Chief editor of the site:
Snitkovsky Arkady Alexandrovich
Chief physician of the professorial dentistry “22 Century”, dentist, orthopedic dentist
Author of the article:
Scientific team of dentistry “22 Century”
Dentists, candidates and doctors of medical sciences, professors
Materials and production of crowns
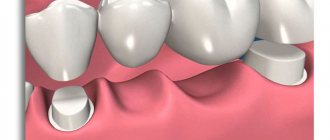
Artificial crowns are permanent prostheses in the form of caps that restore the anatomical shape of the tooth, chewing and aesthetic functions of severely damaged hard dental tissues. When they are manufactured in a dental laboratory, various materials or combinations thereof are used. They have a long history of use in dentistry: the first mentions date back to the 18th century.
Indications for the installation of porcelain crowns
The main indication for the installation of porcelain crowns is the aesthetic restoration of the front teeth:
· wedge-shaped defects and chips that cannot be eliminated using filling material;
Complete destruction of the dental crown;
· enamel hypoplasia;
Abnormalities in tooth color or shape;
· a pronounced change in the shade of tooth enamel that cannot be corrected using professional hygiene methods.
In addition, such designs are suitable for patients who are allergic to metal.
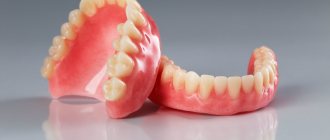
Plastic dentures
The structures are made from acrylic plastic and are used in cases of loss of one tooth or all elements of the dentition. Dentures of this type look very natural, since a shade is used for the base and teeth itself that perfectly matches natural tissues. In the case of complete edentia, plastic dentures rest only on the gingival tissue. Their fixation in the oral cavity occurs through a “closing valve” - a vacuum between the mucous membrane and the prosthesis. If several elements of the dentition are being restored, clasps (metal wires) are used to securely fasten the prosthesis. When replacing one tooth with prosthetics, butterfly prostheses are usually used, the attachment of which to the gum is carried out with special plastic extensions.
Stages of manufacturing and installation of porcelain crowns
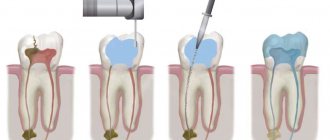
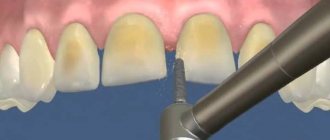
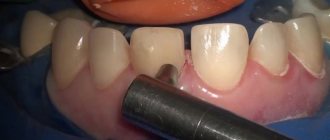
First of all, at the appointment, the dentist examines the patient’s oral cavity, identifies possible contraindications, and, if necessary, carries out a complete sanitation. Only after this can you proceed to the next stage - preparing the tooth for a porcelain crown and selecting the optimal shade for the future design using a special template.
Next, the doctor takes a combined impression of the tooth and the entire dentition. And if the quality of the casts is satisfactory, it is sent to a dental laboratory, where a plaster model is made based on them.
Direct production of a porcelain crown can be carried out in two ways. The first involves layer-by-layer application of porcelain substance, and the second uses injection molding technology. It is the second option that is more modern and gives the structure high strength,
Therefore, it is used in most dental laboratories.
After the impression falls into the hands of a specialist, he uses thin platinum foil to create a mold for the future dental crown and fills it with a porcelain composition, and then exposes it to high temperatures several times.
The final stage of making a porcelain crown is the correction of the structure, its staining and glazing.
After the crown is ready, it is first tried on. If the result suits both the doctor and the patient, it is finally fixed on the previously prepared tooth.
