
The appearance of ulcers (ulcers) with clearly defined boundaries, up to 5 mm in size, marks the beginning of the second stage of the disease. Aphthae can form on the tongue (on its lateral surfaces), on the inner surface of the lips and cheeks. The ulcer is bright red in color, covered with a fibrous coating, and severe pain occurs when touched. As a rule, the inflammatory process at this stage is accompanied by enlargement of the lymph nodes, and it becomes problematic for the patient to eat solid food. Within two weeks, the mucous membrane is restored to its previous state.
However, a chronic form of the disease, characterized by swelling of the mucous membrane, acquiring a pale tint, cannot be excluded. On average, the chronic stage lasts 2 weeks: if treatment is not resorted to, the ulcers can begin to increase in size and bleed, causing a lot of inconvenience.
How many days does it take for stomatitis to go away?
Dentists, like doctors of other specialties, really don’t like asking patients about recovery time. But statistics on the cure of various forms of the disease still exist. And the patient has the right to know how quickly he will restore his health.
Aphthous (bacterial) stomatitis
Causes:
The causative agents of aphthous stomatitis are streptococci, staphylococci, gonococci, mycobacteria, Helicobacter pylori.
Features of the flow:
This form of stomatitis got its name from the name of superficial ulcers on the mucous membrane - aft. They are formed at the slightest decrease in immunity, for example, in spring or autumn, if an untreated bacterial infection is lurking in the patient’s body.
In addition to damage to the mucous membranes of the mouth, acute bacterial stomatitis causes fever and inflammation of the submandibular lymph nodes. The most unpleasant thing about the disease is its very rapid transition to a chronic form and constant relapses.
Treatment:
It is simple to classify aphthous stomatitis, as well as to cure its acute form. For this purpose, rinses with antiseptics (Chlorhexidine, Furacillin), antipyretics (Paracetamol), and antibiotics (Amoxicillin, Lincomycin) are prescribed.
To prevent the disease from becoming chronic, it is important to identify the pathogen. To do this, a bacterial culture of the afts is carried out, and blood tests may be prescribed for the presence of antibodies. And after determining the culprit of the disease, the dentist will hand over the patient to a specialized specialist: a therapist (pediatrician), gastroenterologist, infectious disease specialist or venereologist.
The recovery period with timely initiation of treatment for acute aphthous stomatitis is 7-10 days. When self-medicated, the disease quickly turns into an ulcerative form, which does not heal for months.
Viral stomatitis
Causes:
rarely - causative agents of measles, chickenpox, most often - causative agents of herpes. The infection is transmitted by contact and airborne droplets.
Features of the flow:
The disease is severe, with high fever, weakness, nausea and vomiting. Multiple small bubbles filled with liquid form on the mucous membrane. After 3-4 days they burst and heal. But with weakened immunity, new ones immediately form in their place.
Unfortunately, the herpes simplex virus instantly spreads both in the family and in children's groups. And most of us, without knowing it, are its carriers. While the immune system is in order, the virus quietly sleeps in the nerve ganglia. But if you get cold or nervous, stomatitis is right there.
Treatment:
at high temperatures, it is necessary to adhere to bed rest, take antiviral (Acyclovir, Gerpevir) and antipyretic drugs (Nurofen, Paracetamol). Treatment of the oral cavity with local antiseptics (Chlorhexidine) multiple times throughout the day is mandatory. To prevent infection of all household members, it is important to provide the patient with separate dishes and personal hygiene items.
The recovery time for viral stomatitis is 8-10 days. Local immunostimulants, for example, chewable tablets with echinacea, will help prevent the disease from becoming chronic.
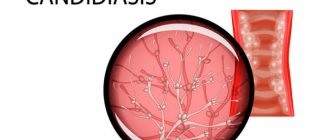
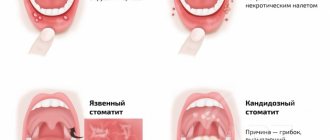
Fungal stomatitis (candidiasis, thrush)
Causes:
The causative agent is the fungus Candida.
Features of the flow
: This form of stomatitis primarily affects children under 3 years of age. Adults are threatened with fungal stomatitis only in the case of a very strong decrease in immunity, for example, with long-term aggressive antibiotic therapy.
