The epidemiology (prevalence) of tongue cancer is on average 5 cases per 100 thousand population.
Among the recorded cases of oral tumors, it accounts for up to 60%. Despite the relatively simple diagnosis of this disease, there are advanced cases - people often do not notice the signs or ignore the symptoms of tongue cancer.
Causes of inflammation of the papillae on the tongue
If you have an inflammatory process in your mouth, contact your dentist immediately. Family dentistry in St. Petersburg is a clinic where every patient will be provided with assistance. The doctor will determine the causes of the disease and prescribe treatment. Problems may arise:
- When the patient’s diet includes excessive amounts of sour, sweet, spicy foods;
- If chronic stress develops in the body;
- When the patient received a tongue injury, burn, cuts, punctures;
- If the organ is affected by an allergic reaction;
- For some diseases of internal organs;
The surface of the muscular organ changes significantly under aggressive influence. The provoking factor is xerostomia, disease of the salivary glands, Sjogren's syndrome, diabetes mellitus. With glossitis, the sensitivity of the papillae increases. During the examination, the doctor must exclude HPV, leukoplakia, aphthous stomatitis, syphilis, and oral fibroma. Children are examined for scarlet fever.
Sometimes the disease can be triggered by acid reflux, gastritis, throat infections, systemic inflammation of the gingival tissues when the pathogenic microorganism develops rapidly. Taking some medications can cause pain. High concentrations of alkali or acid have a negative effect on the condition of the muscular organ. Injuries on the tongue can occur from a hard brush, dentures, or tartar.
Prevention methods, prognosis of tongue cancer
You can reduce the likelihood of developing the disease by giving up bad habits: smoking, drinking alcohol and chewing tobacco. If there is dental pathology that contributes to chronic injury to the mucous membrane, the oral cavity is sanitized: dentures are reinstalled, fillings are treated, and the bite is corrected.
Maintaining basic oral hygiene can significantly reduce the risk of developing cancer. In terms of prognosis, regular preventive examination by a dentist is important, during which the first signs of cancer can be noticed, which allows a person to be referred to an oncologist in a timely manner.
With radical combined treatment of tongue cancer in the early stages, the five-year survival rate approaches 90%; in advanced cases it drops to 60%. If treatment is started at the metastatic stage, the five-year survival rate is less than 35%, even in Moscow.
Symptoms
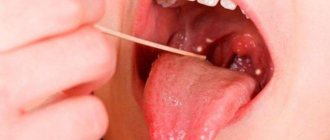
When the papillae on the tongue become inflamed, tissue sensitivity increases significantly and taste changes. Patients complain of unpleasant discomfort in the mouth. The taste spectrum is distorted and becomes unnatural. In addition, a number of other symptoms appear.
- Noticeable tissue swelling.
- Marked increase in size of the papillae.
- Tingling and itching.
- Burning, mild soreness.
If you do not consult a dentist in time, complications may develop: lingual eruptive papillitis. This disease occurs over a long period of time with an increase in body temperature. Most often the disease affects children. An alarming symptom is the appearance on the surface of the vocal organ of bubbles (pustules) filled with a transparent liquid. When the first signs of illness appear, you should immediately visit the dentist. Timely treatment of the disease minimizes complications and speeds up recovery.
Folded tongue
A folded tongue is a congenital structural anomaly characterized by the appearance of deep folds resembling wrinkles on the back of the tongue. The mucous membrane is not damaged, and the person does not experience any discomfort. The folds are located in the longitudinal and transverse directions and can appear both in childhood and in adulthood. Sometimes a folded tongue is a symptom of Melkersson-Rosenthal disease, but in general it is a variant of a normally developed organ.
Folded tongue
The reasons for the appearance of a folded tongue are not clear. No treatment is required, but it is necessary to regularly remove food debris from the folds. If you do not take care of your tongue, it may become inflamed and cause bad breath.