A laboratory technician performs the following manipulations:
Making diagnostic models of jaws
- Making diagnostic models of jaws;
- Making temporary crowns (if they are not made directly by a doctor in the office using a silicone key - a special material is applied to the area of interest and retains its shape when hardened); as a rule, the help of a technician is required in case of severe initial destruction - in this case, he casts a model using an impression, models the damaged areas on it with wax, and from this structure, using a key, makes temporary restorations;
- Making working models from supergypsum based on final impressions;
- Making a wax reproduction of the final restoration followed by a step-by-step replacement of materials (for example, casting a base for a combined structure, followed by application and firing of ceramic mass).
In addition to the traditional manufacturing method, there is also the so-called milling from ready-made blocks on a computer-controlled machine (CAD/CAM technology, for example CEREC, EVEREST). Using an optical system, an impression is taken (essentially scanned) either of the prepared area directly in the oral cavity, or of a model, then the data is transferred to a computer, where the image is processed by a special program, a model of the future restoration is built, which can be corrected, and then sharpened and finalized ( painted and glazed to give a shine comparable to natural). Now this is the most accurate way to create structures of various sizes and lengths (up to the entire dental arch), because human involvement and therefore possible inaccuracies are reduced to a minimum. The next step will obviously be the development of 3D printing technologies.
Benefits of porcelain crowns
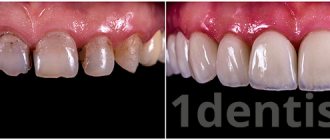
· High aesthetics. Porcelain has almost ideal optical characteristics. It very accurately conveys the natural shade and translucency that are characteristic of natural tooth enamel.
· Hypoallergenic design and inert material. Porcelain does not have thermal conductivity, so tooth sensitivity to temperature changes is reduced. Since the crown does not contain a single gram of metal, it can be installed in patients who are allergic to it.
· Long service life. With proper care, the structure will last a very long time, approximately 10-15 years, without losing its performance characteristics.
· Resistant to staining and darkening. Porcelain crowns do not lose their shade and shine, maintaining their original appearance for a long time.
· Minimum adaptation time. The patient quickly gets used to the lightweight and comfortable design.
· Easy to care for. Crowns do not require special care. It is enough to use a high-quality toothbrush and toothpaste, and treat them with care.
Prosthetic structures based on lithium silicate glass ceramics
Crowns made on the basis of lithium silicate glass ceramics are used in modern orthopedic and dental practice much less often than porcelain and zirconium prostheses. As a rule, this material is used for the manufacture of solid prosthetic structures that do not have a ceramic frame.
Disadvantages of lithium silicate glass ceramics
Despite all the advantages of lithium silicate glass ceramics (variety of shades, translucency), crowns made on its basis are considered relatively fragile and cannot be used for prosthetics of teeth experiencing significant chewing load.
It is important to remember that ceramic dentures cannot be installed for people suffering from:
- bruxism,
- mental illnesses,
- having a deep bite.
That is why, before prosthetics, it is necessary to obtain professional advice about the presence of side effects and contraindications from an experienced dentist at the orthopedic department of dentistry “A.Dent”.
Disadvantages of porcelain crowns
· High cost of construction. It is due to the complexity of technical work, which requires very high professionalism from a specialist.
· Relative fragility of the material. Patients have to avoid eating solid foods.
· Restrictions on indications. Porcelain crowns are not placed on all teeth.
· Manufacturing of single crowns only. Porcelain is not suitable for creating and installing bridges.
Comparative characteristics of artificial crowns
| Variety | Positive traits | Negative qualities |
| Metal (stamped and cast); | Stamped – gentle preparation (only the most protruding part of the crown around the circumference is ground); | Cast – hardness and bioinertness of noble alloys (does not interact with the body). |
| Combined (metal-ceramics) |
|
|
| Plastic and composite (currently used only as temporary) |
|
|
| Metal-free (ceramic and zirconium dioxide-based) |
| The relative fragility of pressed ceramics (IPS Emax technology, used only in the anterior part of the dental arches) |
Date of publication: September 20, 2020 Last update: September 22, 2022 © 2020 Professorial Dentistry “22 Century”. All rights reserved.