A characteristic feature of the disease is a white cheesy coating on the oral mucosa. At the initial stage, it is easy to remove with a regular napkin. Later, this process becomes painful, erosions and minor bleeding occur.
Treatment:
Since fungal stomatitis mainly affects children, doctors often prescribe decoctions of medicinal herbs, such as sage and chamomile, as antiseptics for treating the oral cavity. The treatment regimen must include antifungal drugs (Futsis, Fluconazole, Nystatin, Candida drops) and immunomodulators (Viferon, Interferon).
The recovery time for candidiasis directly depends on the state of the immune system. For some, therapy will help in 4-5 days, for others it will be difficult to overcome the disease in a month.
Catarrhal stomatitis
Causes:
poor oral hygiene, use of other people's personal hygiene items, pockets of infection in the mouth - caries, tartar, trauma to the mucous membrane from hot food, sharp objects, chipped teeth or fillings, biting the cheeks.
Features of the flow:
catarrhal stomatitis occurs more often than others. It does not give such vivid visual symptoms as aphthous or fungal, so it is often detected at a very advanced stage.
Often the only sign of catarrhal stomatitis for a long time is only bad breath. It cannot be removed by diet or careful hygiene. A little later, patients notice increased salivation and inflammation of the gums. After a while, a yellowish coating will appear on the tongue, and bleeding of the soft tissues will begin.
Treatment:
catarrhal stomatitis is perfectly curable. This does not require antibiotics or antifungals. It is enough to rinse your mouth several times a day with either a decoction of sage, chamomile, a solution of calendula tincture, or use the pharmaceutical antiseptic Chlorhexidine. The anti-inflammatory and analgesic drug Cholisal will also significantly speed up the healing process.
When the traumatic factor disappears, the exacerbation process does not last long: 3-5 days. But, if the cause is not eliminated, for example, a chipped tooth, the healing process will take longer each time. Over time, ulcerative necrotic lesions form on the mucous membrane, to combat which the dentist will have to use the entire arsenal of the most powerful medications.
Allergic stomatitis
Causes:
allergens, which can be food and medicine, oral care products, and even the materials from which fillings, crowns, and orthodontic systems are made.
Features of the flow:
allergic stomatitis is the most severe form of the disease. It begins with slight discomfort: swelling and redness of the mucous membrane. If contact with the allergen continues, erosions form on the gums, tongue, inner surface of the lips and cheeks, and unbearable itching appears.
Over time, it becomes painful for patients not only to talk and eat, but even to breathe air through their mouths. At the same time, the general condition is steadily deteriorating. And if the irritant is not removed, even Quincke's edema and death are possible. Fortunately, sluggish allergic stomatitis is much more common: it does not produce such pronounced symptoms and does not lead to death, although it torments the patient for years.
Treatment:
The main task of the doctor is to identify the causative agent of the allergy. Without this, no drugs will lead to recovery. You can temporarily stop an allergic reaction with antihistamines (Fenistil, Claritin).
The recovery time for allergic stomatitis directly depends on the speed of identifying the allergen and eliminating contact with it. Under the most favorable circumstances, the doctor will overcome the disease in 10-15 days.
How is stomatitis treated in adults?
Complex treatment should be carried out only under the supervision of a doctor. On the one hand, it is important to eliminate the cause of the disease, on the other hand, to alleviate the symptoms and stimulate the restoration of the oral mucosa. The doctor prescribes both local and general therapy, depending on the form of stomatitis.
The following groups of drugs may be used in treatment5:
- antibacterial, antiviral or antifungal (depending on the pathogen);
- antiallergic drugs;
- anti-inflammatory drugs;
- enzymes;
- agents that stimulate the restoration of the oral mucosa;
- drugs that enhance immunity and improve metabolism.
For some forms of stomatitis, the doctor may prescribe combination medications. For example, Metrogyl Denta®, which is indicated for the treatment of aphthous stomatitis7,8,10.
Metrogyl Denta® is a dental gel that contains metronidazole, which has an antibacterial effect, and the antiseptic chlorhexidine8. This combination can suppress the activity of various types of microorganisms and helps fight infection7,8.