Localization
If the papilla on your tongue is inflamed, visit the dentist. Only he will be able to correctly determine the causes of the disease, find out what caused the damage to the mucous membrane of the mouth and the body of the tongue. The area where the disease is localized plays an important role in making the correct diagnosis. Pathology can cover the entire organ, part of it, or the sides. Based on this factor and the clinical picture, we can assume what exactly caused the inflammation.
In all languages
When the mucous layer of an organ is affected over its entire surface, the most common cause is a thermal or chemical burn. One can assume the infectious nature of the pathology. If the damage is severe, there may be no taste at all. Patients complain of severe burning.
On the root
Most often, the papillae on the tongue at the base become inflamed due to the action of allergens. The affected root of the muscular organ causes difficulties such as the perception of bitterness, because the inflammatory process has affected the circumvallate papillae. They are the ones responsible for this function. The patient's salivation increases, and the tissues in the oral cavity swell. This condition can also be caused by problems with the digestive system, too high or low acidity of gastric juice. It is on the back of the speech organ that bacterial or fungal glossitis is localized.
On the tip
The disease can affect the tip. This often occurs due to mechanical injuries or damage. The edge of the tongue is the first to come into contact with excessively hot food or aggressive drinks, which burns this area. Soft tissues often rub against sharp chips of crowns and are subject to accidental biting.
Side
The delicate surface on the sides often suffers from various anomalies. Leaf-shaped, conical, filamentous, mushroom-shaped structures are exposed by the teeth. This leads to an increase in the papillae, their hyperemia due to mechanical damage from fangs and molars. Also provoking factors are painful microorganisms and burns of chemical origin.
The most common types of glossitis
The most common occurrences in dental practice are:
- acute catarrhal glossitis;
- tongue abscess;
- desquamative glossitis.
Acute catarrhal glossitis is the most common type of inflammation. Inflammation can be caused by microbes or mechanical damage to the tongue. The predominant symptoms are pain, redness and swelling.
A tongue abscess is the appearance of an abscess in the tongue. The abscess can be superficial, under the mucous membrane, or maybe in the thickness of the tongue. Abscesses in the thickness of the tongue, in addition to pain in the tongue, can cause a disturbance in the general condition. A person develops a fever, a headache, and weakness. Most often occurs due to injury to the tongue.
Desquamative glossitis, also known as “geographic tongue,” most often appears in children. It appears in the form of various spots on the tongue, which look like a white coating, alternating with areas of pink mucous membrane. There are no changes other than appearance. Scientists have identified a clear reason for it. The main factors are believed to be bacteria, allergic reactions and hormonal imbalances.
Diagnostics
Basic diagnostic methods in dentistry allow a thorough examination to be made in order to make the correct diagnosis. During the initial examination, the dentist determines the size of the pathological zones, appearance, color, and shape of the organ. The doctor finds out whether there is swelling of the tongue, ascertains plaque and its localization, abrasions, punctures, eczema, ulcers. The health of gum tissue and teeth is important.
In order to determine the type of pathogen and the form of the disease, a number of tests are prescribed:
- Histological smear;
- Sensitivity is determined using a special test;
- A general blood test is informative;
Systemic pathologists are also excluded: HIV, syphilis, hepatitis, AIDS. If necessary, the patient is referred for consultation to a gastroenterologist, dermatologist, endocrinologist, otolaryngologist, or immunologist.
Features and structure
To understand how diseases are diagnosed by language, you first need to understand the physiological structure. A healthy human tongue has a soft pink tint, a smooth surface and a moist environment. It is made up of muscles, which makes it very mobile. The back area of the tongue that connects to the lining of the mouth is called the root.
The shade, shape and presence of lesions play an important role in identifying various diseases. The front (the most mobile part) is called the “body” of the tongue. The top area is called the "back". All zones in the tongue are covered with small papillae, the main function of which is to distinguish the taste of the food a person eats. For the same reason, such papillae make it a little velvety to the touch. Since ancient times, the tongue has been considered an organ of health. It was by this method that in most cases the patient was diagnosed, without using modern diagnostic techniques such as blood tests or ultrasound.