Varieties of porcelain designs
Dental porcelain is an excellent material that provides ample opportunities for aesthetic restoration. Several types of structures are made from it:
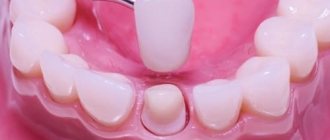
· Veneers. These are thin plates designed to hide minor defects in tooth enamel. They cover only the front surface of the tooth. Porcelain, composite or zirconium dioxide can be used in their manufacturing process.
· Tabs. These are microprostheses made in a dental laboratory. They help solve more serious dental problems with teeth and are used, for example, in cases of severe decay of the crown or the presence of a large carious cavity.
· Crowns. The most versatile design that allows you to achieve a “Hollywood” smile. They are installed on the front teeth during aesthetic restoration.
Classification:
By purpose:
- Restorative;
- Abutment (used in bridges ; they replace not only a defect within the coronal part of a tooth, but also a missing tooth or several teeth).
By design features:
- Full (cover the prepared stump from all sides), partial (three-quarter, half-crowns) leave the outer surface of the crown open;
- Telescopic (double; used in removable prosthetics, the first cone-shaped is fixed on the stump, the second, restoring the tooth, is part of the removable part and is put on the first).
According to the material used:
- Metal (noble or base alloys);
- Non-metallic (ceramics, zirconium dioxide, plastic, composite);
- Combined (metal-ceramics, metal-plastic).
By fixation method:
- Cemented (for prosthetics of natural teeth or on implants);
- Screw (used only for prosthetics on implants - artificial analogues of natural roots, strengthened inside the bone tissue of the jaws).
By service life:
- Permanent;
- Temporary - provisional (used at the stages of manufacturing the final ones to protect the stump from irritants, restore contacts with other teeth and for aesthetic purposes, including to form the contour of the gums ).
Metal ceramics or porcelain: what to choose?
This question arises among patients quite often. After all, each design has its own advantages and disadvantages. Thus, metal ceramics are distinguished by their high strength and affordable price, and porcelain has excellent aesthetic characteristics. Typically, the choice between them depends on which tooth needs to be restored. Crowns made of metal-ceramics are most often installed on chewing teeth, and porcelain crowns are installed on incisors and canines. However, if a porcelain crown has a zirconia framework, it can be used to restore any tooth.
Advantages of artificial crowns:
Advantages of artificial crowns
- Increasing the physical and mechanical characteristics of the crown of a natural tooth due to the circular coverage of the dental stump with a solid structure;
- The ability to reproduce or correct the appearance of the crown in the desired direction;
- The ability to perform the function of a supporting element of a fixed or removable prosthesis.
If all conditions are met, the possible disadvantages of this design (for example, bleeding, temporary whitening or a feeling of pressure in the area of the adjacent gum) are mild or completely absent. However, it should be understood that while performing a restorative and, to a certain extent, preventive function, orthopedic treatment does not affect the main cause of caries - the acid produced by plaque microorganisms. This means that daily personal oral hygiene measures must be carried out in full.
Each type of crown is characterized by its own manufacturing technology: metal ones are cast or stamped, plastic and composite ones are polymerized, ceramic ones are sintered, pressed, milled. Those previously used (stamped with plastic lining, partial, metal-plastic) are now rarely used. Despite this circumstance, at the present stage of development there is a sufficient variety of options to find the optimal solution in each case.
The choice of material and technology depends on the objectives of the individual clinical situation.
What kind of crowns are placed on the front teeth?
The front incisors are not used for chewing food, so when prosthetics for this group of teeth there are more requirements for aesthetics and restoration of correct occlusion. But the material of the prosthesis must be strong enough to withstand the load when biting. To create crowns, metal alloys, metal-ceramics, ceramics (porcelain), zirconium oxide, E-max metal-free ceramics, plastic, etc. are used. The cost, appearance, and durability of the restoration depend on the material.