Metrogyl Denta® is widely used in dentistry; it is approved by the Dental Association of Russia (StAR)9. The duration of treatment, dose and frequency of use is determined by the doctor, depending on the degree of damage and severity of the disease.
The appearance of stomatitis may mean that a person has a weakened immune system or that the mucous membrane has been affected by some damaging factor. And sometimes redness and painful sores in the mouth are symptoms of a chronic disease1. A dentist helps to understand the causes and cope with inflammation, and if stomatitis has “deeper roots,” specialized specialists are involved in the treatment. After therapy, it is important to do everything to prevent the disease from occurring again. You need to regularly visit the dentist, replace dentures if they cause mechanical injury, monitor oral hygiene and give up bad habits1,5.
The information in this article is for reference only and does not replace professional advice from a doctor. To make a diagnosis and prescribe treatment, consult a qualified specialist.
to come back to the beginning
How long does stomatitis last in children?
In children, just like in adults, the speed of recovery directly depends on the type of disease. Approximate period: 7-14 days. If you consult a doctor in a timely manner and start treatment immediately, this time is enough to cope with the disease.
Often recovery is delayed due to the fault of the parents themselves. For example, they did not monitor the timely taking of medications and the implementation of treatment procedures, ignored the doctor’s recommendation to take additional tests, or turned to a pediatric dentist only after long-term self-medication did not lead to a positive result.
But sometimes even the most responsible parents cannot cope with stomatitis for a long time. Alas, this happens. This disease is insidious and multifaceted, its course depends on many factors, and is often unpredictable even for an experienced doctor.
Diagnostic methods
Dentists, pediatricians and pediatric infectious disease specialists treat inflammatory diseases of the mouth in children. During the appointment, the doctor will examine your complaints, review your medical history to identify risk factors, and conduct a physical examination.
As a rule, a general and instrumental examination of the mouth is sufficient to make a preliminary diagnosis, since different forms of stomatitis manifest themselves as peculiar ulcers. Additional research may be required to clarify the nature of the disease.
How to understand that stomatitis has passed?
The fact that the disease is a thing of the past is indicated by the complete return of dental health to the level that preceded the disease. This:
- disappearance of ulcers and aphthae;
- stop bleeding gums;
- extinction of the inflammatory process;
- no pain when talking or eating;
- getting rid of bad breath.
Despite the fact that recovery is obvious to the patient, only a doctor can put an end to treatment. As a rule, this does not require additional tests. Treatment regimens have been verified over years of experience, and a routine examination is quite sufficient to confirm a cure.
Often the patient’s well-being returns to normal after 2-3 days, the ulcers heal, and the pain recedes. It is important not to stop treatment at this point. Antibiotics, antiviral and antifungal drugs are taken in courses for a reason. Their duration directly depends on the life cycle of pathogens. To completely destroy some it will take 5 days, others – 20. And only a doctor can determine the duration of treatment!
If you ignore the prescriptions and stop taking the medications, stomatitis will return at the first slight decrease in immunity. And it will be more difficult to cure him.
Diagnosis of stomatitis
Usually, a visual examination of the patient is sufficient to make a diagnosis. If stomatitis is suspected, which is the result of diseases of the internal organs, consultations with highly specialized specialists are prescribed.
If the disease is of infectious origin, the patient is sent for laboratory tests:
- taking a swab from the mouth to determine the type of pathogens;
- blood test to detect antibodies to pathogens of internal organ infections;
- ELISA or PCR (polymerase chain reaction) is a study of biomaterial to identify pathogens of infectious diseases.
If stomatitis is accompanied by a significant deterioration in health or elevated body temperature, it is necessary to undergo general blood and urine tests. Diagnostics allows you to assess the general condition of the body and identify pathologies that cause inflammatory processes in the oral cavity.
Can stomatitis go away on its own?
Stomatitis can go away on its own without treatment, especially if we are talking about the catarrhal form. For example, while eating, the cheek was injured by a bone, and untreated caries caused infection of the wound. But the human immune system is in perfect order, and even if any infections are sleeping in the body, the defense system does not give them the slightest chance to wake up.