Treatment
The diagnostic result allows you to prescribe treatment. Therapeutic dentistry has new methods and technologies that will return the patient to health.
- The patient is advised to adjust his diet and reduce spicy and sour foods in his diet. Dishes should not be hot.
- Fillings and dentures that injure the mucous membranes need to be replaced.
- You should have your oral cavity professionally sanitized.
- Remove soft and hard deposits on crowns.
- Cure caries, gum inflammation.
The therapeutic course may include taking antibiotics, anti-inflammatory drugs, and a course of treatment for diseases of internal organs. Regular visits to the dentist are a way to prevent oral problems and complications of existing diseases.
An injured, inflamed muscle organ requires tissue regeneration. For this purpose, drugs containing carotene are prescribed: Aekol, Retinol, Chlorophyllipt, Lugol. Ointment applications are made from Solcoseryl and Cholisal. For pain, anesthetics are used: Trimecaine solution, Anastezin emulsion. Patients are recommended medications to stimulate the body's defenses and vitamins.
If the disease is infectious, a scraping is first done. A pathogenic microorganism is identified in the laboratory. Then therapy is carried out according to the obtained strains. Candidiasis is eliminated with fluconazole. Acyclovir is prescribed against herpes. Metrogil-denta treats protozoal infections.
Black tongue
Definition and symptoms
Black (hairy) tongue is a condition in which the surface of the tongue becomes keratinized and there is hyperplasia of the filiform papillae. The epithelium sloughs off, and bacteria begin to multiply on the lesions, producing a dark pigment, as a result of which the tongue becomes brown or black. The colored papillae resemble short hair in appearance, hence the name. The lesion spreads along the center line of the tongue, acquiring an oval or triangular shape.
Black tongue
The papillae reach a length of up to 2 cm and a diameter of up to 2-3 mm. Black tongue is not an independent pathology, but a symptom of various diseases or a consequence of the influence of a number of provoking factors. Occurs most often in men over 40 years of age. The disease occurs in two stages - in the first, the papillae grow and thicken without changing color. Timely treatment can prevent darkening and eliminate symptoms. During the second stage, the papillae begin to become keratinized and blacken.
Reasons for development
Factors causing lesions are divided into three groups:
- physical and chemical: antibiotic therapy, alcoholic beverages, cigarette smoke, insufficient oral hygiene, burn of the mucous membrane of the tongue;
- infectious: candidiasis, systemic fungal infections;
- pathological conditions of the body: fever, dehydration, decreased saliva production, metabolic disorders, diseases of the stomach and intestines, impaired trophism of the papillae of the tongue.
Treatment
Therapy consists of eliminating provoking factors, treating concomitant pathologies and following a diet. When diagnosing, diseases of the stomach and intestines, diabetes and fungal infection should be excluded. If candidiasis is detected, in addition to the main treatment, rinsing the mouth with salicylic acid and resorcinol is prescribed.
It is undesirable to eat salty, sour and bitter foods, which aggravate the course of the disease. If the papillae are severely overgrown, the cryodestruction method is used. The overgrown tissues are exposed to cold, after which they are removed.
Article on the topic: Candidiasis balanoposthitis in men
Prevention and prognosis
Prevention consists of timely treatment of the main pathologies, daily cleaning of the tongue with a special brush, and giving up alcohol and smoking. With adequate therapy and elimination of provoking factors, the prognosis is favorable, the tongue returns to normal within a few weeks.