Advantages and disadvantages
Positive traits:
- The main advantage of this type of structure is its visual similarity to natural teeth. In addition, their appearance does not change over time - porcelain crowns always remain the same as they were on the day they were made.
- Bioinert and hypoallergenic. The material is absolutely indifferent to the human body, the immune system “does not see” it, so the method is excellent for people who are sensitized and sensitive to allergens. The most common hypersensitivity is to plastic monomers and non-precious metal alloys.
- Durability, hardness and stability. Baked and pressure-pressed ceramics are able to cope with any loads placed on the teeth, except for targeted impacts and improper use (gnawing thread, cracking nuts, and so on).
Speaking of durability:
The chewing muscles in total provide colossal strength, about 200 kg. Naturally, in everyday life we do not use it to its full potential, but this feature sometimes helps (in self-defense, for example). After acquiring new teeth, reinforced with orthopedic structures, people are sometimes deceived by the fact that they can now do more - they begin to use reinforced rows not only for food. This should not be done under any circumstances, because no fabric or product can withstand true chewing force.
Disadvantages of ceramic crowns:
- Slight surface abrasiveness. The material is not perfectly homogeneous. On the one hand, this is good, since it allows you to imitate natural enamel, but on the other hand, when the restoration comes into contact with non-prosthetic antagonists and “neighbors,” natural tissues begin to wear out.
- The fragility of dental ceramics cannot be compared with ordinary glass, but it can still break off upon impact, so restorations must be protected from injury.
- Incomplete fit of the cap to the stump. Ceramics shrink somewhat when packed and baked. Only initially solid raw materials, such as zirconium oxide, for example, are protected from this. And porcelain, metal and composite change their performance depending on the state of aggregation and temperature.
All of the above disadvantages are relative. Surface imperfections can be leveled out by final grinding and glazing, and the fit can be improved by high-quality fitting of the product.
In general, the functionality and hardness of ceramics satisfies all requirements , and therefore enjoys stable popularity among patients and dentists. Pure porcelain structures are somewhat more expensive than metal-ceramic ones, so they are included in premium services, but they are more affordable than other metal-free analogues.
Comparison: plastic or porcelain teeth
It is important not to allow the porcelain crown to overheat during processing, as this can cause a crack to appear, followed by possible separation of part of it.
When comparing plastic and porcelain crowns, it is worth noting the advantageous aspects of polymer products:
- crowns made of plastic do not have the fragility that is inherent in porcelain;
- abrasive processing or grinding of plastic crowns is much easier;
- Reliability in operation of plastic teeth is determined by the ease of their installation.
At the same time, porcelain teeth are not subject to changes in their inherent size and shape. They do not soften or deform when exposed to temperature conditions. Porcelain products are less susceptible to abrasion of work surfaces due to their increased hardness. The same comparative criteria can be applied when choosing material for removable dentures.
Content:
- Advantages and disadvantages
- Manufacturing method
- Indications and contraindications
- Care tips, service life
Previously, such products were used to restore the dentition only in the frontal part , but now the techniques have been improved, so they can also restore the lateral parts. Their installation on molars is not recommended, since most of the chewing force occurs in this area, so a product with a metal frame covered with veneer is required.
Contraindications for use
Experts do not recommend installing porcelain if, during an examination of the oral cavity, the doctor reveals certain conditions. Some of them:
- insufficient hardness of the dental bone tissue;
- inflammatory processes in the acute stage;
- severe occlusion disorders;
- chronic periodontal disease in the acute stage;
- absence of a large number of teeth.
All contraindications are considered absolute and have nothing to do with the fact that the material has high hardness and almost does not wear off. This often leads to overload of the periodontium of supporting teeth, thereby worsening the course of pathologies. In addition, there are a number of relative contraindications:
- bruxism (dysfunction of the masticatory muscles);
- “living” pulp of the incisors on the lower jaw;
- excessive abrasion of enamel;
- pathologies of occlusion, which are associated with strong crossing of the incisors.