In this case, stomatitis will actually go away on its own in 5-7 days. But if you add at least rinses with antiseptics, recovery would occur within 3-4 days. But it’s not even the speed of healing that’s important, but the guarantees. So, if you consult a doctor in a timely manner, in 99% of cases the patient will be healthy within 2 weeks.
In the absence of treatment, the probability of forgetting about the problem in such a short period of time is less than 50%. For one simple reason: there are at least 5 varieties of the disease, and several times more pathogens. And only a doctor can determine the culprit of stomatitis.
If symptoms of stomatitis appear in a child, the parent’s task is to immediately seek professional help. For adults, we can recommend the following: if stomatitis does not go away on its own, there is no point in delaying visiting a doctor for longer than 7 days. Without medication, the disease will not go away.
Do not ignore preventive visits to the dentist.
It is enough to visit a specialist 1 – 2 times a year, which will allow you to promptly identify any dental problem at an early stage of development. This means that its elimination will be quick, easy and without complications.
By clicking the “request a call” button you agree to the personal data processing policy.
What is aphthous stomatitis
The exact mechanisms of development of aphthous stomatitis are still unknown.
It is generally accepted that with aphthous stomatitis, the infection enters the oral cavity, but does not cause a protective reaction in the body's immune cells. They simply do not recognize the pathogen. The infection changes the composition of saliva, this causes the activity of lymphocytes and the immune system attacks areas of the oral mucosa as a foreign chemical agent.
As a result of this confrontation, erosions form on the mucous membrane.
Aphthae have a round or oblong shape with a diameter of up to 5 mm. Outwardly, they resemble ulcers, covered with a white or gray coating and outlined with a red rim. On the mucous membrane, aphthae are located in groups or separately.
If more than three canker sores have formed in the mouth, this is a severe form of stomatitis. Despite their small size, the ulcers are painful and interfere with eating and talking. With stomatitis, the temperature may rise and weakness may appear.
If a person's immune system is weak, it will continue to interpret the presence of foreign chemicals in the mouth as a danger and canker sores will become chronic. Therefore, it is important to start treatment of aphthous stomatitis on time and carry it out under the supervision of a doctor.
Consequences of advanced stomatitis
Complications of stomatitis are scary and varied. So, if treatment is not started in time for an infant, he will refuse to eat, which in turn will lead to weight loss and growth retardation. Lack of treatment for the disease at any age is guaranteed to reduce immunity, and is likely to provoke a sore throat or pharyngitis. Herpes stomatitis often results in decreased vision. And ignoring the aphthous form of the disease is fraught with scarring of soft tissues and even limiting the mobility of the jaw bones.
If bacterial stomatitis is left untreated, the disease very quickly turns into an intractable ulcerative form. If viral and fungal stomatitis is not treated, it will return again and again due to stress, colds, and vitamin deficiency. Well, the allergic form of the disease can even lead to death.
Why can stomatitis not go away for a long time?
If stomatitis is difficult to treat, most likely the disease has already become chronic or recurrent. The reason for this, with proper prescriptions and compliance with all doctor’s recommendations, may be:
- immunodeficiency states;
- chronic diseases of the nasopharynx: sinusitis, pharyngitis, tonsillitis;
- chronic diseases of the gastrointestinal tract: dysbacteriosis, colitis, gastritis, gastric ulcer;
- permanent injury to the gums and tongue from dental plaque, dentures, the edge of a chipped tooth or poorly fitting braces;
- allergies to toothpaste, mouthwash, medications, filling material.
Constant stress and depression have a detrimental effect on your health. They seriously reduce immunity, provoking the development of many diseases, including stomatitis.
Bad habits, such as smoking and eating seeds, also interfere with recovery. In both cases, the mucous membrane and tongue are constantly injured by hot smoke or the sharp edge of sunflower seeds.
Causes
Among the causes of stomatitis in adults, general and local ones are distinguished1. The latter include any damaging factors that act directly on the mucous membrane (too hot food, chemicals, mechanical damage), the general ones include chronic diseases of internal organs not related to the oral cavity (infectious, allergic, systemic), as well as metabolic disorders substances1.
In the first place in terms of prevalence are infectious stomatitis - viral, fungal or bacterial2.