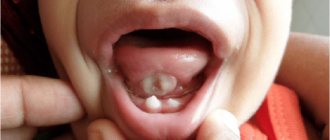
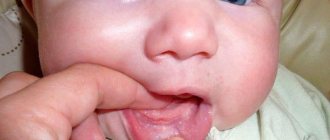
Inflammation of the papillae on a child's tongue
If the child’s body is weakened and he complains of discomfort in the mouth and pain in the muscle organ, parents should immediately show him to the pediatrician and pediatric dentist. The doctor will determine whether his papillae are red and whether there is an inflammatory process in the mouth. Once the diagnosis is made, therapy is prescribed. As a preventive measure, parents should ensure that the baby regularly brushes his teeth and rinses his mouth thoroughly. Children's immunity is not strong enough, so the body cannot cope with the disease on its own. The situation is complicated by the fact that children are curious; they put most objects in their mouths. To avoid serious complications, take your child to the dentist regularly.
Thrush as a cause of white plaque
Thrush in the mouth of newborns appears in 15% of children under one year of age. The causative agent of the disease is the Candida fungus. It enters the child’s body from the outside or during childbirth/breastfeeding (provided that the fungus is in the body of a nursing woman), actively affecting the oral mucosa.
Causes of thrush in newborns
Candidiasis is more common in premature babies
Candidiasis will not occur without a fungus - that’s for sure. And the factors due to which the disease will receive an impetus for development are varied.
- Anatomical features of the structure of mucous membranes in newborns. The protective function of the oral mucosa in babies is just developing, so the ability to repel germs is imperfect. In the first months after birth, children have low salivation, and the amount of antifungal components in saliva is extremely small.
- Any damage to the inner shell greatly increases the risk of catching a fungal infection.
- Immunodeficiency in the body. A lack of immune cells and insufficient activity of all other defense mechanisms is observed in all babies at the beginning of life. But the period when the immune system is weakened is the optimal time for the development of diseases, including candidiasis.
- Imbalance of intestinal microflora. For the first time after birth, healthy microflora in the intestines is at the formation stage. An imbalance of microflora and further thrush can cause intestinal infections.
- Candidiasis can develop after taking antibacterial agents. The intestinal microbial community is not able to recover after therapy, which means Candida fungi can become more active.
- Prematurity. The risk of candidiasis is greatest in premature babies - due to the fact that they are less resistant to all of the above factors.
There are 3 forms of candidiasis in a child:
- Easy. White grains with the consistency of cottage cheese form in the mouth. Typical location: tongue, cheek area. The condition does not cause concern for the baby.
- Moderate weight. A coating of cheesy consistency partially affects the oral cavity. Redness of the mucous membrane is observed, attempts to remove plaque are accompanied by bruising.
- Heavy. High-density plaque covers almost the entire oral cavity and cannot be removed. The baby cries and may refuse to feed.
It is necessary to visit a doctor at the first manifestations of the disease to prevent its development. In the initial stages, thrush responds well to treatment.
How to treat thrush
Therapy for thrush includes the use of local (ointments, suppositories, creams) and general (tablets, injections) agents.
Medicines are chosen exclusively by a pediatrician - drugs that are effective for treating an adult can negatively affect a child due to the risk of adverse reactions.
Of the entire list of drugs against candidiasis, only 2 are used to treat young children:
- Fluconazole;
- Nystatin.
The dosage will be chosen by a specialist taking into account the baby’s weight and the severity of the disease. Timely treatment starts guarantees a quick recovery.
Interesting
Pigs are more sensitive than people. The person is a fairly average taster. He only has 3 thousand taste analyzers. The whale, which swallows a lot of fish without even chewing, has only a few or none at all. The pig, oddly enough, is more taste-sensitive than humans: it has 5,500 taste analyzers. A cow has 35,000 of them, and an antelope has more than 50,000! So not only do animals have a sense of taste, but many of them are much better tasters than humans. Marine animals are often covered in taste buds on the outside. Fish, for example, sense taste over the entire surface of their body. But creatures such as flies and butterflies can taste with their paws. Snakes and lizards use language for this purpose, but not quite in the same way as we do. They seem to shoot out the tip of their tongue, which catches small particles of food. These particles are delivered using the tongue to a special organ in the upper part of the mouth, which tastes and smells food.