When these limitations are eliminated by the method of complex treatment, the necessary conditions are created for the manufacture of porcelain prostheses.
Before and after installation
How and why dental crowns are removed
A well-made dental crown can be worn for decades, of course, if the material from which it is made is designed for this. However, standard recommendations are to replace it every 10 years or more frequently as required.
Premature removal is carried out when certain unpleasant symptoms appear, most often indicating incorrect installation. So, crown removal is carried out when the following symptoms appear:
Crown pain
Although modern techniques for working with materials make it possible to ensure a filigree match of the crown to the prepared tooth, sometimes situations arise that the patient complains of pain in the crown. Of course, it is not the tooth that hurts, but the tooth on which it is installed. Among the causes of pain, caries is the leading cause; less often, pain occurs with untreated roots.
Unpleasant smell
The appearance of a putrid odor may be due to the fact that food particles are packed under the crown. Due to the inability to remove them even with the help of high-quality teeth cleaning, they become contaminated with bacteria and decompose, which is accompanied by a putrid odor.
Advantages and disadvantages
Advantages
- High precision fit to dental tissues due to the correct anatomical shape;
- crown thickness is 0.3-0.5 mm, which avoids deep tooth preparation;
- durability – service life is 15-25 years;
- the possibility of spraying and cladding to improve the aesthetics of the structure;
- recreating the correct occlusion and chewing surface of the teeth;
- affordable price for manufacturing and installation.
Flaws
- Increased abrasion of the enamel of antagonist teeth;
- the need for turning;
- high thermal conductivity (due to the proximity of the pulp, discomfort and pain may occur);
- risk of allergies (except for structures made of precious metals);
- low aesthetics (excluding metal ceramics).
What metal alloys are used
The designs have several options. Cast crowns are made from metal alloys with high strength:
- Chromium-cobalt alloys (CHS)
are high-alloy steels, characterized by density, elasticity, good fluidity (in the molten state), and high resistance to oxidation and corrosion.
The mechanical viscosity of CHS is higher than that of gold alloys. A prosthesis made from casting material based on chromium with the addition of cobalt and nickel is able to withstand high mechanical loads without deformation or destruction. The service life of such structures is 12-15 years
, and the price is the most affordable. The main disadvantages are poor aesthetics and the risk of developing allergies. - Gold-based alloys
are characterized by high strength and corrosion resistance.
The high plasticity of the material allows you to create dentures that fit exactly to the dental tissues and gums. Gold solid-cast tooth crowns have properties identical to natural enamel and do not damage opposing units. They have an antibacterial effect, are biocompatible with body tissues, and do not cause allergies or rejection. To give the material sufficient strength, gold is combined with palladium, platinum, copper, and silver. Service life - 20-25 years
. Cons: poor aesthetics, high price. - Titanium alloys
– the strength of titanium prostheses is 9-10 times higher than that of structures made from other materials. Biocompatible, inert to chemical and temperature influences, the material does not have a destructive effect on antagonist teeth. Prostheses made of titanium alloys are lightweight, have precise marginal and internal fit, and are used to compensate for single defects as part of long-distance bridges. Disadvantages - titanium is difficult to process and has low adhesion to ceramics, which increases the risk of chipping the outer coating.
The crown material is selected according to the clinical picture. The doctor takes into account the specifics of the situation, offers several effective options, among which the patient chooses the optimal one in terms of price, aesthetics, and functional properties. Metal-ceramic structures are more aesthetically pleasing than all-metal or metal-plastic crowns. Plastic cladding quickly absorbs foreign odors and coloring pigments, and changes color within a few months. It is not able to withstand a full chewing load and begins to crack and chip.