The presence of various microorganisms in the oral cavity is normal. In a healthy, intact state, the mucous membrane can resist infection. However, with a decrease in local immunity, injury or poor hygiene, pathogens can penetrate deeper layers and cause inflammation1,3,4.
The soft tissues of the oral cavity can be injured by improperly fitted dentures, pieces of food or sharp chips on the teeth. Inflammation is often provoked by thermal or chemical factors, for example, very hot or spicy food, cosmetics3.
The following factors also contribute to the development of stomatitis3,4,6:
- allergic reactions1;
- poor oral hygiene;
- dental diseases;
- heredity;
- stress;
- hormonal disorders;
- diseases of the gastrointestinal tract;
- smoking.
A drug can become an irritant that provokes inflammation; for example, stomatitis in patients with bronchial asthma occurs during the use of inhalers with glucocorticosteroids (hormonal anti-inflammatory drugs)3. Also, the protective barrier of the mucous membrane is exposed to harmful substances in the air with which a person comes into contact due to professional activities3,5.
What to do if stomatitis does not go away?
When the disease does not subside, the main thing is to be patient. If additional tests have not been done yet, now is the time to do them. If the dentist recommends seeing a gastroenterologist or otolaryngologist, you need to listen to him. He doesn't do this because he wants to get rid of the patient. It’s just that in some cases it is more effective to fight the disease not alone, but with a team of specialists. The main thing is to identify the cause of the disease. And, unfortunately, in rare cases this can take months.
Types of stomatitis
In medicine, it is customary to distinguish two types of stomatitis:
- acute gingivostomatitis, which is caused by various viral infections;
- recurrent stomatitis (caused by staphylococci, immune diseases and problems with the gastrointestinal tract). As the name suggests, the disease tends to occur again and again - periods of exacerbation occur in autumn and spring, when there is a lack of vitamins.
Separately, it is worth highlighting herpetic stomatitis, which affects not only the immune system, but also the nervous system. It occurs most often in children under 3 years of age: during this period, firstly, the influence of maternal immunity on the baby’s body rapidly weakens, and secondly, the child begins to go to kindergarten, where he interacts with other children who may already be infected with the virus herpes.
How to prevent relapse?
If once stomatitis has already made itself felt, it is worth making some changes in your life that will help avoid relapse:
- do not put off dental treatment until later;
- do not ignore nasopharyngeal diseases;
- treat gastrointestinal problems in a timely manner;
- supplement your oral hygiene with a rinse and irrigator;
- Make a habit of eating vegetables or fruits at every meal;
- take a course of multivitamins twice a year;
- avoid injuring the oral mucosa with hot and cold foods;
- take care not only of your physical, but also of your mental health: get enough sleep, rest on time, pamper yourself.
It is especially important if you are prone to stomatitis to choose a competent dentist. At the first visit, you need to tell him about past problems so that the doctor can prevent the development of the disease. For example, be as careful as possible when removing tartar or immediately prescribe gum treatment with Metrogil Denta gel when installing a prosthesis.
Author: Elena Grunina Dentist-therapist, endodontist. Work experience more than 9 years.
The information is for reference only. Before treatment, consultation with a doctor is necessary.
Treatment of traumatic stomatitis
The choice of treatment tactics for traumatic stomatitis is largely determined by the nature of the damage that caused the inflammation. Therefore, first of all, the specialists of the Doka-Dent clinic eliminate the traumatic factor:
- Irritating dentures and braces are adjusted or remade;
- if the cause of traumatic stomatitis is a broken tooth, it is treated and restored;
- Tartar deposits are removed with professional cleaning.
Then the dentist proceeds directly to the treatment of traumatic stomatitis. If there are minor injuries, the wounds are washed with antiseptics. More serious lesions are anesthetized and then treated with anti-inflammatory drugs. If the wound is penetrating and deep enough, stitches may be required.
Further treatment of traumatic stomatitis is carried out mainly at home. The doctor prescribes various products for rinsing, applications and other procedures that should ensure the speedy healing of ulcers, erosions and wounds. In addition, the clinic specialist gives the patient the necessary recommendations that will help avoid relapses. Then a date for a follow-up appointment is set, at which the doctor will assess the success of the treatment.