Alternative Methods
Zirconium Durable crowns with high aesthetics, suitable for anterior and posterior teeth
Ceramic Esthetic crowns for single restorations and dental bridges (up to 3 units)
Metal-ceramic Inexpensive, durable crowns are chosen for premolars, molars and dental bridges (up to 4-5 units)
Article Expert
Meliksetyan Daniel Oganesovich Dentist-orthopedist, doctor of the highest category
Work experience: more than 17 years
What determines the cost of a dental crown?
The final cost of prosthetics is influenced by several important factors:
Pricing policy for a specific dentistry: All private clinics target a specific cohort of consumers with approximately the same level of income. Therefore, the cost of the same prosthesis can vary dramatically. DENT Academy does not offer the lowest prices - we offer very high-quality work at an adequate cost.
Cost of materials: It is logical that plastic dentures are much cheaper than zirconium dioxide, so when choosing a specific type of dental crown, you should focus on your financial capabilities. Our clinic specialists will help you choose the best option that combines high quality with an affordable price.
The clinic has its own dental laboratory: The technological process of making dentures is financially very expensive. If there is no laboratory, the clinic is forced to enter into an agreement with an independent laboratory. Naturally, the cost of such prostheses will increase, if only because of logistics costs.
Qualification of personnel: it is natural that when a doctor with extensive experience and work experience receives more money for it, accordingly, the cost of his work will be higher than that of a young specialist who has no experience and whose quality of work is unknown. The price of dentures also includes the cost of paying for the work of a dental technician, whose qualifications largely determine the quality of the manufactured crown, especially when it comes to high-tech structures.
Indications and contraindications
Magnificent, aesthetically pleasing, bioinert and practical ceramic dentures are an excellent choice for allergy sufferers and people with high cosmetic requirements.
Porcelain crowns are used for:
- partial or complete destruction of teeth in the frontal or lateral group, both single and multiple defects in a row;
- the need to do sustainable whitening;
- installation of bridges, clasp, plate prostheses and implants.
There are few contraindications:
- some malocclusions, in which there is a risk of chipping ceramics or damaging your own dental tissues;
- advanced pathologies of periodontal tissues, if the necks and roots are exposed, too mobile;
- excessive fragility of the enamel: if the prosthetic bed is unstable, nothing can rest on it.
Not all contraindications are absolute: you can straighten the bite, splint mobile units, carry out anti-inflammatory therapy, and replenish lost bone tissue. If desired, and in conditions of unquestioning adherence to medical recommendations, you can achieve amazing success in treatment at the dentist.
Care tips, service life
Proper and timely care allows patients to enjoy porcelain crowns for about 15 years. To extend the time of using reproductions, doctors advise:
- avoid impacts - do not bite off anything too hard, be careful when eating (do not hit the crowns with a spoon or cup);
- do not clench your jaw too much - if you have such a habit, you should take the time to learn how to control muscle tension or make sleep guards if you have bruxism;
- Do not combine cold and hot foods to prevent the ceramics from cracking (coffee with ice cream, hot drinks outside in freezing temperatures).
Care is quite simple: brush your teeth twice a day, and also visit the clinic for regular preventive examinations and hygiene. It is necessary for the doctor to examine the edges of the crowns so as not to miss the moment when decementing begins. If the seal is broken, cariogenic bacteria can get under the product.
Also, the dissolution of cement can accelerate with chronic inflammatory lesions of the gums, so be conscious of your health and consult with your dentists on all issues of concern.
How is the color of the prosthesis selected?
To select the shade of new teeth, the Vita color scale is used. It looks like a small strip with enamel samples attached to it. The color range is indicated by the letters AD, with additional numerical markings from 1 to 4. The higher the number, the lighter the shade. The Vita scale includes 16 basic colors. Plus, there are special dyes, thanks to which you can achieve a complete shade identical to real teeth.
The choice of color is carried out in natural light, so as not to distort the perception of shades. The dentist takes each sample to the teeth in turn and determines the most optimal option.